Engineering:Discoverer 34
 CORONA KH-2 satellite | |
| Names | CORONA 9027 DISCOVERER XXXIV |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Optical reconnaissance |
| Operator | United States Air Force / NRO |
| Harvard designation | 1961 Alpha Epsilon 1 |
| COSPAR ID | 1961-029A |
| SATCAT no. | 00197 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | DISCOVERER XXXIV |
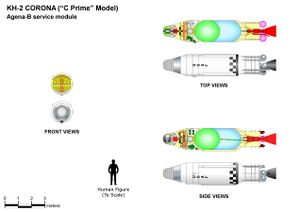
| Spacecraft type | CORONA KH-2 |
| Bus | Agena B |
| Manufacturer | Lockheed Corporation |
| Launch mass | 1,150 kg (2,540 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 5 November 1961, 20:00:30 GMT[1] |
| Rocket | Thor-Agena B (Thor 330 / Agena 1117) |
| Launch site | Vandenberg, LC-75-1-1 |
| Contractor | Douglas Aircraft Company / Lockheed Corporation |
| Entered service | 5 November 1961 |
| End of mission | |
| Decay date | 7 December 1962 |
| Landing date | SRV 553 |
| Landing site | Not attempted |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit[2] |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 227 km (141 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 1,011 km (628 mi) |
| Inclination | 82.70° |
| Period | 97.20 minutes |

DISCOVERE 34, also known as CORONA 9027, was a United States optical reconnaissance satellite which was launched on 5 November 1961. It was the ninth of ten CORONA KH-2 satellites, based on the Agena B.[3]
Launch
The launch of DISCOVERER 34 occurred at 20:00:30 GMT on 5 November 1961.[1] A Thor-Agena B launch vehicle was used, flying from Launch Complex 75-1-1 at the Vandenberg Air Force Base.[1] Although the satellite achieved orbit, and was assigned the Harvard designation 1961 Alpha Epsilon 1, the launch was unsuccessful. An anomalous angle taken during ascent resulted in the spacecraft being placed into an unusable orbit.[4] It was the second consecutive KH-2 launch failure; the previous mission, Discoverer 33, had failed to achieve orbit due to a separation failure.
DISCOVERER 34 was launched into a low Earth orbit, with a perigee of 227 km (141 mi), an apogee of 1,011 km (628 mi), 82.7° of inclination, and a period of 97.20 minutes.[2] The satellite had a mass of 1,150 kg (2,540 lb),[5] and was equipped with a panoramic camera with a focal length of 61 cm (24 in), which had a maximum resolution of 7.6 m (25 ft).[6] Images were to have been recorded onto 70 mm (2.8 in) film, and returned in a Satellite Recovery Vehicle (SRV). The Satellite Recovery Vehicle to be used by DISCOVERER 34 was SRV-553. Due to the launch failure, and a problem with a gas valve on the spacecraft, recovery of the SRV was not attempted.[4] Discoverer 34 decayed from orbit on 7 December 1962.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Launch Log". Jonathan's Space Report. 21 July 2021. https://planet4589.org/space/log/launchlog.txt.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Trajectory: DISCOVERER 34 (1961-029A)". NASA. 28 October 2021. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/displayTrajectory.action?id=1961-029A.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ Krebs, Gunter (7 February 2018). "KH-2 Corona". Gunter's Space Page. https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/kh-2.htm.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lindborg, Christina; Pike, John (9 September 2000). "KH-3 Corona". Federation of American Scientists. http://www.fas.org/spp/military/program/imint/kh-3.htm.
- ↑ Wade, Mark. "KH-3". Encyclopedia Astronautica. http://www.astronautix.com/craft/kh3.htm.
- ↑ "Corona". Mission and Spacecraft Library. NASA. http://msl.jpl.nasa.gov/programs/corona.html.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
 |
