Engineering:X-ring chain
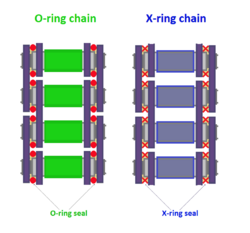
The X-ring chain is a specialized type of sealed roller chain used to transfer mechanical power. Like the standard O-ring chains it is also used in high-performance motorcycles. It uses X-ring seal to keep lubricant (usually grease) in place.
It has higher performance (in terms of durability, lifetime, and power loss) than O-ring chains as it has less friction while providing adequate lubrication and protection against foreign elements which also increases reliability.[1] It can last twice as long as the O-ring chain under some circumstances.[2]
Development
The X-ring chain is developed from O-ring chain which in turn is developed from non-O-ring chain. While the regular O-ring chain has high durability, it also has more friction (compared to other types of roller chains) due to distortion of the O-ring due to pressure from the inner and outer chain plates.[3] This results in loss of power in the transmission. Therefore, X-ring chain was developed by replacing O-ring seal with X-ring seal which greatly reduced friction and increased durability.[1]
Design
Like the O-ring chain it has sealing rings which keep the contaminant (dirt) out, and lubricant in between the pins and bushings. This is known as internal lubrication. However, unlike O-ring chain, it has X-shaped seal which does not experience increased surface area (which is in contact with the chain plates) when under pressure. Therefore the friction in X-ring chain does not increase much when pressure is applied by the chain plates. Due to their unique shape, they have two additional sealing surfaces to a traditional O-ring.[4]
| Chain type | Standard roller | O-ring chain | X-ring chain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lubrication | Externally lubricated | Self lubricating (Internal) | Self lubricating (Internal) |
| Durability | Low | High | Very High |
| Efficiency | High | Relatively low | Very High |
| Maintenance | Frequent | Less frequent, special care | Least frequent, special care |
| Stretching | Regular | Limited | Limited |
| Cost | Relatively cheaper | Relatively expensive | Relatively expensive |
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "O Ring and X Ring Chains ¦ Motorcycle Chains ¦ Technical Help ¦ Bike Torque Racing". http://www.biketorqueracing.co.uk/btr-tech-station/btr-tech-station-chain-and-sprockets/o-ring-and-x-ring-chains.
- ↑ "O-Ring vs.X-Ring and Patching Tires | Ask the Geek" (in en). Sport Rider. http://www.sportrider.com/tech/o-ring-vsx-ring-and-patching-tires-ask-geek.
- ↑ SevenRockCityCycles. "WHAT’s THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN O-RING and X-RING CHAINS? – Rock City Cycles" (in en-US). https://www.rockcitycycles.com/whats-the-difference-between-o-ring-and-x-ring-chains/.
- ↑ "O-Ring vs.X-Ring and Patching Tires" (in en). https://www.cycleworld.com/sport-rider/o-ring-vsx-ring-and-patching-tires-ask-geek/.
- ↑ "Drive Chains: O Ring/ X Ring Vs Non-O Ring Standard Chains » BikesMedia.in" (in en). https://www.bikesmedia.in/reviews/drive-chains-o-ring-x-ring-vs-non-o-ring-standard-chains.html.
External links
 |
