Engineering:Roller coaster element
Roller coaster elements are the individual parts of roller coaster design and operation, such as a track, hill, loop, or turn. Variations in normal track movement that add thrill or excitement to the ride are often called "thrill elements".
Common elements
Banked turn
A banked turn is when the track twists from the horizontal plane into the vertical plane, tipping the train to the side in the direction of the turn. Banking is used to minimize the lateral G-forces on the riders to make the turn more comfortable. When a banked turn continues to create an upward or downward spiral of approximately 360 degrees or more, it becomes a helix.
Brake run
A brake run on a roller coaster is any section of track meant to slow or stop a roller coaster train. Brake runs may be located anywhere or hidden along the circuit of a coaster and may be designed to bring the train to a complete halt or to simply adjust the train's speed. The vast majority of roller coasters do not have any form of braking on the train but rather forms of braking that exist on track sections. One notable exception is the scenic railway roller coaster, which relies on an operator to manually control the speed of the train.
On most roller coasters, the brakes are controlled by a computer system. Some older coasters have manually operated friction or skid brakes, some with a pneumatic assist. These are either engaged at the control panel or operated by pulling or pushing large levers in the station.
Buzz bars
Single-position lap bars on wooden roller coasters are sometimes referred to as "buzz bars," a slang term named for the buzzing sound that some bars make as they lock or release. The term can be misleading as the buzzing sound only occurs on Philadelphia Toboggan Company (PTC) trains when the solenoid that releases the bar is out of alignment. There are other train types, such as NAD and even some PTC trains, that feature a single-position lap bar that has a mechanical release and therefore does not produce a buzzing sound. Most parks have switched to individual ratcheting lap bars, similar to the lap bars found on steel coasters. Ironically some of the earlier ratcheting lap bar conversions use a solenoid release and can also produce a buzzing sound. It can be argued that single-position buzz bars afford riders more air time on roller coasters, as ratcheting lap bars tend to lock further during the ride in many installations.
The traditional "pirate ship" style thrill ride often utilizes this type of restraint, as does the Troika.
Drive tire
A drive tire, or squeeze tire depending on its usage, is essentially a motorized tire used to propel a roller coaster train along a piece of track. Although they are most often used in station areas and brake runs, they can also be used to launch trains at greater speeds. However, they are generally used to propel the train at speeds between 5-8 mph. The Incredible Hulk Coaster at Universal's Islands of Adventure is notable for using drive tires to launch the train up an incline. Some roller coasters, most noticeably Vekoma Roller Skaters (Vekoma's version of a junior coaster) and Zierer Tivoli/Force (also junior coasters) also use drive tires instead of a chain on lift hills. Drive tires are also used to power other types of amusement rides, such as ferris wheels, Pirate Ships, and other spinning rides. The Olympia Looping traveling roller coaster at Barth, Alpina Bahn and Mindbender at Galaxyland at the West Edmonton Mall also feature a drive tire instead of a chain on their lift hill.
Drive tires are often used in one of two ways on roller coasters. When oriented horizontally, drive tires are often put in pairs so as to "squeeze" a portion of the train as it crosses that section of track. In this case, it is usually the brake fin that is used to propel or slow the train with the tires. When oriented vertically, they contact the underside of the train as it crosses a particular section of track. This underside area is a flat area which often has a grated metal surface to increase friction between the car and the tire. One disadvantage of vertical drive tires is that rainy weather can greatly reduce friction between the tire and the train, possibly causing the train to slightly overshoot its intended position and cause an emergency stop.
Headchopper
A headchopper is any point on a roller coaster where the support structure of the ride or the track itself appears to come very close to the passengers' heads. All headchoppers are, of course, designed so that even the tallest rider, with both hands up, would be unable to touch the structure; although if a rider exceeding the maximum height does board the coaster it could be potentially dangerous. Headchoppers are most common on wooden roller coasters but are also found on many steel roller coasters.
The inverted coaster equivalent is a foot chopper. Foot choppers are designed such that riders' legs appear to come close to the ride's support structure, water, or other ride surroundings. For example, Dragon Challenge at Islands of Adventure had many foot choppers, where the riders' feet come within feet of the ride's supports. Vekoma's Suspended Looping Coasters also feature an intense foot chopper during an in-line-twist, in which the train approaches a section of track directly below, making it appear that the riders' feet will impact the track if the train remains on that course, but the train undergoes an in-line-twist right before the obstruction, twisting the riders onto their backs as the above track crosses safely over the track below.
On Wing Coasters designed by Bolliger & Mabillard, keyhole elements are common. These elements feature both headchopper and foot chopper effects. The train seats riders in pairs on both sides of the track and passes through the center of an object, giving the illusion that the train and its passengers have just enough clearance to fit.[1][2]
Helix
A helix is a balanced spiral, generally exceeding 360°. Helixes can spiral upward or downward.
Launch track

A launch track is a section of a launched roller coaster in which the train is accelerated to its full speed in a matter of seconds. A launch track is always straight and is usually banked upward slightly, so that a train would roll backward to the station in the event of a loss of power.
A launch track serves the same basic purpose as a lift hill—providing energy to the train—but accomplishes it in an entirely different manner. A lift hill gives the train potential energy by raising it to the highest point in the track (and not significantly accelerating it). A launch track gives the train kinetic energy by accelerating it to the maximum designed speed (while not significantly raising the height of the track).
A launch track normally includes some form of brakes. Depending on the type of coaster, these brakes may be used in every run of the coaster (this is normally found on a shuttle roller coaster where the launch track also serves as the main brake run) or they may only come into play when a rollback occurs, normally on a complete-circuit coaster such as Stealth, Top Thrill Dragster, Kingda Ka, Rock 'n' Roller Coaster Starring Aerosmith and Xcelerator. In either case, the brakes are retracted to allow trains to launch and are engaged at all other times.
Lift hill

A lift hill, or chain lift, is often the initial upward section of track on a typical roller coaster that initially transports the roller coaster train to an elevated point. Upon reaching the top, the train is then disengaged from the lift hill and allowed to coast through the rest of the roller coaster's circuit.
Lift hills usually propel the train to the top of the ride via one of a few different types of methods: a chain lift involving a long, continuous chain which trains hook on to and are carried to the top; a drive tire system in which multiple motorized tires push the train upward; a cable lift system as seen on Millennium Force; or a linear synchronous motor system as seen on Maverick.
Launch lift hills are similar to launch tracks, but inclined rather than flat. Sometimes, launch lift hills serve the same purpose as lift hills but offer faster transport to the top of the lift hill; or they are sometimes used to power the train up into an element, like the Incredible Hulk Coaster at Universal Orlando. Launch lift hills use mostly linear synchronous motors or linear induction motors but sometimes use drive tires.
Linear induction motor
The linear induction motor is a simple but powerful type of electric motor used to propel the cars. Rather than using a standard enclosed spinning rotor and drive wheels, there is a long flat magnetic pole plate with closely spaced electric coils. This pole plate mounts on the track underneath the car and a matching metal plate attached to the car moves across the magnetic pole faces. By applying a multiphase alternating current to the poles, the pole plate induces eddy currents into the moving plate and can be used to accelerate or brake the car.
Compared to other drive mechanisms, the linear motor is typically maintenance-free. The pole faces on the track and moving plate attached to the car do not need to touch, and the gap between them can be quite wide to accommodate any side-to-side car motion, so there is no friction or wear between them. Further, the magnetic coil assembly on the driving pole plates are either potted or sealed in a weathertight enclosure, so that rain, vibration, and dust do not affect motor performance or cause drive motor slippage.
On-ride camera
An on-ride camera is a camera mounted alongside the track of a roller coaster that automatically photographs all of the riders on passing trains. They are usually mounted at the most intense part of the ride, to capture the best possible pictures. The pictures are available for viewing and purchase at a booth outside the ride's exit. On some rides, such as Saw: The Ride at Thorpe Park, Rocky's Rapids at Indiana Beach, and Hollywood Rip Ride Rockit at Universal Studios Florida, video, as well as still photographs, can be purchased upon exiting the ride.
Pre-drop
A pre-drop, or preliminary drop, is any small hill following the lift hill that precedes the main drop. After a train is hauled up the lift and begins to descend down the hill in a standard configuration, the force of gravity pulls the train cars that are still hooked to the lift. When a pre-drop is used, the tension and stress on the lift mechanism is reduced prior to the train's release. The element is commonly found on early B&M roller coasters, as well as older roller coasters from other manufacturers. An alternative name "trick hill" comes from the illusion created from the pre-drop, which "tricks" riders into thinking they have already started the main descent, when in fact they haven't.
Station
The station is the area where guests waiting in a line queue board a roller coaster. The line often divides into lanes to allow guests to board each row. In addition to boarding, passengers also exit the ride within the station, but this is not always at the same location where boarding passengers are waiting.
Train
A roller coaster train describes the vehicle(s) which transports passengers around a roller coaster's circuit. More specifically, a roller coaster train is made up of two or more "cars" which are connected by some sort of specialized universal joint. The vehicle is called a "train" due to its similarities with a railroad train. Individual cars vary in design, often carrying multiple passengers each. Some roller coasters, notably Wild Mouse roller coasters, operate with individual cars instead of trains.
Tunnels

Some roller coasters feature tunnels, and they may include special effects such as lighting, fog, and sound. The Iron Rattler at Six Flags Fiesta Texas, for example, features a darkened, above-ground tunnel.[3]
Non-inverting track elements

Camelback
A camelback or camelback hill is a hump-shaped hill that travels in a straight line designed to lift riders out of their seats and provide a feeling of weightlessness, commonly known as airtime.[4][5] It produces negative g-force to achieve the effect.[6][7] The term has been used to describe a series of smaller hills typically found near the end of a track's layout, which is a common finale on older wooden coasters.[7][8] A modern coaster's implementation of a camelback can be a much larger, single hill often found earlier in the track's layout.[4][9]
Double dip

A double dip element, also known as a double drop or double down, is created when a hill is divided into two separate drops by a flattening out of the drop midway down the hill. Two notable rides featuring this element are Jack Rabbit located at Kennywood and Jack Rabbit located at Seabreeze, both of which are roller coasters designed by John A. Miller in 1920. The inverse of this element is known as a double up, where two inclines are separated by a level piece of track. Stampida at Portaventura Park is an example that incorporates both a double dip and a double up element.
Hammerhead turn

A hammerhead turn is based on a flying maneuver by the same name and is similar to, but not the same as, a 180-degree overbanked turn (). The train enters the element with a steep slope up and a slight curve in the direction opposite that of the overall turn (a so-called "priming" of the turn). The train then banks heavily to the side opposite the initial curve and finishes its climb while it negotiates the overall turn, beginning its descent midway through the turn. The second half of the element is the same as the first half, but in reverse order. While negotiating a hammerhead turn element, the train makes a turn of more than 180 degrees; however, because of the entry and exit curves, the overall effect is that of a 180-degree turn that exits toward the direction from which it entered, roughly parallel to the portion of track preceding the hammerhead turn. Hammerhead turns are found on some B&M hypercoasters. Examples of these coasters are Nitro at Six Flags Great Adventure, Behemoth at Canada's Wonderland, Diamondback at Kings Island and Mako at SeaWorld Orlando.
Horseshoe
A horseshoe is a type of turnaround maneuver found on Maurer Rides GmbH's Spinning Coaster model. The horseshoe is essentially a 180-degree turnaround with high banking so that riders are tilted at a 90-degree angle or more at the top at the element. The horseshoe is named that way because the element is shaped roughly like a horseshoe, with a semicircular shape at the top. It is found on coasters such as Dragon's Fury at Chessington World of Adventures and Laff Trakk at Hersheypark.
Junior Immelmann loop

A junior Immelmann loop is similar to a normal Immelmann loop, except riders are not inverted and only roll to 90 degrees instead of 180 degrees. The element first appeared on Black Mamba at Phantasialand.[10]
Non-inverting cobra roll
A non-inverting cobra roll is similar to a cobra roll, except the half-loops at the entrance and exit level out before reaching 180 degrees, and the train therefore does not invert. Kondaa at Walibi Belgium is the only ride to feature this element.[11]
Non-inverting loop

The non-inverting loop is a variety of loop that, when coming up, twists similar to a heartline roll, leaving riders completely right-side-up when at the top of the loop. Some roller coasters with this element include Hollywood Rip Ride Rockit at Universal Studios Florida, Shock at Rainbow MagicLand, Superman: Ultimate Flight at Six Flags Discovery Kingdom, Flying Aces at Ferrari World, Soaring with Dragon at Hefei Wanda Theme Park, DC Rivals Hypercoaster at Warner Bros. Movie World and Tempesto at Busch Gardens Williamsburg.
Overbanked turn

An overbanked turn is a turn or curve in which the track tilts beyond 90 degrees, usually in the 100-120 degree range. The element is common on large steel roller coasters, particularly those built by Intamin and Rocky Mountain Construction. Two examples of an overbanked turn in the United States are the first turn-around on Superman the Ride at Six Flags New England, and Millennium Force at Cedar Point in Sandusky, Ohio, which features four separate and two consecutive overbanked turns.
A Stengel dive combines an overbanked turn with a camelback hill. The train first goes up a regular camelback hill, then quickly tilts beyond 90 degrees at the very top. It is the only roller coaster element named after its designer, in this case Werner Stengel. Examples of roller coasters that feature this element include Goliath at Walibi Holland and Thunderbolt at Luna Park.
Speed hill
A speed hill, also known as a high-speed float,[12] is an airtime element commonly found in Bolliger & Mabillard steel coasters and Rocky Mountain Construction wooden coasters. The element is a mini-version of camelback entered at a high speed, which results in significant negative G-forces that exceed a typical camelback. Leviathan at Canada's Wonderland[13] and Outlaw Run at Silver Dollar City are two roller coasters that feature this element.[12]
Top hat

A top hat, also known as top cap, is an element typically found on launched coasters. The element consists of 90-degree ascent up a hill, followed by a 90-degree descent; the train exits in the same direction from which it entered. In a standard configuration, the track twists so that the train does not invert during the ride. The defunct Top Thrill Dragster at Cedar Point and still operating Kingda Ka at Six Flags Great Adventure — the only two strata coasters in existence[14] — are two roller coasters that feature a top hat element.
In a top hat inversion, also called an inside top hat or inverted top hat, the track makes a 90-degree twist as the train approaches the top. The train is on the inside of the element, and once it reaches the apex, the train is inverted. Mr. Freeze Reverse Blast at Six Flags St. Louis is one example that features this variant.
Wave turn
A wave turn, commonly found on Rocky Mountain Construction roller coasters, is a 90-degree banked turn that incorporates a small camelback hill.[15] The airtime feature separates wave turns from typical banked turns.[15] When a train banks either right or left into an inclined turn, it traverses an airtime hill while banked at 90 degrees.[16] The element finishes with the train exiting in the opposite direction that it entered.[15]
Inverting elements
Banana roll
A banana roll is an inversion element named after its shape that is similar to an elongated cobra roll.[17][18][19] It first appeared on Takabisha at Fuji-Q Highland in 2011.[17][20] The element may invert riders once, as it does on Takabisha and TMNT Shellraiser (Nickelodeon Universe),[18][21] or it may invert riders twice as it does on Steel Curtain at Kennywood.[19]
Batwing

A batwing is a heart-shaped roller coaster element that features two inversions. The train goes into a reverse sidewinder, followed by a sidewinder.[22] It is the inverse of a cobra roll.
Like other inversions, this element has different names depending on the roller coaster's manufacturer. It is most commonly known as a batwing, which is the term used by Bolliger & Mabillard (B&M). Afterburn at Carowinds and Montu at Busch Gardens Tampa Bay are two examples that feature this element. It was first marketed as a Kamikaze Kurve by Arrow Dynamics during the construction of Orient Express at Worlds of Fun, which opened in 1980.[23] Arrow would later refer to the element as a boomerang in future projects, such as the defunct Great American Scream Machine at Six Flags Great Adventure.[citation needed] One variation of the batwing is known as a bowtie, where the entrance and exit of the inversion are in the same direction.[24] Dragon Mountain at Marineland of Canada is the only coaster to feature this element, according to the Roller Coaster DataBase.[24][25]
Bent Cuban eight
A bent Cuban eight is a double inversion element that features two "bent and twisted" Immelmann loops that are connected back to back.[26] Designed by Maurer Rides GmbH, the element only appears on two X-Car roller coaster models from the company, including G Force that was at Drayton Manor Theme Park.[27][28]

Butterfly
A butterfly is sometimes found on Vekoma roller coasters. A butterfly begins like a vertical loop, but as the track goes up, it twists 45 degrees to one side or the other, and then when it is headed down the track twists back. The maneuver is then repeated but in reverse. It is essentially the same in construction as a batwing or boomerang except for the coaster exiting the construct traveling in the same direction as it began. An example of this is found on Goudurix in Parc Astérix in Plailly, France , or Blue Hawk at Six Flags Over Georgia.
Cobra roll

The cobra roll is a roller coaster inversion that resembles the shape of a cobra head when flaring its hood. The element consists of two half vertical loops facing the same direction joined together by two half corkscrews that each twist in opposite directions. As the train completes the first half loop, it turns perpendicular into a half corkscrew, completing a first inversion. This is immediately followed by another half corkscrew that twists in the opposite direction into the other half vertical loop, completing a second inversion. The train exits the cobra roll traveling in the opposite direction from which it entered.
Vekoma's Boomerang was the first model to incorporate a cobra roll, and the first Boomerang installation was Sea Serpent at Morey's Piers in 1984.
Corkscrew

A corkscrew inversion resembles a helix that rotates riders 360 degrees perpendicular to the track. It was named for its resemblance of a corkscrew tool, which is used to remove bottle corks. Unlike vertical loops, riders remain facing forward for the entire duration of the inversion. The corkscrew was the first modern-day inversion element to be featured on a roller coaster. It first appeared in 1975 with the release of Corkscrew, a roller coaster at Knott's Berry Farm designed by Arrow Dynamics. The element was well-received and became a staple of many early roller coasters that inverted riders.
Corkscrews commonly exist in pairs, where the end of one leads straight into the next. Another configuration involves interlocking corkscrews, where two corkscrews are intertwined, with each crossing over the other's track. Both Nemesis Inferno at Thorpe Park and Medusa at Six Flags Great Adventure feature interlocking corkscrews. Bolliger & Mabillard introduced a variation of the corkscrew that the company calls a flat spin. Flat spins snap riders quickly through the inversion at varying speeds, as opposed to a standard corkscrew that rotates riders at slower, constant speeds.
Cutback
A cutback is a roller coaster inversion similar to a corkscrew, except the second half of the element is reversed. The train exits the inversion in the opposite direction from which it entered. Arrow Dynamics debuted the feature on Drachen Fire at Busch Gardens Williamsburg in 1992. It can also be found on other coasters such as Twisted Timbers at Kings Dominion, Steel Curtain at Kennywood Park, and Wonder Woman Golden Lasso Coaster at Six Flags Fiesta Texas.
Demonic Knot
A demonic knot is a roller coaster inversion that features an inclined dive loop followed by an inclined immelmann. Flug der Dämonen, at Germany's Heide Park Resort, is the only ride to feature this inversion.
Dive drop
A dive drop[29] (also known as a Wing Over Drop[30]) is a roller coaster inversion in which a half-inline twist is performed at the top of a lift hill, leading into the initial drop. Examples that feature this element include The Swarm at Thorpe Park, X-Flight at Six Flags Great America, and GateKeeper at Cedar Point.[30][31]
Dive loop
A dive loop, also known as a diving loop, is a type of B&M and Gerstlauer roller coaster inversion whose inspiration was taken from a stunt plane maneuver. It is the reverse of an Immelmann loop. The track twists upward and to the side and then dives toward the ground in a half-vertical loop. This element is common on many B&M roller coasters. Arrow and Vekoma use a similar version of the element known as a reverse sidewinder, as seen in Arrow's Cyclone at Dreamworld in Australia and Vekoma's Blue Hawk at Six Flags Over Georgia.

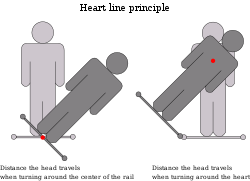
Heartline roll
A heartline roll, also known as a barrel roll, is a roller coaster inversion in which the rider performs a 360-degree roll. The center of the train rotates on one axis. The track changes in elevation to keep the train moving in the same line in which it entered the element. In an in-line twist, a similar element, the track remains straight at the same elevation. The point of rotation is either above or below the rider's point of view, unlike a heartline roll which keeps the point of rotation near the middle. An example of this element is Colossus at Thorpe Park, which features five heartline rolls, or The Smiler, which has its first inversion as a heartline roll.

Immelmann
An Immelmann is a popular inversion found on many B&M roller coasters. In an Immelmann, riders enter a half-loop followed by a half twist and then exit the element traveling in the opposite direction making a 180-degree turn. The inversion is similar to the sidewinder which exits closer to 90°, or perpendicular to the entrance point. An Immelmann loop becomes a dive loop if the entrance and exit points are reversed. The name "Immelmann" comes from the Immelmann turn, an aircraft maneuver named after the World War I German fighter pilot Max Immelmann.[32] Immelmanns are commonly found as the first element on B&M Dive Coasters. A notable example is Valravn at Cedar Point, which has an Immelmann loop immediately following the first drop.

Inclined dive loop
An inclined dive loop is essentially a dive loop that has been tilted. Instead of exiting vertically, an inclined dive loop exits at an angle. The only two examples are on Hydra the Revenge at Dorney Park & Wildwater Kingdom and GateKeeper at Cedar Point.
Inclined loop

An inclined loop, also known as an oblique loop, is a 360° loop that has been tilted at an angle. It is not entered vertically, like a vertical loop, or horizontally like a helix. Instead, it is usually entered at an angle between 45° and 80°. Inclined loops can be found on B&M stand-up roller coasters, B&M Wing Coasters, and B&M Floorless Coasters. Examples include: Rougarou at Cedar Point; Green Lantern at Six Flags Great Adventure; Riddler's Revenge at Six Flags Magic Mountain; and The Swarm at Thorpe Park.

In-line twist
An in-line twist is a roller coaster inversion in which the rider performs a 360-degree roll. The in-line twist is often found on flying coasters and wing coasters, such as Galactica at Alton Towers, Batwing at Six Flags America, Superman: Ultimate Flight at Six Flags Over Georgia, Firehawk at Kings Island, Manta at SeaWorld Orlando, Raptor at Gardaland and The Swarm at Thorpe Park. It can be confused with a heartline roll, also known as a barrel roll. In a heartline roll the center of the train rotates on one axis so the height of the average rider's heart never changes, whereas during an in-line twist the train rotates around the track and there is usually little to no elevation difference in the track. It can also provide hangtime.
Norwegian loop

A Norwegian loop is an element made out of two elements: a dive loop, then an Immelmann; forming an inversion that looks like two side by side loops. This element is similar to the flying coasters pretzel loop, except that the train goes through a twist when entering and exiting the loop. It may also been seen as a normal loop entered from the top. It was first introduced on Speed Monster in TusenFryd, Norway (hence why it is called a "Norwegian" Loop).[33] Other examples of a Norwegian Loop can be found on Hersheypark's roller coaster Fahrenheit and Helix at Liseberg.

Pretzel knot
A pretzel knot is an element similar to the batwing, except the entrance and exit of the inversion is formed differently. In a pretzel knot, the twisted formation of the element's entrance and exit resembles a pretzel shape as opposed to a batwing's heart shape. The defunct Moonsault Scramble at Fuji-Q Highland was the first coaster to feature this element.[34] The second was Banshee at Kings Island.[34]
Pretzel loop

The pretzel loop is a large inversion found on flying coasters from Bolliger & Mabillard. The element debuted on Superman: Ultimate Flight at Six Flags Over Georgia and has been used on many other B&M flying coasters since then.[35] It consists of a downward half loop and upward half loop. The entrance and exit points of the loop overlap at its peak forming a shape resembling a pretzel.[36]
Raven turn
A raven turn is a half-inversion which looks like half a loop followed by a drop and then levels out near the same height as it began. The raven turn is only usable on either flying roller coasters or 4D roller coasters at the moment and has only been used on three 4D coasters and one flying coaster.[37]
The general term raven turn refers to any inversion that follows the design described above; however, there are two types of raven turns. Assuming the train is going round the half-loop first, an inside raven turn is where the rails are below the train at the start whereas an outside raven turn is one in which the rails are above the train at the start of the element. X² at Six Flags Magic Mountain, Eejanaika at Fuji-Q Highland, and Dinoconda at China Dinosaurs Park are examples of raven turns.[38]

Roll over
This element, known as a roll over on roller coasters built by Vekoma, is an inversion featuring two half loop halves, connected by two opposite-facing half inline twists. This inversion can be found on the most Vekoma SLCs.
Sea serpent
The sea serpent is a roller coaster element with two inversions similar to a cobra roll, but the train enters and exit in the same direction.[39] It features two vertical loop halves connected by two half corkscrews that face in opposite directions. The second half loop is on the opposite side in comparison to a cobra roll, which changes the exit's direction.[39] Examples featuring this element include Vekoma's Rock 'n' Roller Coaster Starring Aerosmith located at Disney's Hollywood Studios and The Smiler at Alton Towers.[40][41]
Sidewinder
A sidewinder is an inversion element where riders enter a half-loop followed by a half-corkscrew, and then exit the element perpendicular to the direction in which they entered. The element is commonly found on Arrow and Vekoma roller coasters. It is similar to the Immelmann loop, with the exception that riders exit in a different direction usually 90 degrees from the entrance point. When travelled in reverse it is simply a Reverse Sidewinder.
Twisted horseshoe roll

A twisted horseshoe roll is an inversion element that begins with a corkscrew that leads into a 180-degree banked turn and ends with another corkscrew that rotates in the opposite direction as the first.[42] Two roller coasters that feature this element are Maverick at Cedar Point (United States) and Blue Fire at Europa-Park (Germany).[43]

Vertical loop
A vertical loop is one of the most common roller coaster inversions in existence. It is a continuous, upward-sloping section of track that eventually completes a 360-degree turn, inverting riders halfway into the element. They are ellipses in the shape of an oval or teardrop. Early roller coaster designs attempted vertical loops that were more circular, resulting in massive g-force that were dangerous to riders. The first successful implementation in the modern era of roller coasters was on Great American Revolution which opened at Six Flags Magic Mountain in 1976.

Arrow Dynamics designed two roller coasters that featured interlocking loops, which consist of one vertical loop perpendicular to the other. Loch Ness Monster at Busch Gardens Williamsburg opened in 1978 followed by Orient Express at Worlds of Fun in 1980. The Lightnin' Loops installation at Six Flags Great Adventure featured two looping roller coasters with similar interlocking loops.
Zero-g roll

A zero-g roll or zero-gravity roll is a roller coaster inversion where the track twists 360 degrees as it rises and falls in elevation, usually at the crest of a hill. The element gets its name from the weightless effect of zero g-force that a rider experiences during the inversion.[44][45][46]
Zero-g stall
A zero-g stall or zero-gravity stall, sometimes called a Top Gun stall, is an inversion where the track twists 180 degrees during ascent, and at its crest, remains inverted for a short section of track. It then twists another 180 degrees during descent, usually in the opposite direction of the initial twist. Similar to a zero-g roll, riders experience a feeling of weightlessness during the short inverted section.
The stall element is commonly found on Rocky Mountain Construction (RMC) installations including Goliath and Wildfire. S&S has also included this element in Kennywood's Steel Curtain.
Visual elements
Splashdown

A splashdown is a visual element in which the ride vehicle physically interacts with a body of water, forcefully spraying or jetting water on impact. Splashdowns can be used as a natural braking system, and some coasters feature pathways for non-riding visitors to view or get wet from the splashdown element. There are two types.
- A natural splashdown is an element in which the track of the vehicle partially submerges underwater. It is featured on several roller coasters such as Matterhorn Bobsleds at Disneyland.
- A scoop splashdown is an element in which each train is equipped with two tubes – called scoops – on the rear sides of each train. The scoops are angled upward, causing water to spray as the train passes close to a body of water. A number of Bolliger & Mabillard coasters feature the element, such as Griffon at Busch Gardens Williamsburg, SheiKra at Busch Gardens Tampa, and Diamondback at Kings Island. Depending on the width of the train and the angle of the scoops, the effect can produce different results, such as two distinct streams (Griffon) or one large plume (Diamondback).
Water spout
A water spout is a visual element encompassing a number of different methods to simulate a roller coaster's interaction with a body of water – the ride vehicle does not make contact with the water. Water spouts are intended to be visually appealing. The following are some examples of roller coasters that utilize this effect.
- Atlantis Adventure at Lotte World in South Korea features a variety of water effects including water spouts that fire in synchronized fashion in more than one area of the ride.
- Hyperion at Energylandia in Poland has a water feature immediately before the final brake run.[47]
- The Incredible Hulk at Universal's Islands of Adventure has a water spout that fires immediately following its zero-G roll as the train dives toward the water below.
- Manta at SeaWorld Orlando utilizes both water spouts and fountains that synchronize at the point the train dips toward the water, giving the illusion it is skimming the water's surface.
- Maverick at Cedar Point features several water spouts that fire upward as the train rounds a turn.
See also
- Physics of roller coasters
References
- ↑ MacDonald, Brady (11 April 2012). "X-Flight wing coaster premieres at Six Flags Great America in May". Los Angeles Times. http://articles.latimes.com/2012/apr/11/news/la-trb-xflight-six-flags-great-america-04201211.
- ↑ Chavez, Jon (14 August 2012). "Park's 1st 'winged' coaster to debut at Cedar Point in 2013". Norwalk Reflector. http://www.norwalkreflector.com/content/parks-1st-winged-coaster-debut-cedar-point-2013.
- ↑ "Iron Rattler — Ups Downs and Upside Down - Roller Coasters and Theme Parks". http://www.upsdownsandupsidedown.com/iron-rattler/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bullock, Joel (March 5, 2015). "Fury 325 vs Intimidator: Differences & Similarities". The Coaster Critic. http://www.thecoastercritic.com/2015/03/intimidator-vs-fury-325-differences-similarities.html.
- ↑ Urbanowicz, Steven J. (2002). The Roller Coaster Lover's Companion: A Thrill Seeker's Guide to the World's Best Coasters. Citadel Press. p. 137. ISBN 9780806523095. https://archive.org/details/rollercoasterlov00stev. "roller coaster camelback hill."
- ↑ "More details on Rip Ride Rockit coaster, plus video". Orlando Attractions Magazine. April 23, 2009. http://attractionsmagazine.com/more-details-on-rip-ride-rockit-coaster-plus-video/.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Roller Coaster Glossary". Ultimate Rollercoaster. http://www.ultimaterollercoaster.com/coasters/glossary/#c.
- ↑ "Types of elements". American Coasters. http://www.americacoasters.com/Resources/?page=typesofinversions.
- ↑ "Gatekeeper: The Ride - Facts and Figures". Cedar Point. https://www.cedarpoint.com/gatekeeper/the-ride.
- ↑ Template:Cite RCDB
- ↑ "Non Inverting Cobra Roll". https://rcdb.com/18882.htm.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "Fact Sheet". Silver Dollar City. August 9, 2012. http://silverdollarcity2013.com/wp-content/plugins/download-monitor/download.php?id=Click+here+to+download+PDF.
- ↑ White, Kevin (July 19, 2014). "Canada's Wonderland". http://www.lifeisarollercoaster.org/canadas-wonderland/.
- ↑ "Kingda Ka vs. Top Thrill Dragster". thecoastercritic.com. November 16, 2006. http://www.thecoastercritic.com/2006/11/what-is-hyper-coaster.html.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Winslett, Jim. "Lightning Rod". http://www.ellocoaster.com/lightning-rod.
- ↑ Murphy, Mekado (July 23, 2014). "New Twists for Wooden Roller Coasters". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2014/07/27/travel/new-twists-for-wooden-roller-coasters.html.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Euro-Fighter: Takabisha". Gerstlauer Amusement Rides GmbH. https://www.gerstlauer-rides.de/references/reference-list/asia/takabisha-en-US/.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 "Takabisha – world's steepest drop". Park World Online. October 9, 2014. https://www.parkworld-online.com/takabisha-worlds-steepest-drop/.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Stilwell, Andrew (July 19, 2018). "Kennywood Unveils "The Steel Curtain" for 2019". https://www.coaster101.com/2018/07/19/kennywood-unveils-steel-curtain-for-2019/.
- ↑ Marden, Duane. "Element: Banana Roll". RCDB. https://rcdb.com/r.htm?ot=2&el=10183.
- ↑ Template:Cite RCDB
- ↑ "Batwing". Glossary. Roller Coaster Database. http://rcdb.com/g20.htm.
- ↑ "New Roller Coaster at Worlds of Fun". St. Joseph News-Press. November 24, 1979. https://www.newspapers.com/clip/56998760/new-roller-coaster-at-worlds-of-fun/.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 "Bowtie". https://rcdb.com/8871.htm.
- ↑ Template:Cite RCDB
- ↑ "G Force". https://www.coaster-net.com/g-force.html.
- ↑ Weisenberger, Nick (September 2, 2014) (in en). The 50 Most Terrifying Roller Coasters Ever Built. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. pp. 56. ISBN 978-1500699963.
- ↑ Template:Cite RCDB
- ↑ Template:Cite RCDB
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 "The Ride". Cedar Point. 13 August 2012. http://www.cedarpoint.com/gatekeeper/the-ride.
- ↑ Template:Cite RCDB
- ↑ Glaser, Susan (May 9, 2013). "Cedar Point's new GateKeeper roller coaster one wild and winged ride". The Plain Dealer. http://www.cleveland.com/travel/index.ssf/2013/05/cedar_pointsnew_gatekeeper_rol.html.
- ↑ "Norwegian Loop". Glossary. Roller Coaster DataBase. http://rcdb.com/g268.htm.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 "Pretzel Knot". https://rcdb.com/r.htm?ot=2&el=8897.
- ↑ "Superman - Ultimate Flight". rcdb.com. https://rcdb.com/1568.htm.
- ↑ "Pretzel Loop Element". RCDB.com. http://rcdb.com/r.htm?ot=2&el=8888.
- ↑ "Raven Turn". Glossary. Roller Coaster Database. http://rcdb.com/g65.htm.
- ↑ "COASTER-net.com v8 > Ride Gallery > X, Six Flags Magic Mountain". http://www.coaster-net.com/six-flags-magic-mountain.html.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 "Inversions". CoasterForce. http://www.coasterforce.com/coasters/inversions.
- ↑ Template:Cite RCDB
- ↑ Template:Cite RCDB
- ↑ McCarthy, Erin (October 2009). "5 Roller Coasters Mega-Engineered to Make You Scream". Popular Mechanics. http://www.popularmechanics.com/technology/engineering/4268380#slide-1.
- ↑ "Element: Twisted Horseshoe Roll". RCDB.com. http://rcdb.com/r.htm?ot=2&el=8922.
- ↑ Salterq, Rosa (May 2, 2001). "Coaster riders: Get ready to fall heels over head". Morning Call. http://www.chicagotribune.com/business/careers/sns-coasters-talon-story.html#page=1.
- ↑ Hernandez, America (August 28, 2014). "Missing Colossus? Magic Mountain's new ride has an old look, with a techno twist". Los Angeles Register. http://www.losangelesregister.com/articles/colossus-604113-coaster-twisted.html.
- ↑ "Le Vampire". COASTER-net.com. August 25, 2013. http://www.coaster-net.com/le-vampire.html.
- ↑ "Energylandia Hyperion POV 4K Mounted and Drone". YouTube. 2018. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ICQiouhaUX8.


