Engineering:Trilliant cut
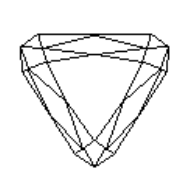
A trilliant cut, sometimes called a trillion, trillian, or Trielle is a triangular type of gemstone cut. The cut has many variations. It may have curved or uncurved sides. The shape of the top surface, or table, also varies. Stones typically have 31-50 facets.[1]
Creation
The trilliant cut was introduced by the Asscher brothers in Amsterdam. In the early 1960s Leon Finker created his version on the "triangular brilliant cut diamond", which he called the trillion cut. Finker had a large diamond cutting factory in New York, and Henry Meyer Diamond Company, who was also cutting triangular brilliant diamonds, used the same diamond cutters, though their stones were cut slightly differently.
Henry Meyer referred to his diamond cut as "trilliant", while Finker called his cut trillion.
When Finker's son, Marvin Finker, entered the business in the early 1970s, he decided to patent the cut that his father was cutting and he trademarked the term "Trillion" for their now patented triangular brilliant cut diamond.
They used the term "Trillion" and "Trilliant" in a stylized design until they lost the trademark in 1986 when a federal court judge decided that the words "Trillion" and "Trilliant" were phonetically equivalent.[2] Since trilliant was a concatenation of the generic term "triangular brilliant", it could no longer be a registered trademark.
Finker gave the term "trillion" to the trade in a half-page advertisement in the New York Times and announced that their patented cut would be known as Trielle and TRIELLE in a stylized design.
Now that the trademark had been canceled, the term "trillion cut" is used to refer to all triangular-shaped gems, even step cut and cabochon stones. Triangular brilliant and triangular modified brilliant are the generic terms used by GIA when referring to non-branded diamonds.[3]
Straight
The cut displays a very sharp brilliance or fire if the diamond is cut to the correct depth allowing good scintillation. It is generally cut with a 1:14 length to width ratio with straight edges. This straight edged trillion cut is usually used for accent gemstones, on either side of a main, larger stone of a ring.
Curved
This is a softer version of the uncurved version, with three soft points and curved sides. The length to width ratio should still be 1:1, keeping the gemstone proportioned. This cut is unusual, but can be found in pieces as a solitary gem or as an accent gem. The curved triangular brilliant is commonly known as trilliant. A reuleaux triangle has the same ratio.
See also
References
- ↑ "Trilliant Cut Diamonds - Education". https://www.77diamonds.com/trillion-cut-diamonds.html.
- ↑ Leon Finker, Inc. v. Schlussel, 469 F. Supp. 674 (S.D.N.Y. 1979).
- ↑ Proprietary patented diamond cuts gia.edu Spring 2004
External links
 |
