Engineering:KVM Splitter
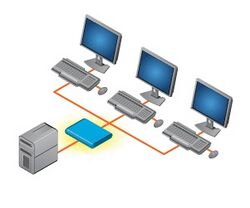

A KVM (Keyboard Video Mouse) Splitter, also known as a Reverse KVM switch, is a hardware device that allows users to control a single computer from one or more sets of keyboards, video monitors, and mice. With a KVM splitter, users access the connected computer consecutively rather than simultaneously. It differs from a KVM Switch which allows multiple computers to be controlled, usually, by a single keyboard, monitor and mouse.
Types
There are two main functional designs of KVM splitters:
- Emulation
- In an emulation based design, the KVM splitter feeds the emulated controls from the active keyboard and mouse to the connected computer. A PS/2 KVM splitter must be emulation based, because PS/2 computers only have two PS/2 connectors – one designated for a keyboard and one for a mouse. In contrast, a USB computer tends to have multiple USB ports, which are not designated for a specific device. Keyboards, mice, external storage devices, printers, etc. can be connected to the USB ports on a computer. USB KVM splitters can also be emulation based, but they tend to be built using a hub-based design.
- Hub Based
- When a KVM splitter is hub based, it functions similar to having multiple keyboards and mice connected to a single computer. Instead of sending one emulated signal to the computer based on an active keyboard and mouse, the hub-based splitter continuously feeds the active controls and emulation is not needed.
Signals
Common input and output video signals for KVM splitters include HDMI, DVI, and VGA. Keyboard and mouse input and output signals are PS/2 or USB. Some KVM splitters also offer additional USB input ports to connect peripheral devices, such as external hard disk drives and printers, which can be shared across all users.
Monitor
As one computer is feeding video for multiple monitors, there are a few ways KVM splitters can handle the potentially different DDC and EDID transmissions from the monitors.[1]
- Pass-through: the KVM splitter transfers the EDID data directly from a display connected to the primary port to a source. If all monitors are identical, this will not be an issue. However, if different monitors are used, the EDID from the primary monitor may not be compatible with others.
- Built-in: the KVM splitter fakes the EDID data using an EEPROM with a generic EDID. This provides less compatibility as there is no communication between the monitors and the computer, and monitors that do not support the generic EDID may not work.
- EDID learning: the KVM splitter reads EDID from all connected monitors and creates a new EDID table with the common resolutions amongst the displays. This ensures the best compatibility when many different monitors are used.
Usage
A KVM Splitter can be used by multiple users to control a single computer from multiple locations. Any user can access the computer and its programs from their workstation. There are a few activation modes KVM splitters operate in, which limits simultaneous user activity.
- User specific: only one selectable user is active, other users can view what is happening.
- Instantaneous mode: different users can immediately access the computer after the last keystroke or mouse movement by the active user.
- Delay mode: a selectable delay, e.g. 5 seconds, occurs before another user can access the computer after the last keystroke or mouse movement by the active user.
The method of switching from one user to another depends on the KVM splitter and supported modes of operation. Rotary switches, active electronic switches, push buttons or automatic activation via keystrokes/mouse are some of the switching methods commonly used.
KVM Splitters can be combined with KVM switches and KVM extenders (which provide a way to relocate keyboard, monitor, and mouse to a far distance from the computer) to set up more complex configurations. For example, multiple users can access the same computer without the need for physical proximity to the computer. A common industrial application is to allow access to a computer located in a cleanroom from outside, to restrict the level of contamination. By providing access to multiple users through a KVM splitter, pollutants can be minimized by reducing the need for the users to enter the cleanroom.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Edid Handling in Repeater Devices - KVM Splitters, KVM Extenders, etc.". https://www.networktechinc.com/edid.html. Retrieved 12 August 2015.
- ↑ "5 Common Applications Of KVM Splitter". 11 August 2015. https://medium.com/@huisian/5-common-applications-of-kvm-splitters-d34892933847. Retrieved 12 August 2015.
External links
 |
