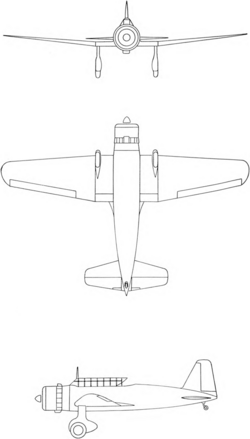
Engineering:Mitsubishi Ki-51
| Ki-51 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Mitsubishi Ki-51 | |
| Role | Light bomber/dive bomber |
| Manufacturer | Mitsubishi Jukogyo KK |
| First flight | mid-1939 |
| Primary user | Imperial Japanese Army Air Service |
| Number built | 2,385[1] |
The Mitsubishi Ki-51 (Army designation "Type 99 Assault Plane"; Allied nickname "Sonia") was a light bomber/dive bomber in service with the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. It first flew in mid-1939. Initially deployed against Chinese forces, it proved to be too slow to hold up against the fighter aircraft of the other Allied powers. However, it performed a useful ground-attack role in the China-Burma-India theater, notably from airfields too rough for many other aircraft. As the war drew to a close, the Japanese began using them in kamikaze attacks. Total production was around 2,385 units.
On the day Hiroshima was destroyed by an atomic bomb, a single Ki-51 was responsible for the last Japanese sinking of a US warship, sinking USS Bullhead (SS-332) with all hands.
Charles Lindbergh, flying a P-38 Lightning, shot down a Ki-51.[2]
Variants
- Prototypes: two built
- Service trials: 11 built
- Ki-51: 2,372 built (Manufacturers: Mitsubishi (1,462), Tachikawa Army Air Arsenal (913)) until March 1944
- Ki-51A: reconnaissance version.
- Ki-51B: assault version with armor and bomb racks to carry 200 kg (441 lb) of bombs. It could also be fitted with an aerial camera.
- Mansyu Ki-71: three prototypes built by Mansyu with retractable landing gear, did not enter production.[3]
Operators
 Japan
Japan
 Indonesia
Indonesia
- Indonesian Air Force - In late 1945, the Indonesian People's Security Army (TKR) captured some aircraft at Japanese bases, including Bugis Air Base in Malang. Most aircraft were destroyed during the Indonesian National Revolution of 1945–1949. Two Yokosuka K5Y "Cureng", and a Ki-51 "Guntei" carried out a bombing operation against the Dutch on July 29, 1947.
 China
China
- Communist Chinese (captured): The last 4 of around 100 Ki-51s were retired in 1953.
 Republic of China
Republic of China North Korea
North Korea
- Following independence, transferred from the Soviet Union.
 South Korea
South Korea
- Used by South Korean Airforce during Korean War
Specifications (Ki-51)
Data from Japanese Aircraft of the Pacific War[4]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 9.21 m (30 ft 3 in)
- Wingspan: 12.1 m (39 ft 8 in)
- Height: 2.73 m (8 ft 11 in)
- Wing area: 24 m2 (260 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 1,873 kg (4,129 lb)
- Gross weight: 2,798 kg (6,169 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 2,920 kg (6,437 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Mitsubishi Ha-26-II 14-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engine, 710 kW (950 hp)
- Propellers: 3-bladed variable-pitch propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 424 km/h (263 mph, 229 kn) at 3,000 m (9,800 ft)
- Range: 1,060 km (660 mi, 570 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 8,270 m (27,130 ft)
- Time to altitude: 5,000 m (16,000 ft) in 9 minutes 55 seconds
- Wing loading: 117 kg/m2 (24 lb/sq ft)
- Power/mass: 0.24 kW/kg (0.15 hp/lb)
Armament
- Guns:
- 2× fixed, forward-firing 7.7 mm (.303 in) Type 89 machine guns (replaced with 2× 12.7 mm (.5 in) Ho-103 machine guns in later models)
- 1× 7.7 mm (.303 in) Te-4 Machine gun rearward-firing machine gun.
- Bombs: 200 kg (441 lb) bombs (normal operations); 250 kg (551 lb) for suicide operations[4]
See also
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Aichi D3A
- Douglas SBD Dauntless
- Ilyushin Il-2
- Junkers Ju 87D
- Kawasaki Ki-32
- Mitsubishi Ki-30
Related lists
Notes
- ↑ Angelucci, Enzo (1988). Combat aircraft of World War II. p. 26. ISBN 0-517-64179-8.
- ↑ "Charles Lindbergh and the 475th Fighter Group." Lightning Strikes.
- ↑ Francillon 1979, p. 180.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Francillon 1979, p. 181.
Bibliography
- Francillon, René J. (1979). Japanese aircraft of the Pacific War. London: Putnam. ISBN 0-370-30251-6. OCLC 6124909. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/6124909. (new edition 1987 by Putnam Aeronautical Books, ISBN:0-85177-801-1.)
- Green, William; Swanborough, Gordon (n.d.). "Pentagon Over the Islands: The Thirty-Year History of Indonesian Military Aviation". Air Enthusiast Quarterly (2): 154–162. ISSN 0143-5450.
- Soumille, Jean-Claude (September 1999). "Les avions japonais aux couleurs françaises" (in French). Avions: Toute l'Aéronautique et Son Histoire (78): 6–17. ISSN 1243-8650.
External links
 |