Engineering:Directional control valve
Directional control valves (DCVs) are one of the most fundamental parts of hydraulic and pneumatic systems. DCVs allow fluid flow (hydraulic oil, water, steam, air ect) into different paths from one or more sources. DCVs will usually consist of a spool inside a cylinder which is mechanically or electrically actuated. The position of the spool restricts or permits flow, thus it controls the fluid flow.,
Nomenclature
The spool (sliding type) consists of lands and grooves. The lands block oil flow through the valve body. The grooves allow oil or gas to flow around the spool and through the valve body. There are two fundamental positions of directional control valve namely normal position where valve returns on removal of actuating force and other is working position which is position of a valve when actuating force is applied. There is another class of valves with 3 or more positions that can be spring centered with 2 working position and a normal position.
Classification
Directional control valves can be classified according to:
- number of ports
- number of positions
- actuating methods
- type of spool
Example: A 4/2 directional control valve would have four ports and two spool positions.
Ports are located on the manifold to which the directional control valve is mounted, and are used as connection points to the system. Typically the ports are labelled with a single letter:
- P, pressure, or supply
- Supply of high-pressure working fluid to be supplied to actuator by the valve.
- T, tank, drain, or return
- Working fluid from actuator returned to be repressurised from the valve.
- A, actuator
- Working fluid through the valve for the action of the actuator.
- B, actuator, opposing
- Working fluid through the valve to opposing action of actuator.
- X, external operation
- Working fluid to operate the valve.
- Y, external operation, opposing
- Working fluid to operate the valve in opposition, or to return to pilot valve.
Number of positions
Including the normal and working positions, which a valve spool can take, there are valves with two position and three position. Proportional valves operate over an electric variable input signal, and the position of the spool is proportional to the command signal.
Operating methods
Manual, spring, electrical, pneumatic, and hydraulic.
Manual
Manually operated valves work with simple levers or paddles where the operator applies force to operate the valve. Spring force is sometimes used to recover the position of valve. Some manual valves utilize either a lever or an external pneumatic or hydraulic signal to return the spool.
Mechanical
Mechanically operated valves apply forces by using cams, wheels, rollers, etc., hence these valves are subjected to wear.
Hydraulic
A hydraulically-operated directional control valve works at much higher pressures than its pneumatic equivalent. They must therefore be far more robust in nature so are precision machined from higher quality and strength materials.
Solenoid
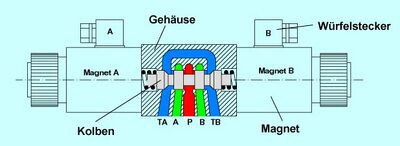
They are widely used in the hydraulics industry. These valves make use of electromechanical solenoids for sliding of the spool. Because simple application of electrical power provides control, these valves are used extensively. However, electrical solenoids cannot generate large forces unless supplied with large amounts of electrical power. Heat generation poses a threat to extended use of these valves when energized over time. Many have a limited duty cycle. This makes their direct acting use commonly limited to low actuating forces.
Often, a low power solenoid valve is used to operate a small hydraulic valve (called the pilot) that starts a flow of fluid that drives a larger hydraulic valve that requires more force.
A bi-stable pneumatic valve is typically a pilot valve that is a 3 ported 2 position detented valve. The valve retains its position during loss of power, hence the bi-stable name.
Bi-stability can be accomplished with a mechanical detent and 2 opposing solenoids or a "magna-latch" magnetic latch with a polarity sensitive coil. Positive opens and negative closes or vice versa. The coil is held in position magnetically when actuated.
Type of spool
Spool is of two types namely sliding and rotary. Sliding spool is cylindrical in cross section, and the lands and grooves are also cylindrical. Rotary valves have sphere-like lands and grooves in the form of holes drilled through them.
Specification
Directional control valves are generally specified using the number of ports and the number of switching positions. It can be represented in general form as np/ns, where np is the number of ports connected to the direction control valve and ns the number of switching positions.
In addition, the method of actuation and the return method can also be specified. A hypothetical valve could be specified as 4-way, 3-position direction control valve or 4/3 DCV since there are four ports and three switching positions for the valve. In this example, one port is called the pressure port which is connected to the pump; one port is the tank port and is connected to the tank (or reservoir); and the two remaining ports are called working ports and are connected to the actuator. Apart from characteristics of valve the fluid suitable for valve, working temperature and viscosity also thought upon before selecting a particular type of valve.
Symbolic representation
While working with layouts of hydraulic machinery it is cumbersome to draw actual picture of every valve and other components. Instead of pictures, symbols are used for variety of components in the hydraulic system to highlight the functional aspects. The symbol for directional control valve is made of number of square boxes adjacent to each other depending on the number of positions. Connections to the valve are shown on these squares by capital letters.usually they are named only in their normal position and not repeated in other positions.actuation system of the valve is also designated in its symbol.
Two-way two-position directional control valve
A gate valve is an example of a 2W/2P directional control valve that either turns on or off the flow in normal or working positions depending on the need of the application. Here arrow indicates that fluid flow is taking place whereas the other position shows the cut-off position.
Four-way two-position directional control valve
4/2 valve has four connections to it and two valve positions. Normally, one port is open to flow from the pump.
Four-way three-position directional control valve
It has one way for pump (P), one for reservoir (R) or tank (T) and two for the inlet to the actuator. And it has 3 positions: one normal, one cross way, and one straight way.
See also
External links
