Engineering:Breguet Leviathan
| Breguet 22 Leviathan | |
|---|---|

| |
| Role | 22-seat, twin-engine airliner |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Société Anonyme des Ateliers d'Aviation Louis Breguet |
| First flight | 1922-3 |
| Number built | 1 |
| Developed from | Breguet 20 |
The Breguet Leviathan was a family of large all-metal biplane aircraft built in France in the early 1920s. The Breguet XX and XXI were notable for being powered by Breguet-Bugatti multiple engines, in two forms. The Breguet XXI was powered by individual Breguet-Bugatti U.16 engines initially and Lorraine-Dietrich 8b engines in tandem later. The Breguet XXII had accommodation for about twenty passengers and was destroyed during a 1923 transport aircraft competition. Development of all three aircraft types was halted largely due to technical issues with power-plants and aircraft structure.
Development and design
Breguet XX and Breguet XXI

In 1922 Breguet Aviation flew both their all-metal Breguet 19, a bomber/reconnaissance aircraft and the Breguet XX. The latter was another all-metal biplane but much larger and powered by a Bréguet-Bugatti 32A Quadimoteur Type A, (two Bréguet-Bugatti U.24 engines mounted in tandem on a cradle, driving a single output shaft),[1] with a single output shaft, for the first time on 20 June 1922. The engine assembly was placed in the forward fuselage and drove the nose-mounted single propeller via a shaft running through the forward engine half's cylinder banks from the combining gearbox between the two engine halves.[2][3][4][5]

A bomber variant, the Breguet XXI, was also built with limited success; the partially built fuselage was displayed at the 1921 Paris Aero Salon, clearly showing the installation of the Bréguet-Bugatti 32A Quadimoteur Type A engine.[6] The Breguet XXI was later fitted with a Bréguet-Bugatti 32B Quadimoteur Type B, which grouped four 8-cylinder banks around a combining gearbox in an 'H' configuration.[1]

Breguet XXII
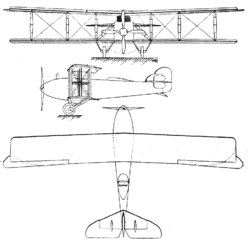
Unlike the very successful Breguet XIX, the Breguet XX and XXI proved unsatisfactory and were developed into the otherwise very similar Breguet XXII, which had a pair of Breguet-Bugatti U.16s mounted between the wings on either side.[4] Since the double engines could continue to run with one half shut down;[4] the Breguet XX and XXI and XXII were sometimes referred to as four-engined aircraft (e.g.L'Aerophile[7]). Moving the engines from the fuselage to the wings freed the fuselage for a passenger cabin which could hold 22, a large number in those days. The Type XX, Type XXI and Type XXII were all referred to as Breguet Leviathan by contemporaries.[7][8]
The fuselages of the Type XX, Type XXI and Type XXII were similar flat-sided structures based on four cross-braced longerons, each of three parts. Since the nose of the XXII did not terminate in a propeller, the high cockpit of the XX was replaced with a blunt-nosed cabin, curved in planform, for the pilot.[2] Behind him the passenger seats in the Type 22 were in pairs, each with their own window. Boarding and disembarking were reported as a little difficult.[4][7] The wing-mounted engines led to revised wing plans and structures. The Breguet 22 had equal-span, unstaggered wings of rectangular plan and three bays. The innermost bay was defined by the engine by the engine mountings, which placed the U.16s with their four-blade tractor propellers on multiple struts midway between the two wings. Radiators were mounted on the sides of the engine cowling. The outer bays were formed by single interplane struts with forked junctions into the wings, assisted by cross-bracing. At the rear the tail was, like that of the Type 20, quite small and conventional with the tailplane mounted on top of the fuselage but now carrying a pair of small additional fins. The landing gear was also conventional, with each fixed mainwheel mounted on a pair of substantial V-form legs from the wing spars under the inner bay.[4] The Breguet-Bugatti engines soon proved unreliable and by early 1923 the Type 22 was described as powered by four 270 hp (200 kW) Lorraine-Dietrich 8Bd water-cooled mounted in tractor/pusher pairs.[9][10]
The sole Type 22 was destroyed in a fire following a forced landing in mid-September 1923 whilst competing for the Grand Prix pour Avions de Transport.[11]
Variants

- Breguet XX Leviathan
- (Breguet 20 Leviathan) A large all-Duralumin biplane airliner powered by a Bréguet-Bugatti 32A Quadimoteur Type A multi-engine, mounted inside the forward fuselage.
- Breguet XXI Leviathan
- (Breguet 21 Leviathan) A bomber version of the Breguet XX / XXII, powered initially by a Quadimoteur Type A multi-engine, but later fitted with a Bréguet-Bugatti 32B Quadimoteur Type B multi-engine, both mounted inside the forward fuselage.
- Breguet XXII Leviathan
- (Breguet 22 Leviathan) A development of the Breguet XX powered initially by two individual Bréguet-Bugatti U.16 engines mounted conventionally between the wings and later by four Lorraine-Dietrich 8B V-8 engines mounted in tandem between the wings.
Specifications (Breguet XXII 2x Breguet-Bugatti U.16 engines)
Data from L'Aérophile 1 January 1923:Les Avions du VIII Salon de l'L'Aéronautique[12], Flight 28 December 1922:Louis Breguet - Paris[4], L'Aérophile 15 December 1922:Les Avions Stand par Stand - Breguet "Leviathan" XXII[7], Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1924[13]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2/3
- Capacity: 25 including crew
- Length: 14.016 m (46 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 25.538 m (83 ft 9 in)
- Height: 5.135 m (16 ft 10 in)
- Wing area: 140 m2 (1,500 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 3,150 kg (6,945 lb)
- Gross weight: 6,400 kg (14,110 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 1,500 l (396 US gal; 330 imp gal)
- Powerplant: 2 × Breguet-Bugatti U.16 U-16, (two straight-eight engines in parallel), water-cooled in-line piston engines, 360 kW (480 hp) each
- Propellers: 4-bladed fixed pitch propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 170 km/h (110 mph, 92 kn) at 2,000 m (6,600 ft)
- Range: 1,100 km (680 mi, 590 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 4,000 m (13,000 ft)
- Wing loading: 46 kg/m2 (9.4 lb/sq ft)
- Power/mass: 0.1065 kW/kg (0.0648 hp/lb)
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Bréguet-Bugatti 32A and 32B Quadimoteurs". 17 January 2015. https://oldmachinepress.com/2015/01/17/breguet-bugatti-32a-and-32b-quadimoteurs/. Retrieved 10 March 2018.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Breguet Leviathan" (in French). L'Aérophile: 8–9. 1 July 1922. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k6554866j/f209.image.
- ↑ Lémonon, E-H (3 November 1921). "Le Breguet "Leviathan"" (in French). Les Ailes (20): 2–3. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k65559666/f2.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 "Louis Breguet - Paris". Flight XIV (52): 784–5. 28 December 1922. http://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1922/1922%20-%200784.html.
- ↑ "Le "Leviathan" a volé" (in French). Les Ailes (55): 1. 6 July 1922. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k96071869/f1.item.r=Breguet%20leviathon.zoom.
- ↑ "THE PARIS AERO SHOW 1921". Flight XIII (47 (no. 674)): 778-779. 24 November 1921. https://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1921/1921%20-%200779.html. Retrieved 10 March 2018.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 "Les Avions Stand par Stand - Breguet "Leviathan" XXII" (in French). L'Aérophile: 8–9. 15 December 1922 – 1 January 1923. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k6554866j/f398.image.
- ↑ "The Paris Aero Show". Flight XIV (51): 762. 21 December 1922. http://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1922/1922%20-%200762.html.
- ↑ "Le Grand Prix des Avions de Transport" (in French). L'Aérophile 31: 291–2. 1 October 1923. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k6555017m/f297.image.
- ↑ "Note". L'Aérophile 31: 137. 1 March 1923. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k6555017m/f144.
- ↑ "Les Grandes Épreuvres de l'Année" (in French). L'Aérophile 32. 1 February 1924. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k6554816n/f80.
- ↑ "Les Avions du VIII Salon de l'L'Aéronautique" (in French). L'Aérophile 31: XVIII. 1 January 1923. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k6555017m/f392.
- ↑ Grey, C.G., ed (1924). Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1924. London: Sampson Low, Marston & company, ltd.
