Engineering:Quoin



Quoins (/kɔɪn/ or /kwɔɪn/) are masonry blocks at the corner of a wall.[1] Some are structural, providing strength for a wall made with inferior stone or rubble,[2] while others merely add aesthetic detail to a corner.[3] According to one 19th-century encyclopedia, these imply strength, permanence, and expense, all reinforcing the onlooker's sense of a structure's presence.[4]
Stone quoins are used on stone or brick buildings. Brick quoins may appear on brick buildings, extending from the facing brickwork in such a way as to give the appearance of generally uniformly cut ashlar blocks of stone larger than the bricks. Where quoins are decorative and non-load-bearing a wider variety of materials is used, including timber, stucco, or other cement render.
Techniques

Ashlar blocks
In a traditional, often decorative use, large rectangular ashlar stone blocks or replicas are laid horizontally at the corners. This results in an alternate, quoining pattern.
Alternate cornerstones
Courses of large and small corner stones are used, alternating between stones of different thickness, with typically the larger cornerstones thinner than the smaller.[citation needed]
Alternate vertical
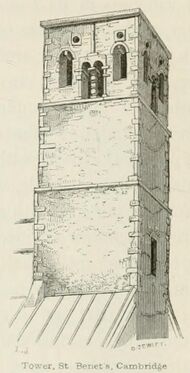
The long and short quoining method instead places long stone blocks with their lengths oriented vertically, between smaller ones that are laid flat. This load-bearing quoining is common in Anglo-Saxon buildings such as St Bene't's Church in Cambridge, England.[5]
References
- ↑ Rankine, William J. M. (1862). A Manual of Civil Engineering. Griffin, Bohn, and Co. p. 385. https://archive.org/details/amanualcivileng03rankgoog.
- ↑ Charles F.Mitchell. Building Construction. Part 1. First Stage or Elementary Course. Second Edition—Revised. Published by B.T. Batsford, 52 High Holborn. 1889. Page 48.
- ↑ "Definitions for: Quoin". http://blogmybrain.com/scrabble-word-finder/word/quoin.htm.
- ↑ Encyclopaedia Perthensis. 576: John Brown. 1816. https://books.google.com/books?id=J0pQAAAAMAAJ&q=quoin+architecture&pg=PA576.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Rickman, Thomas (1848). An attempt to discriminate the styles of architecture in England : from the Conquest to the Reformation : with a sketch of the Grecian and Roman orders : notices of numerous British edifices :and some remarks on the architecture of a part of France (Fifth ed.). London: John Henry Parker. p. Appendix-xxii. https://archive.org/details/stylesofarchitec00rick.
External links
| Look up quoin in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
 |
