Engineering:Gallery (New Orleans)

In New Orleans, a gallery is a wide platform projecting from the wall of a building supported by posts or columns. Galleries are typically made of cast iron (or wrought iron in older buildings) with ornate balusters, posts, and brackets.
The intricate iron balconies and galleries of the French Quarter are among the renowned icons of New Orleans.[1]
Terminology

City of New Orleans has specific definitions for platforms that project from the face of the building. Specifically, it distinguishes between balconies and galleries. The platform projection of balconies typically has a width of up to 4 feet (1.2 m). They do not have any supporting posts and typically lack a roof structure. Galleries are wider platforms that project over the property lines to cover the full width of the public sidewalk, and they have supporting posts or columns at the street curb.[2] Galleries may or may not have a roof cover.[2]
The city also uses the term "gallery" in other contexts. A side gallery is a porch on the side of a shotgun house used as an exterior corridor of the house. Double gallery is used to describe a specific house type called double-gallery house that has galleries across the facade of both first and second floors. The galleries on both floors are within the property line and typically covered by the roof of the main house. Triple gallery is similar but for three-story buildings.[2] However, when describing multi-level galleries that are attached to townhouses (not describing a house type), the term double galleries is used to describe galleries that are attached to the second and third floors of a townhouse with posts on the curb.[3][4]
History
New Orleans was founded in early 1718 by the French as La Nouvelle-Orléans, under the direction of Louisiana governor Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville.[5] During the early French settlement, houses were constructed in the Creole cottage style – simple, one-story structures with timber board walls. Local builders adapted the architecture to the tropical climate by adding wooden galleries with roof covers. These galleries served a dual purpose, providing protection from the elements and embracing the pleasant, airy designs influenced by the French style in the West Indies. They were also used as a transition space between private and public areas.[6][7]
In a 1731 plan, high hip-roof houses in New Orleans were spaced across city blocks, surrounded by gardens, and positioned with their front sides either directly at or near the sidewalk. Some of these houses had full front galleries. An example of such house style with raised basement can still be seen at Madame John's Legacy. Although the house was destroyed and rebuilt in 1788, it retained its original design circa 1730.[8] By the mid-18th century, New Orleans was transformed into a French Village with picket-fenced gardens and wooden galleries.[7]
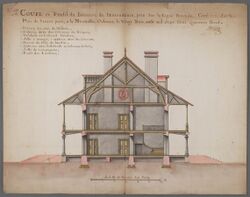
In 1749, the Intendance building plan was drawn by Ignace François Broutin with a design of two-story galleries. It was the earliest record of such design in Louisiana, but the building was not built.[8][9]
In 1763 following Britain's victory in the Seven Years' War, the French colony west of the Mississippi River—plus New Orleans—was ceded to the Spanish Empire as a secret provision of the 1762 Treaty of Fontainebleau.[10] The Spanish viewed the Province of Louisiana as a buffer zone to protect their Mexican colony, they did not invest in transforming local culture in New Orleans, known to the Spanish as La Nueva Orleans.[6] By 1765, almost every building had a gallery across the front on the first floor. Many two-story buildings had two-story galleries.[8]
Major fires in 1788 and 1794 completely destroyed a large amount of houses built during the French period. The Spanish administration imposed stricter building codes banning timber construction and wooden shingles. New buildings must be constructed with fire resisting stucco-covered brick and clay tiles. However, there was no evidence of Spanish architects involved in the reconstruction. During the Spanish period, population in New Orleans increased significantly. New two and three story masonry and stucco townhouses were built to keep up with the population. The new buildings were kept as continuation of French colonial architecture.[6] An influx of refugees from French colony Saint-Domingue (now Haiti) during the Haitian Revolution starting in 1791 brought surveyors and architects to New Orleans reinforcing French architectural traditions.[11] Certain architectural elements were borrowed from the Spanish including arched openings on the ground floor, courtyards at the rear of the buildings and wrought iron balconies on building facades.[7] The earliest recorded attempt to extend a balcony to cover the entire sidewalk was in December 1789 when Don Joseph de Orue y Garbea petitioned the Spanish Cabildo for a permit to build a gallery for his house. The permit was granted.[8][12]
In residential streets such as Royal Street, shops were set up on the ground floor and living quarters were on upper floors of Creole townhouses. The style followed Creole cottages which did not have hallways, and rooms were used in multi-purposes. Cramped living space created a need for residents to find a relief. Those townhouses were built with continuous balconies with hand-wrought iron railings installed on street and courtyard sides to provide light and fresh air.[6]
Installing wrought-iron cantilevered or bracketed balconies created new demands for blacksmiths during that period until 1825 when Leeds Iron Foundry introduced cast iron technology with a faster build process to New Orleans. It also allowed iron to be molded to create highly decorative patterns and intricate filigree that were popular in the 19th century. At that point, the mixture between wrought iron and cast iron railings in balconies started to appear.[7]

Meanwhile, the needs for maximizing living space in an urban setting continued.[6] Some home owners extended second floor balconies to cover the whole sidewalk, still without a roof. Early designs of galleries were based on wrought-iron balcony railings such as cathedral arch pattern, and scrollwork. Cast iron posts were used to support the extended galleries. A surviving example can be still seen at 529-531 Governor Nicholls Street.[13]
Highly ornate multi-story cast iron galleries appeared in the 1850s. The first multi-story galleries were known to be of the Pontalba Buildings which were built between 1849 and 1851.[7] The Pontalba's galleries were cast in New York with initials AP of Micaela Almonester, Baroness de Pontalba on them.[14][15] A series of eleven buildings on St. Peter Street between Royal Street and Cabildo Alley known as the LaBranche Buildings were built in 1840. Beginning in 1850, cast iron galleries were added to those buildings having a different pattern in each building.[14][16] From 1852 to 1856, Touro Buildings were built with cast-iron-lace double galleries that wrapped around the entire city block on Canal Street between Royal Street and Bourbon Street.[7] In 1858, elaborated galleries were added to beautify the brick townhouse at 900-902 Royal Street owned by Miltenberger who was an agent of Wood and Perot of Philadelphia, a cast-iron manufacturer, as a way to showcase the company's product.[17][14]
-
Pontalba's monogram (AP) on ironwork
-
Cast iron galleries of two LaBranche buildings
-
Touro Buildings in 1895
-
The 1858 galleries of the Miltenberger Houses
The second half of 19th century saw an explosive growth of houses with iron galleries. Out of 2,244 buildings in the French Quarter inspected by a researcher, 51 percent of townhouses and 11 percent of commercial buildings were with iron-lace galleries with average build years of 1853 to 1855 in styles inspired by the Pontalba and Touro buildings.[7] Some highly ornate galleries were built as part of building construction, for example, the second floor gallery of 817-821 Toulouse Street was built when the two-story Greek Revival building was constructed circa 1860.[18] Some multi-story galleries were put up along with building renovation projects, for example, the third floor addition in 1870 of 624 Dumaine Street came with ornate galleries for the second and third floors.[19] Some were simply replacements of older iron balconies of the buildings, for example, 730 Dumaine Street had iron galleries that replaced the original balconies of the 1832 house.[20]
The popularity of cast iron galleries in New Orleans waned in the 1860s during the American Civil War when Leeds Iron Foundry redirected its iron production to support the Confederate. By the 1880s, those galleries with cast-iron ornaments lost its uniqueness as the molded patterns repeated in many buildings throughout city's streets and they were seen as out of style.[21] During that period, several conversions of simpler designs of wrought-iron balconies to galleries continued. Some examples can be seen at 601-603 Barracks Street, 400-406 Dauphine Street, and 600-616 St. Peter Street.[22][23][24] The later is notable in that the wrought-iron railing that was built by master blacksmith Marcellino Hernandes for the original narrower balcony of the late 18th century building was extended to the full sidewalk width in the 1880s. When the building was rebuilt in 1964, the railing was moved back to serve a narrower balcony to imitate the original building design.[24] In 2013, balcony was extended once again to become a gallery. With all those rebuilds, the same original railing survived to today.[25][14]
-
Galleries on upper floors of 624 Dumaine Street
-
View from 730 Dumaine Street gallery
-
Wrought iron gallery of 601-603 Barracks Street
-
Covered gallery of 400-406 Dauphine Street
By the early 20th century, fashion had changed to match modern architecture. A large amount of cast-iron galleries on Canal Street was removed from the buildings to give a modern look. The destruction also happened in other wealthier districts outside of the French Quarter. In the 20th century, the French Quarter area was crowded and considered to be a poorer neighborhood. There was little incentive for property owners to invest in upgrading their buildings to the modern time. Most of the buildings were unchanged from their 19th century styles.[14][21] New ornate galleries constructed in this period became rare. An exception to this was a replacement of the mid-nineteenth century cast iron balconies with ornamental cast iron galleries at 936-942 Royal Street in the late 1930s.[26] In 1937, the city established the Vieux Carré Commission that started a preservation movement to prevent destruction of architectural heritage in the French Quarter including a preservation of iron galleries.[7] By the late 20th century, ironwork was carefully incorporated into new building constructions. A notable example was the Royal Sonesta hotel built between 1968 and 1969. The buildings took the entire block on Bourbon Street between Bienville Street and Conti Street. The exterior was built to follow the style of traditional row houses surrounding an internal courtyard. Multi-story decorative galleries that wrapped around the buildings followed the form of those Miltenberger and LaBranche buildings.[27][14]
Enduring for nearly two centuries, the iron galleries in the French Quarter have persevered through a series of events. The Capture of New Orleans that happened quickly during the Civil War left the city unscratched. Neglect from property owners in the early 20th century contributed to the buildings remaining unchanged. Finally, the establishment of the Vieux Carré Commission prevented the ironwork from becoming scrap metal to support World War II. These factors have collectively preserved the unique appearance of the French Quarter that we see today.[21][14][7]
Architectural details
-
Simple posts on the first floor and more ornate on upper floors[2]
-
Metal outriggers are used to support galley's deck[2]
-
A gallery with patterns of oak leaves and acorns[29]
-
Fire escapes at 700-708 Royal Street used to be part of the galleries but they no longer meet the building code.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "How "Keeping up with the Pontalbas" sparked a decorative ironwork trend in 19th-century New Orleans". Preservation Resource Center of New Orleans. https://prcno.org/keeping-pontalbas-sparked-decorative-ironwork-trend-19th-century-new-orleans/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Guidelines for Porches, Galleries and Balconies (PDF) (Technical report). City of New Orleans Historic District Landmarks Commission. January 2019. 09-12. Retrieved January 1, 2024.
- ↑ "335 Decatur St.". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=11089.
- ↑ "817-819 Chartres St.". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=18517.
- ↑ Campanella, Richard (2008). "II: Settling the Landscape". Bienville's Dilemma: A Historical Geography of New Orleans. Lafayette, LA: Center for Louisiana Studies, University of Louisiana at Lafayette. pp. 113–114. ISBN 978-1887366854. http://www.richcampanella.com/assets/pdf/Bienvilles%20Dilemma_Part2_Settling%20the%20Landscape.pdf. Retrieved July 12, 2014.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Sexton, Richard (2003). New Orleans: Elegance and Decadence (illustrated, revised ed.). Chronicle Books. pp. 16–17. ISBN 9780811841313. https://books.google.com/books?id=fgopZSwQAl8C&printsec=frontcover. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 Campanella, Richard (December 8, 2018). "City signature: Now a mainstay, iron-lace galleries were a long time coming to the streets of New Orleans". The Advocate. https://www.nola.com/entertainment_life/vintage/city-signature-now-a-mainstay-iron-lace-galleries-were-a-long-time-coming-to-the/article_b60c66e2-00cb-5cbe-9f76-06e4154e3172.html.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Louisiana buildings, 1720 - 1940: the historic American buildings survey (1. print ed.). Baton Rouge, La.: Louisiana State Univ. Press. 1997. pp. 19, 32–34, 54. ISBN 9780807120545. https://books.google.com/books?id=YmOUaJxyFpwC&printsec=frontcover. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ↑ Sexton, Richard; MacLean, Alex (1999). Vestiges of Grandeur: Plantations of Louisiana's River Road. Chronicle Books. p. 18. ISBN 9780811818179. https://books.google.com/books?id=aL8YFv7aMTsC&pg=PA18. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ↑ Neidenbach, Elizabeth (June 22, 2020). "The Treaty of Fontainebleau" (in en). https://64parishes.org/entry/the-treaty-of-fontainebleau-2.
- ↑ Toledano, Roulhac (1996). The National Trust guide to New Orleans. New York: Preservation Press John Wiley & Sons. p. 11. ISBN 9780471144045. https://books.google.com/books?id=pFDfEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA11. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ↑ "Digest of the Acts and Deliberations of the Cabildo Chronological--1789". City Archives New Orleans Public Library. http://archives.nolalibrary.org/~nopl/inv/digest/digest1789.htm.
- ↑ "529-531 Governor Nicholls St.". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=22695&tab=3.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 14.5 14.6 Magill, John (February 11, 2014). "Mardi Gras from a Balcony". The French Quarterly. https://frenchquarterly.com/history/mardi-gras-balcony.
- ↑ Malone, Lee (2003). The Majesty of New Orleans. Pelican Publishing. pp. 92–95. ISBN 9781455608171. https://books.google.com/books?id=oJhJJYe51FUC&printsec=frontcover. Retrieved January 2, 2024.
- ↑ "621 St. Peter St.". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=18502.
- ↑ "Miltenberger Houses". https://sah-archipedia.org/buildings/LA-02-OR22.
- ↑ "817-821 Toulouse St.". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=18733.
- ↑ "624 Dumaine St.". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=18533&tab=3.
- ↑ "730 Dumaine St.". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=18607.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 Fricker, Jonathan (May 1, 2021). "New Orleans’ cast iron age". Preservation Resource Center of New Orleans. https://prcno.org/new-orleans-cast-iron-age/.
- ↑ "601-603 Barracks St.". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=22813.
- ↑ "400-406 Dauphine Street". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=11434.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 "600-616 St. Peter St.". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=18470-01&tab=3.
- ↑ "Le Petit Theatre / Tableau Restaurant". Moses Engineers. https://mosesengineers.com/projects/le-petit-theatre-tableau-restaurant/.
- ↑ "936-942 Royal St.". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=18553.
- ↑ "312-316 Bourbon St.". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=11310.
- ↑ "1127-1129 Chartres St.". The Historic New Orleans Collection. https://www.hnoc.org/vcs/property_info.php?lot=22776.
- ↑ "Miltenberger Houses". Society of Architectural Historians. https://sah-archipedia.org/buildings/LA-02-OR22.
External links
 |








![Simple posts on the first floor and more ornate on upper floors[2]](/wiki/images/thumb/2/25/DumaineGreenBalconyJuly08.jpg/169px-DumaineGreenBalconyJuly08.jpg)
![Metal outriggers are used to support galley's deck[2]](/wiki/images/thumb/0/04/Dauphine_Street%2C_French_Quarter%2C_19_July_2021_-_02.jpg/169px-Dauphine_Street%2C_French_Quarter%2C_19_July_2021_-_02.jpg)
![A motif of grapes and vines on the galley of 1127-1129 Chartres Street[2][28]](/wiki/images/thumb/1/14/French_Quarter_Balcony.jpg/169px-French_Quarter_Balcony.jpg)
![A gallery with patterns of oak leaves and acorns[29]](/wiki/images/thumb/c/c7/French_Quarter_%22Cast-Iron_Balcony_%26_Floral_Baskets%2C%22_New_Orleans%2C_Louisiana%2C_U.S.A.jpg/330px-French_Quarter_%22Cast-Iron_Balcony_%26_Floral_Baskets%2C%22_New_Orleans%2C_Louisiana%2C_U.S.A.jpg)
![Fire escapes at 700-708 Royal Street used to be part of the galleries but they no longer meet the building code.[2]](/wiki/images/thumb/e/e9/St_Peter_Street_Balconies_French_Quarter%2C_New_Orleans%2C_June_1958.jpg/500px-St_Peter_Street_Balconies_French_Quarter%2C_New_Orleans%2C_June_1958.jpg)
