Engineering:DODGE (satellite)
From HandWiki
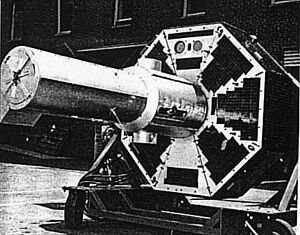 The DODGE satellite | |
| Mission type | Technology |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA / United States Air Force |
| COSPAR ID | 1967-066F |
| SATCAT no. | 2867 |
| Mission duration | 3 years |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory |
| Launch mass | 200 kilograms (430 lb) |
| Dimensions | 2.4 by 1.2 metres (7.9 by 4.0 ft) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | July 1, 1967, 13:15:01 UTC |
| Rocket | Titan IIIC |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral Air Force Station LC-41 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | MEO |
| Semi-major axis | 39,841.6 kilometres (24,756.4 mi) |
| Perigee altitude | 33,278.8 kilometres (20,678.5 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 33,662.5 kilometres (20,916.9 mi) |
| Inclination | 11.6 degrees |
DODGE (Department of Defense Gravity Experiment) was a satellite whose primary purpose was to conduct experiments in gravity-gradient stabilization at near-geosynchronous altitudes. Its secondary objectives included measuring the Earth's magnetic field, and taking pictures of the entire Earth's disk in both black-and-white and color. It was launched atop a Titan IIIC rocket on July 1, 1967, and operated for over three years. DODGE carried ten knobbed booms oriented along three different axes, that could be independently extended and retracted by ground command.[1]
DODGE first achieved successful stabilization 12 days after launch,[1] and took the first color picture of the complete Earth disk.[2]

References
See also
- Department of Defense
