Engineering:Ichcahuipilli
The ichcahuīpīlli, known in Spanish as escaupil,[1] was a Mesoamerican military soft body armor similar to the European gambeson that was commonly used by the Aztecs and the Tlaxcaltecs. It was constructed of densely packed, unspun cotton stitched between two layers of fabric.[2] The name is derived from the Nahuatl words ichcatl "cotton" and huīpīlli "shirt".

Use
Ichcahuipilli armor was a lightweight, multifunctional garment worn on the torso of the warrior, designed to provide blunt-force trauma protection against clubs and batons, slash protection from obsidian macuahuitl, and projectile protection from arrows and atlatl darts.[3] Ichcahuipilli were made of successive layers of packed cotton, and sewn in diamond-shaped patterns. Wearers usually wore the ichcahuipilli directly on their skin, however, the most experienced warriors, especially those of the orders of eagle and jaguar warriors, used it to complement a tlahuiztli suit.[2]
Upon contact with a shot projectile, the dense fibrous materials of the vest would absorb the energy of the shot and dissipate it on a much larger area, stopping the bullet or arrow in the vest.
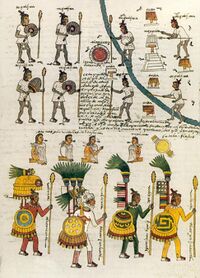
Atlatl darts in particular were found to regularly penetrate European chainmail. Ichcahuipilli was so effective at stopping arrows, darts, and even lead musket shot,[4] Spanish soldiers often discarded their own, heavier plate armor, which was uncomfortable in the warmer, moist Mexican climate and prone to rust, in favor of indigenous armor which was lighter and comparatively maintenance-free.[5][6]
Variations
Most ichcahuipilli were made in a vest style that covered the torso down to the hips; however, various other designs were made and worn by Aztec soldiers of different ranks and warrior societies. The armor came in sleeved variations or in surcoat designs that covered most of a warrior's body down to the knees.
Popular culture
For SpikeTV's reality program Deadliest Warrior, a piece of material designated as ichcahuipilli armor was tested against the iron-tipped arrows of the Azande pima and botto. The armor was able to stop the arrows and even ward off some of them. It was later determined that although the arrows penetrated the material, the arrows were stopped and penetration was minimal enough to not cause any serious injury.
See also
- Aztec warfare
- Armor
- Linothorax
- Gambeson
References
- ↑ "escaupil" (in es). Real Academia Española. https://dle.rae.es/escaupil. Retrieved 7 August 2020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Hassig, Ross (1988). Aztec Warfare: Imperial Expansion and Political Control. p. 88. ISBN 978-0806127736.
- ↑ Powell, Philip Wayne (1977). Mexico's Miguel Caldera : the taming of America's first frontier, 1548-1597. Tucson: University of Arizona Press. ISBN 0-8165-0569-1. OCLC 3090055.
- ↑ Phillips, Charles "The Complete Illustrated History of the Aztec & Maya: The Definitive Chronicle of the Ancient Peoples of Central America & Mexico - Including the Aztec, Maya, Olmec, Mixtec, Toltec & Zapotec" 2015.
- ↑ "Ichcahuipilli" (in es). 2012. http://www.enciclopediagro.org/index.php/indices/indice-cultura-general/914-ichcahuipilli.
- ↑ Phillips, Charles (2006–2007). The Complete Illustrated History of the Aztecs & Maya: The definitive chronicle of the ancient peoples of Central America & Mexico - including the Aztec, Maya, Olmec, Mixtec, Toltec & Zapotec. Hermes House. p. 94. ISBN 1-84681-197-X. OCLC 642211652.
 |
