Engineering:Fairchild 91
| Fairchild 91 A-942 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Fairchild XR-942-B "Kono," belonging to explorer Richard Archbold | |
| Role | Flying boat airliner |
| Manufacturer | Fairchild |
| Designer | Alfred Gassner |
| First flight | 5 April 1935[1] |
| Primary user | Pan Am |
| Number built | 4[1] |
The Fairchild 91, (a.k.a. A-942), was a single-engine eight-passenger flying boat airliner developed in the United States in the mid-1930s.[2]
Design
Fairchild designed the aircraft in response to a Pan American Airways request[2] for a small flying boat to operate on their river routes along the Amazon and Yangtze. The result was a conventional high-wing cantilever monoplane with its radial engine mounted above the wing in a streamlined nacelle. Before construction of the prototype was complete, however, Pan American no longer required the aircraft to operate in China, and Fairchild modified the design to optimise it for the tropical conditions of Brazil.
Operational history
After the first two aircraft were delivered, Pan American cancelled the remaining four aircraft on its order, discovering that the two aircraft they had already purchased were capable of handling their entire Amazon River demand; the Model 91 had become a victim of its own success. Fairchild completed one more airframe under the designation A-942-A. The sole A-942-B was specially built for the American Museum of Natural History [regn. no. NR777], to be used by naturalist Richard Archbold on his second expedition to New Guinea in 1936-37.[1] The prototype was sold to the Spanish Republican Air Force , but was captured by the Spanish Nationalists and was used by them until 1938. One of the privately owned A-942s served with the RAF in Egypt for a time.
Note: Some sources state that seven aircraft were built, but this is incorrect, probably brought about by confusion due to the frequent changes in engine installations.[1]
Variants
- Fairchild 91 Baby Clipper[1]
- The initial version built to a Pan American specification for use on river-based sectors, initially powered by a 750hp Pratt & Whitney S2EG Hornet.[2] Three built,[NC14743 (prototype with retractable wing floats, and Zap flaps), NC14744 = PP-PAP, NC15952 = PP-PAT].
- Fairchild A-942-A[1]
- Alternative designation for the Fairchild 91
- Fairchild 91B Jungle Clipper[1]
- Specially equipped for NYC Museum of Natural History, initially powered by a 700hp Wright F-52 Cyclone.[2] One built, NR777.[1]
- Fairchild A-942-B[1]
- Alternative designation for the Fairchild 91B.
- Fairchild XSOK-1
- Proposed U.S. Navy scout variant; cancelled before any aircraft were built.[3]
Specifications (A-942-A)
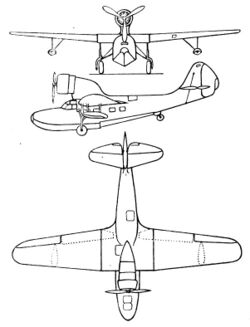
Data from [1]
General characteristics
- Crew: two pilots
- Capacity: eight passengers
- Length: 46 ft 8 in (14.22 m)
- Wingspan: 56 ft 0 in (17.07 m)
- Height: 14 ft 8 in (4.47 m)
- Wing area: 483 ft2 (44.9 m2)
- Empty weight: 6,596 lb (2,992 kg)
- Gross weight: 10,500 lb (4,763 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney R-1690, 800 hp (600 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 167 mph (269 km/h)
- Range: 665 miles (1,070 km)
- Service ceiling: 15,600 ft (4,755 m)
- Rate of climb: 840 ft/min (4.3 m/s)
References
Notes
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 http://aerofiles.com/_fair.html
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Taylor, Michael J.H. . Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation”. Studio Editions. London. 1989. ISBN 0-517-69186-8
- ↑ Johnson, E.R. (2009). American Flying Boats and Amphibious Aircraft: An Illustrated History. Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Company. p. 339. ISBN 978-0786439744. https://books.google.com/books?id=AtqOSxG9N1YC&pg=PA339&lpg=PA339&dq=Fairchild++%22SOK%22+amphibian&source=bl&ots=0fPuMYx5Bs&sig=ZvCCjsNTWtefIGbEV6rYTUCQmXY&hl=en&sa=X&ei=QB0XUcLmNJGI8QTQyIDgDA&ved=0CDEQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q&f=false.
Bibliography
- Taylor, Michael J.H. . Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation”. Studio Editions. London. 1989. ISBN 0-517-69186-8
- World Aircraft Information Files. London: Bright Star Publishing. pp. File 894 Sheet 04.
- [1]
External links
