Engineering:Morane-Saulnier AR
| Type AR, MS.35 | |
|---|---|

| |
| MS.35R | |
| Role | Trainer |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Morane-Saulnier |
| First flight | 1915 |
| Primary user | Aéronautique Militaire |
| Number built | >400 |
The Morane-Saulnier AR was a trainer aircraft produced in France during and after the First World War.[1][2]
Design and development
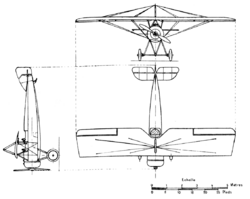
Developed from the Morane-Saulnier LA reconnaissance aircraft, the AR was a wire-braced parasol-wing monoplane of conventional design with two open cockpits in tandem and cross-axle-style tailskid undercarriage.[2] Construction was mostly of fabric-covered wood, but the forward fuselage was skinned in metal.[1]
Large-scale production commenced after the Armistice, with the type now designated MS.35, in a number of subtypes differentiated principally in the engine used.[1][2] Although Morane-Saulnier hoped to sell the type on the civil market as a touring machine,[3] most of the 400 examples built saw service with the French Army, but others were used by the Navy and still others exported to foreign air arms.[1][2] The MS.35s were used in France until 1929, when some of them were purchased by the country's flying clubs.[2]
Variants
- Type AR
- MS.35R - main production version with Le Rhône 9C engine
- MS.35A - version with Anzani engine
- MS.35C - version with Clerget 9C engine
Operators
 France
France
- Aéronautique Militaire
- Écoles de pilotage
- Aéronautique Navale
 Argentina
Argentina
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Brazil
Brazil
 Greece
Greece
 Guatemala
Guatemala
 Paraguay
Paraguay
 Poland
Poland
- (70 examples)
 Romania
Romania
 Soviet Union
Soviet Union
- Soviet Air Force - (60 examples)
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Turkey
Turkey
 United States
United States
- United States Navy
 Uruguay
Uruguay
Specifications (MS.35R)
Data from "Morane-Saulnier Type AR (M.S.35)"
General characteristics
- Crew: Two, pilot and instructor
- Length: 6.30 m (20 ft 8 in)
- Wingspan: 10.57 m (34 ft 8 in)
- Gross weight: 764 kg (1,680 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Le Rhône 9C , 60 kW (80 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 125 km/h (78 mph, 68 kn)
- Service ceiling: 4,600 m (15,100 ft)
Notes
References
- The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft. London: Aerospace Publishing.
- "The Paris Aero Show 1919". Flight: 63–70. 15 January 1920. http://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1920/1920%20-%200066.html. Retrieved 2008-10-06.
- Kotelnikov, V.; Kulikov, V.; Cony, C. (December 2001). "Les avions français en URSS, 1921–1941" (in fr). Avions: Toute l'Aéronautique et son histoire (105): 50–56. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. pp. 684. ISBN 0-7106-0710-5.
- Hirschauer, Louis; Dollfus, Charles, eds (1920). L'Année Aéronautique: 1919-1920. Paris: Dunod. p. 21. https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k6553380s/f33.item.
- Hirschauer, Louis; Dollfus, Charles, eds (1921). L'Année Aéronautique: 1920-1921. Paris: Dunod. p. 29. https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k65534129/f41.item.
- Passingham, Malcolm; Noël (October 1989). "Les avions militaires roumains de 1910 à 1945" (in fr). Le Fana de l'Aviation (239): 14–15, 17–21.
- Wauthy, Jean-Luc; de Neve, Florian (April 1995). "Les aéronefs de la Force Aérienne Belge, deuxième partie 1919–1935" (in fr). Le Fana de l'Aviation (305): 28–33. ISSN 0757-4169.
Further reading
- Lacaze, Henri; Lherbert, Claude (2013) (in fr). Morane Saulnier: ses avions, ses projets. Outreau, France: Lela Presse. ISBN 978-2-914017-70-1.
 |