Engineering:Daewoo Precision Industries K4
| Daewoo Precision Industries K4 K4 고속유탄기관총 | |
|---|---|
 K4 automatic grenade launcher | |
| Type | Automatic grenade launcher |
| Place of origin | South Korea |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1993–present |
| Used by | See Users |
| Wars | War in Afghanistan Iraq War Libyan Civil War |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Agency for Defense Development Daewoo Precision Industries |
| Designed | 1985–1991 |
| Manufacturer | Daewoo Precision Industries (1981–1999) Daewoo Telecom (1999–2002) Daewoo Precision (2002–2006) S&T Daewoo (2006–2012) S&T Motiv (2012–2021) SNT Motiv (2021–present) |
| Produced | 1993–present |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 34.4 kg (75.84 lb) (no tripod) |
| Length | 1,072 mm (42.2 in) |
| Barrel length | 412 mm (16.22 in) |
| Cartridge | 40×53mm grenade |
| Calibre | 40 mm |
| Action | API blowback |
| Rate of fire | 325–378 rounds/min |
| Effective firing range | 1,500 m (1,600 yd) |
| Maximum firing range | 2,200 m (2,400 yd) |
| Feed system | belt-fed, 32 or 48 grenades belt |
| Sights | KAN/TVS-5 night vision scope can be attached[1] |
The Daewoo Precision Industries K4 (Korean: K4 고속유탄기관총; Hanja: K4 高速榴彈機關槍) is a 40×53mm high-speed automatic grenade launcher in use with the Republic of Korea Armed Forces.
The K4 was developed as a complement to the K-201 hand-held grenade launcher (attachable to the K2).
History
The K4 was first developed in 1994.[2]
Design
File:Demonstration of firing of the K4 automatic grenade launcher.webm
It has a weight of 34.4 kg (empty, without accessories) and can fire up to 325 rounds per minute with a firing range of 1.5 km. When needed to be used during night operations, a KAN/TVS-5 night vision scope can be attached onto the receiver.[1]
The K4 is said to visually resemble the Mk 19 AGL.[3]
Users
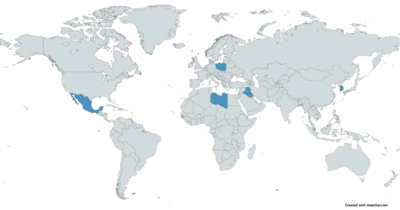
 Iraq: Small numbers used by Iraqi special forces on Humvees.[4]
Iraq: Small numbers used by Iraqi special forces on Humvees.[4] Libya: First export customer, purchased the K4 in 2009.[5]
Libya: First export customer, purchased the K4 in 2009.[5] Mexico: Purchased since 2011.[6]
Mexico: Purchased since 2011.[6] Poland: Several hundred K4s ordered in 2022.[7]
Poland: Several hundred K4s ordered in 2022.[7] South Korea[1]
South Korea[1] Singapore: 17 K4s transferred according to a 2019 SIPRI small arms report.[8]
Singapore: 17 K4s transferred according to a 2019 SIPRI small arms report.[8]
See also
- REDIRECT Template:Link with country
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:
|
- REDIRECT Template:Link with country
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:
|
- REDIRECT Template:Link with country
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:
|
- REDIRECT Template:Link with country
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:
|
- REDIRECT Template:Link with country
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:
|
- REDIRECT Template:Link with country
This page is a redirect. The following categories are used to track and monitor this redirect:
|
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Weapons of the Republic of Korea Marine Corps – Small Arms Defense Journal". http://www.sadefensejournal.com/wp/weapons-of-the-republic-of-korea-marine-corps.
- ↑ "South Korea is the New Arsenal of Democracy". 20 April 2017. https://21stcenturyasianarmsrace.com/2017/04/20/south-korea-is-the-new-arsenal-of-democracy/.
- ↑ "Daewoo K4 40 mm machine gun (Korea, South) - Jane's Armour and Artillery Upgrades". https://www.janes.com/articles/Janes-Armour-and-Artillery-Upgrades/Daewoo-K4-40-mm-machine-gun-Korea-South.html.
- ↑ Vining, Miles (June 19, 2018). "ISOF Arms & Equipment Part 4 – Grenade Launchers & Anti-Armour Weapons". http://armamentresearch.com/isof-arms-equipment-part-4-grenade-launchers-anti-armour-weapons/.
- ↑ "S&T Daewoo Succeeded in First Exporting K4 Automatic Grenade Machine Gun to Libya". S&T Holdings. December 21, 2009. Archived from the original on 2020-03-03. https://web.archive.org/web/20200303115107/http://www.hisntholdings.com/eng/pr/news.html?code=share_notice&p=&page=15&bbsData=bm89Mjg3%7C%7C&search=&searchstring=&mode=view. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ↑ "S&T모티브, 멕시코, 파푸아뉴기니 軍․警에 총기 수출". S&T Motiv. April 10, 2013. http://www.sntmotiv.com/phtml/news_view.php?idx=395&kind=.
- ↑ "Koreańskie granatniki K4 dla Polski". milmag.pl. September 26, 2022. https://milmag.pl/koreanskie-granatniki-k4-dla-polski/.
- ↑ "Archived copy". http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/fileadmin/docs/S-Trade-Update/SAS-Trade-Update-2019.pdf.
External links
Template:API blowback firearms Template:Modern South Korean Infantry Weapons
 |
