Finance:Currency substitution

Currency substitution is the use of a foreign currency in parallel to or instead of a domestic currency.[1]
Currency substitution can be full or partial. Full currency substitution can occur after a major economic crisis, such as in Ecuador. Some small economies, for whom it is impractical to maintain an independent currency, use the currencies of their larger neighbours; for example, Liechtenstein uses the Swiss franc.
Partial currency substitution occurs when residents of a country choose to hold a significant share of their financial assets denominated in a foreign currency or use it as exchange currency, as is currently the case in Venezuela.[2] It can also occur as a gradual conversion to full currency substitution; for example, Argentina was in the process of converting to the U.S. dollar during the 1990s.
Name
"Dollarization", when referring to currency substitution, does not necessarily involve use of the United States dollar.[3] The major currencies used as substitutes are the US dollar and the euro.
Origins
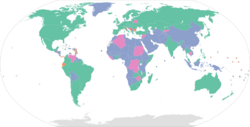
After the gold standard was abandoned at the outbreak of World War I and the Bretton Woods Conference following World War II, some countries sought exchange rate regimes to promote global economic stability, and hence their own prosperity. Countries usually peg their currency to a major convertible currency. "Hard pegs" are exchange rate regimes that demonstrate a stronger commitment to a fixed parity (i.e. currency boards) or relinquish control over their own currency (such as currency unions) while "soft pegs" are more flexible and floating exchange rate regimes.[4] The collapse of "soft" pegs in Southeast Asia and Latin America in the late 1990s led to currency substitution becoming a serious policy issue.[5]
A few cases of full currency substitution prior to 1999 had been the consequence of political and historical factors. In all long-standing currency substitution cases, historical and political reasons have been more influential than an evaluation of the economic effects of currency substitution.[6] Panama adopted the US dollar as legal tender after independence as the result of a constitutional ruling.[7] Ecuador and El Salvador became fully dollarized economies in 2000 and 2001 respectively, for different reasons.[6] Ecuador underwent currency substitution to deal with a widespread political and financial crisis resulting from massive loss of confidence in its political and monetary institutions. By contrast, El Salvador's official currency substitution was a result of internal debates and in a context of stable macroeconomic fundamentals and long-standing unofficial currency substitution. The eurozone adopted the euro (€) as its common currency and sole legal tender in 1999, which might be considered a variety of full-commitment regime similar to full currency substitution despite some evident differences from other currency substitutions.[8]
Measures
There are two common indicators of currency substitution. The first measure is the share of foreign currency deposits (FCD) in the domestic banking system in the broad money including FCD. The second is the share of all foreign currency deposits held by domestic residents at home and abroad in their total monetary assets.[7]
Types
Unofficial currency substitution or de facto currency substitution is the most common type of currency substitution. Unofficial currency substitution occurs when residents of a country choose to hold a significant share of their financial assets in foreign currency, even though the foreign currency is not legal tender there.[9] They hold deposits in the foreign currency because of a bad track record of the local currency, or as a hedge against inflation of the domestic currency.
Official currency substitution or full currency substitution happens when a country adopts a foreign currency as its sole legal tender, and ceases to issue the domestic currency. Another effect of a country adopting a foreign currency as its own is that the country gives up all power to vary its exchange rate. There are a small number of countries adopting a foreign currency as legal tender.
Full currency substitution has mostly occurred in Latin America, the Caribbean and the Pacific, as many countries in those regions see the United States Dollar as a stable currency compared to the national one.[10] For example, Panama underwent full currency substitution by adopting the US dollar as legal tender in 1904. This type of currency substitution is also known as de jure currency substitution.
Currency substitution can be used semiofficially (or officially, in bimonetary systems), where the foreign currency is legal tender alongside the domestic currency.[11]
In literature, there is a set of related definitions of currency substitution such as external liability currency substitution, domestic liability currency substitution, banking sector's liability currency substitution or deposit currency substitution, and credit dollarization. External liability currency substitution measures total external debt (private and public) denominated in foreign currencies of the economy.[11][12] Deposit currency substitution can be measured as the share of foreign currency deposits in the total deposits of the banking system, and credit currency substitution can be measured as the share of dollar credit in the total credit of the banking system.[13]
Effects
On trade and investment
One of the main advantages of adopting a strong foreign currency as sole legal tender is to reduce the transaction costs of trade among countries using the same currency.[14] There are at least two ways to infer this impact from data. The first is the significantly negative effect of exchange rate volatility on trade in most cases, and the second is an association between transaction costs and the need to operate with multiple currencies.[15] Economic integration with the rest of the world becomes easier as a result of lowered transaction costs and stabler prices.[3] Rose (2000) applied the gravity model of trade and provided empirical evidence that countries sharing a common currency engage in significantly increased trade among them, and that the benefits of currency substitution for trade may be large.[16]
Countries with full currency substitution can invoke greater confidence among international investors, inducing increased investments and growth. The elimination of the currency crisis risk due to full currency substitution leads to a reduction of country risk premiums and then to lower interest rates.[3] These effects result in a higher level of investment. However, there is a positive association between currency substitution and interest rates in a dual-currency economy.[17]
On monetary and exchange rate policies
Official currency substitution helps to promote fiscal and monetary discipline and thus greater macroeconomic stability and lower inflation rates, to lower real exchange rate volatility, and possibly to deepen the financial system.[15] Firstly, currency substitution helps developing countries, providing a firm commitment to stable monetary and exchange rate policies by forcing a passive monetary policy. Adopting a strong foreign currency as legal tender will help to "eliminate the inflation-bias problem of discretionary monetary policy".[18] Secondly, official currency substitution imposes stronger financial constraint on the government by eliminating deficit financing by issuing money.[19] An empirical finding suggests that inflation has been significantly lower in economies with full currency substitution than nations with domestic currencies.[20] The expected benefit of currency substitution is the elimination of the risk of exchange rate fluctuations and a possible reduction in the country's international exposure. Currency substitution cannot eliminate the risk of an external crisis but provides steadier markets as a result of eliminating fluctuations in exchange rates.[3]
On the other hand, currency substitution leads to the loss of seigniorage revenue, the loss of monetary policy autonomy, and the loss of the exchange rate instruments. Seigniorage revenues are the profits generated when monetary authorities issue currency. When adopting a foreign currency as legal tender, a monetary authority needs to withdraw the domestic currency and give up future seigniorage revenue. The country loses the rights to its autonomous monetary and exchange rate policies, even in times of financial emergency.[3][21] For example, former chairman of the Federal Reserve Alan Greenspan has stated that the central bank considers the effects of its decisions only on the US economy.[22] In a full currency substituted economy, exchange rates are indeterminate and monetary authorities cannot devalue the currency.[23] In an economy with high currency substitution, devaluation policy is less effective in changing the real exchange rate because of significant pass-through effects to domestic prices.[3] However, the cost of losing an independent monetary policy exists when domestic monetary authorities can commit an effective counter-cyclical monetary policy, stabilizing the business cycle. This cost depends adversely on the correlation between the business cycle of the client country (the economy with currency substitution) and the business cycle of the anchor country.[14] In addition, monetary authorities in economies with currency substitution diminish the liquidity assurance to their banking system.[3][24]
On banking systems
In an economy with full currency substitution, monetary authorities cannot act as lender of last resort to commercial banks by printing money. The alternatives to lending to the bank system may include taxation and issuing government debt.[25] The loss of the lender of last resort is considered a cost of full currency substitution. This cost depends on the initial level of unofficial currency substitution before moving to a full currency substituted economy. This relation is negative because in a heavily currency substituted economy, the central bank already fears difficulties in providing liquidity assurance to the banking system.[26] However, literature points out the existence of alternative mechanisms to provide liquidity insurance to banks, such as a scheme by which the international financial community charges an insurance fee in exchange for a commitment to lend to a domestic bank.[27]
Commercial banks in countries where saving accounts and loans in foreign currency are allowed may face two types of risks:
- Currency mismatch risk: Assets and liabilities on the balance sheets may be in different denominations. This may arise if the bank converts foreign currency deposits into local currency and lends in local currency or vice versa.
- Default risk: Arises if the bank uses the foreign currency deposits to lend in foreign currency.[28]
However, currency substitution eliminates the probability of a currency crisis that negatively affects the banking system through the balance sheet channel. Currency substitution may reduce the possibility of systematic liquidity shortages and the optimal reserves in the banking system.[29] Research has shown that official currency substitution has played a significant role in improving bank liquidity and asset quality in Ecuador and El Salvador.[30]
Determinants of the process
The dynamics of the flight from domestic money
High and unanticipated inflation rates decrease the demand for domestic money and raise the demand for alternative assets, including foreign currency and assets dominated by foreign currency. This phenomenon is called the "flight from domestic money". It results in a rapid and sizable process of currency substitution.[31] In countries with high inflation rates, the domestic currency tends to be gradually displaced by a stable currency. At the beginning of this process, the store-of-value function of the domestic currency is replaced by the foreign currency. Then, the unit-of-account function of the domestic currency is displaced when many prices are quoted in a foreign currency. A prolonged period of high inflation will induce the domestic currency to lose its function as medium of exchange when the public carries out many transactions in foreign currency.[32]: 1
Ize and Levy-Yeyati (1998) examine the determinants of deposit and credit currency substitution, concluding that currency substitution is driven by the volatility of inflation and the real exchange rate. Currency substitution increases with inflation volatility and decreases with the volatility of the real exchange rate.[33]
Institutional factors
The flight from domestic money depends on a country's institutional factors. The first factor is the level of development of the domestic financial market. An economy with a well-developed financial market can offer a set of alternative financial instruments denominated in domestic currency, reducing the role of foreign currency as an inflation hedge. The pattern of the currency substitution process also varies across countries with different foreign exchange and capital controls. In a country with strict foreign exchange regulations, the demand for foreign currency will be satisfied in the holding of foreign currency assets abroad and outside the domestic banking system. This demand often puts pressure on the parallel market of foreign currency and on the country's international reserves.[31] Evidence for this pattern is given in the absence of currency substitution during the pre-reform period in most transition economies, because of constricted controls on foreign exchange and the banking system.[32]: 13 In contrast, by increasing foreign currency reserves, a country might mitigate the shift of assets abroad and strengthen its external reserves in exchange for a currency substitution process. However, the effect of this regulation on the pattern of currency substitution depends on the public's expectations of macroeconomic stability and the sustainability of the foreign exchange regime.[31]
Anchor currencies
Australian dollar
 Kiribati (since 1943; also uses its own coins)[34]: 17
Kiribati (since 1943; also uses its own coins)[34]: 17  Nauru (since 1914; also issues non-circulating Nauran collector coins pegged to the Australian dollar)[34]: 17 [35]
Nauru (since 1914; also issues non-circulating Nauran collector coins pegged to the Australian dollar)[34]: 17 [35] Tuvalu (since 1892; also uses its own coins)[34]: 17
Tuvalu (since 1892; also uses its own coins)[34]: 17  Zimbabwe (alongside the United States dollar, South African rand, Botswana pula, Japanese yen, several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
Zimbabwe (alongside the United States dollar, South African rand, Botswana pula, Japanese yen, several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
Euro
 Andorra (formerly French franc and Spanish peseta; issued non-circulating Andorran diner coins; issues its own euro coins). Since 1278, Andorra has used its neighbours' currencies, at the time the Counties of Foix, in present-day France, and of Urgell, in Catalonia.[34]: 17
Andorra (formerly French franc and Spanish peseta; issued non-circulating Andorran diner coins; issues its own euro coins). Since 1278, Andorra has used its neighbours' currencies, at the time the Counties of Foix, in present-day France, and of Urgell, in Catalonia.[34]: 17  Akrotiri and Dhekelia (Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia); formerly used the Cypriot pound)
Akrotiri and Dhekelia (Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia); formerly used the Cypriot pound) France (used in the overseas territories of the French Southern Territories, Saint Barthélemy, and Saint Pierre and Miquelon. Euro is used in the French overseas and department region of Guadeloupe)
France (used in the overseas territories of the French Southern Territories, Saint Barthélemy, and Saint Pierre and Miquelon. Euro is used in the French overseas and department region of Guadeloupe)
 French Polynesia (pegged to the CFP franc at a fixed exchange rate)
French Polynesia (pegged to the CFP franc at a fixed exchange rate)- Template:Country data NCL (pegged to the CFP franc at a fixed exchange rate)
- Template:Country data WLF (pegged to the CFP franc at a fixed exchange rate)
 Kosovo (formerly German mark and Yugoslav dinar)
Kosovo (formerly German mark and Yugoslav dinar) Monaco (formerly French franc from 1865 to 2002 and Monégasque franc;[34]: 17 issues its own euro coins)
Monaco (formerly French franc from 1865 to 2002 and Monégasque franc;[34]: 17 issues its own euro coins) Montenegro (formerly German mark and Yugoslav dinar)
Montenegro (formerly German mark and Yugoslav dinar) North Korea (alongside the Chinese renminbi, North Korean won, and United States dollar)[36]
North Korea (alongside the Chinese renminbi, North Korean won, and United States dollar)[36] San Marino (formerly Italian lira and Sammarinese lira; issues its own euro coins)
San Marino (formerly Italian lira and Sammarinese lira; issues its own euro coins)- Template:Country data Sovereign Military Order of Malta (issues non-circulating Maltese scudo coins at €0.24 = 1 scudo)
 Vatican City (formerly Italian lira and Vatican lira; issues its own euro coins)
Vatican City (formerly Italian lira and Vatican lira; issues its own euro coins) Zimbabwe (alongside the United States dollar, South African rand, Botswana pula, Japanese yen, several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
Zimbabwe (alongside the United States dollar, South African rand, Botswana pula, Japanese yen, several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
Indian rupee
 Bhutan (alongside the Bhutanese ngultrum, pegged at par with the rupee)
Bhutan (alongside the Bhutanese ngultrum, pegged at par with the rupee) Nepal (alongside the Nepali rupee, pegged at ₹0.625)
Nepal (alongside the Nepali rupee, pegged at ₹0.625) Zimbabwe (alongside the United States dollar, South African rand, Botswana pula, Japanese yen, several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
Zimbabwe (alongside the United States dollar, South African rand, Botswana pula, Japanese yen, several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
New Zealand dollar
 Cook Islands (issues its own coins and some notes.)
Cook Islands (issues its own coins and some notes.) Niue (also issues its own non-circulating commemorative and collector coins minted at the New Zealand Mint, pegged to the New Zealand dollar.)
Niue (also issues its own non-circulating commemorative and collector coins minted at the New Zealand Mint, pegged to the New Zealand dollar.) Pitcairn Islands (also issues its own non-circulating commemorative and collector coins pegged to the New Zealand dollar.)
Pitcairn Islands (also issues its own non-circulating commemorative and collector coins pegged to the New Zealand dollar.) Tokelau (also issues its own non-circulating commemorative and collector coins pegged to the New Zealand dollar.)
Tokelau (also issues its own non-circulating commemorative and collector coins pegged to the New Zealand dollar.)
Pound sterling
British Overseas Territories using the pound, or a local currency pegged to the pound, as their currency:
- Template:Country data British Antarctic Territory (issues non-circulating collector coins for the British Antarctic Territory.)[37]
 British Indian Ocean Territory (de jure, U.S. dollar used de facto; also issues non-circulating collector coins for the British Indian Ocean Territory.)[38]
British Indian Ocean Territory (de jure, U.S. dollar used de facto; also issues non-circulating collector coins for the British Indian Ocean Territory.)[38] Falkland Islands (alongside the Falkland Islands pound)
Falkland Islands (alongside the Falkland Islands pound) Gibraltar (alongside the Gibraltar pound)
Gibraltar (alongside the Gibraltar pound) Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (Tristan da Cunha; alongside the Saint Helena pound in Saint Helena and Ascension; also issues non-circulating collector coins for Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha.)[39]
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (Tristan da Cunha; alongside the Saint Helena pound in Saint Helena and Ascension; also issues non-circulating collector coins for Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha.)[39] South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (alongside the Falkland Islands pound; also issues non-circulating collector coins for South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands.)[40]
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (alongside the Falkland Islands pound; also issues non-circulating collector coins for South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands.)[40]
The Crown Dependencies use a local issue of the pound as their currency:
 Guernsey (Guernsey pound)
Guernsey (Guernsey pound)
 Alderney (issues non-circulating Alderney pound collector coins, backed by both the Pound sterling and Guernsey pound.)[41]
Alderney (issues non-circulating Alderney pound collector coins, backed by both the Pound sterling and Guernsey pound.)[41]
 Isle of Man (Manx pound)
Isle of Man (Manx pound) Jersey (Jersey pound)
Jersey (Jersey pound)
Under plans published in the Sustainable Growth Commission report by the Scottish National Party, an independent Scotland would use the pound as their currency for the first 10 years of independence. This has become known as sterlingisation.
Other countries:
 Zimbabwe (alongside the United States dollar, South African rand, Botswana pula, Japanese yen, several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
Zimbabwe (alongside the United States dollar, South African rand, Botswana pula, Japanese yen, several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
South African rand
 Eswatini (alongside the Swazi lilangeni)
Eswatini (alongside the Swazi lilangeni) Lesotho (alongside the Lesotho loti)
Lesotho (alongside the Lesotho loti) Namibia (alongside the Namibian dollar)
Namibia (alongside the Namibian dollar) Zimbabwe (alongside the United States dollar, South African rand, Botswana pula, Japanese yen, several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
Zimbabwe (alongside the United States dollar, South African rand, Botswana pula, Japanese yen, several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
United States dollar
Used exclusively
 British Virgin Islands (also issues non-circulating British Virgin Islands collector coins pegged to the U.S. dollar)[42]
British Virgin Islands (also issues non-circulating British Virgin Islands collector coins pegged to the U.S. dollar)[42] Caribbean Netherlands (since 1 January 2011)
Caribbean Netherlands (since 1 January 2011) Marshall Islands (issued non-circulating collector coins of the Marshall Islands pegged to the U.S. dollar since 1986)[43]
Marshall Islands (issued non-circulating collector coins of the Marshall Islands pegged to the U.S. dollar since 1986)[43] Micronesia (since 1944)[34]: 17
Micronesia (since 1944)[34]: 17  Palau (since 1944; issued non-circulating Palauan collector coins pegged to the U.S. dollar since 1992)[34][44]
Palau (since 1944; issued non-circulating Palauan collector coins pegged to the U.S. dollar since 1992)[34][44] Turks and Caicos Islands (issued non-circulating Turks and Caicos Islands collector coins denominated in "Crowns" and pegged to the U.S. dollar since 1969)[45]
Turks and Caicos Islands (issued non-circulating Turks and Caicos Islands collector coins denominated in "Crowns" and pegged to the U.S. dollar since 1969)[45]
Used partially
 Argentina (the United States dollar is used for major purchases such as buying properties)
Argentina (the United States dollar is used for major purchases such as buying properties) Bahamas (Bahamian dollar pegged at 1:1 but the United States dollar is accepted)
Bahamas (Bahamian dollar pegged at 1:1 but the United States dollar is accepted) Barbados (Barbadian dollar pegged at 2:1 but the United States dollar is accepted)
Barbados (Barbadian dollar pegged at 2:1 but the United States dollar is accepted) Belize (Belizean dollar pegged at 2:1 but the United States dollar is accepted)
Belize (Belizean dollar pegged at 2:1 but the United States dollar is accepted) Bermuda (Bermudian dollar pegged at 1:1 but the United States dollar is accepted)
Bermuda (Bermudian dollar pegged at 1:1 but the United States dollar is accepted) Cambodia (uses the Cambodian riel for many official transactions but most businesses deal exclusively in dollars for all but the cheapest items. Change is often given in a combination of U.S. dollars and Cambodian riel. ATMs yield U.S. dollars rather than Cambodian riel)[46][47]
Cambodia (uses the Cambodian riel for many official transactions but most businesses deal exclusively in dollars for all but the cheapest items. Change is often given in a combination of U.S. dollars and Cambodian riel. ATMs yield U.S. dollars rather than Cambodian riel)[46][47] Canada (a modest amount of United States coinage circulates alongside the Canadian dollar and is accepted at par by most retailers, banks and coin redemption machines)
Canada (a modest amount of United States coinage circulates alongside the Canadian dollar and is accepted at par by most retailers, banks and coin redemption machines) Congo-Kinshasa (many institutions accept both the Congolese franc and U.S. dollars)
Congo-Kinshasa (many institutions accept both the Congolese franc and U.S. dollars) Costa Rica (uses alongside the Costa Rican colón)
Costa Rica (uses alongside the Costa Rican colón) Ecuador (since 2000; also uses its own coins)[34]: 1
Ecuador (since 2000; also uses its own coins)[34]: 1  El Salvador (uses alongside bitcoin) (see Bitcoin Law and Bitcoin in El Salvador)[48]
El Salvador (uses alongside bitcoin) (see Bitcoin Law and Bitcoin in El Salvador)[48] Haiti (uses the U.S. dollar alongside its domestic currency, the gourde)
Haiti (uses the U.S. dollar alongside its domestic currency, the gourde) Honduras (uses alongside the Honduran lempira)[49]
Honduras (uses alongside the Honduran lempira)[49] Iraq (alongside the Iraqi dinar)
Iraq (alongside the Iraqi dinar) Lebanon (alongside the Lebanese pound)
Lebanon (alongside the Lebanese pound) Liberia (exclusively used the U.S. dollar during the early PRC period, but the National Bank of Liberia began issuing five dollar coins in 1982;[34]: 3 United States dollar still in common usage alongside the Liberian dollar)
Liberia (exclusively used the U.S. dollar during the early PRC period, but the National Bank of Liberia began issuing five dollar coins in 1982;[34]: 3 United States dollar still in common usage alongside the Liberian dollar) North Korea (alongside the euro, North Korean won, and renminbi)[36]
North Korea (alongside the euro, North Korean won, and renminbi)[36] Panama (since 1904; also uses its own coins)[34]: 6
Panama (since 1904; also uses its own coins)[34]: 6  Paraguay (the main currency is the Paraguayan guaraní)
Paraguay (the main currency is the Paraguayan guaraní) Peru (the main currency is the Peruvian sol)
Peru (the main currency is the Peruvian sol) Somalia (alongside the Somali shilling)
Somalia (alongside the Somali shilling) Somaliland (alongside the Somaliland shilling)[50]
Somaliland (alongside the Somaliland shilling)[50] Timor-Leste (uses its own coins)
Timor-Leste (uses its own coins) Uruguay[51] (the main currency is the Uruguayan peso)
Uruguay[51] (the main currency is the Uruguayan peso) Venezuela (alongside the Venezuelan bolívar; due to hyperinflation, USD is used for purchases such as buying electrical appliances, clothes, spare car parts, and food)[52][53]
Venezuela (alongside the Venezuelan bolívar; due to hyperinflation, USD is used for purchases such as buying electrical appliances, clothes, spare car parts, and food)[52][53] Vietnam (alongside the Vietnamese đồng)
Vietnam (alongside the Vietnamese đồng) Zimbabwe (since 2020; alongside the South African rand, British pound, Botswana pula, Japanese yen, several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
Zimbabwe (since 2020; alongside the South African rand, British pound, Botswana pula, Japanese yen, several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
Others
- Algerian dinar:
 Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (de facto independent state, recognized by 45 UN member states, but mostly occupied by Morocco; used in the Sahrawi refugee camps)
Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (de facto independent state, recognized by 45 UN member states, but mostly occupied by Morocco; used in the Sahrawi refugee camps) - Botswana pula:
 Zimbabwe (alongside several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
Zimbabwe (alongside several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar) - Brunei dollar:
 Singapore (alongside the Singapore dollar)
Singapore (alongside the Singapore dollar) - Canadian dollar:
 Saint Pierre and Miquelon (alongside the euro)
Saint Pierre and Miquelon (alongside the euro) - Chinese renminbi:
 Zimbabwe (alongside several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
Zimbabwe (alongside several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar) - Colombian peso:
 Venezuela (mainly in western states, alongside U.S. dollar)
Venezuela (mainly in western states, alongside U.S. dollar) - Danish krone:
 Faroe Islands (also issues its own coins and some notes)
Faroe Islands (also issues its own coins and some notes) Greenland
Greenland
- Egyptian pound:
 Palestine (Palestinian territories)
Palestine (Palestinian territories) - Hong Kong dollar:
 Macao (alongside the Macanese pataca, pegged at $1.032)
Macao (alongside the Macanese pataca, pegged at $1.032) - Japanese yen:
 Zimbabwe (alongside several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar)
Zimbabwe (alongside several other currencies and U.S. dollar-denominated bond coins and bond notes of the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) dollar) - Jordanian dinar:
 West Bank (alongside the New Israeli shekel)
West Bank (alongside the New Israeli shekel) - Mauritanian ouguiya:
 Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (de facto independent state, recognized by 45 UN member states, but mostly occupied by Morocco; used in the Sahrawi refugee camps)
Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (de facto independent state, recognized by 45 UN member states, but mostly occupied by Morocco; used in the Sahrawi refugee camps) - Moroccan dirham:
 Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (de facto independent state, recognized by 45 UN member states, but mostly occupied by Morocco; used in claimed areas under Moroccan control; issues the non-circulating Sahrawi peseta for collectors)
Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (de facto independent state, recognized by 45 UN member states, but mostly occupied by Morocco; used in claimed areas under Moroccan control; issues the non-circulating Sahrawi peseta for collectors) - New Israeli shekel:
 Palestine (Palestinian territories)
Palestine (Palestinian territories) - Russian ruble:
 Abkhazia (de facto independent state, but recognized as a part of Georgia internationally; issues non-circulating collector coins (Abkhazian apsar) pegged to the Russian ruble)[54]
Abkhazia (de facto independent state, but recognized as a part of Georgia internationally; issues non-circulating collector coins (Abkhazian apsar) pegged to the Russian ruble)[54] South Ossetia (de facto independent state, but recognized as a part of Georgia internationally; issues non-circulating collector coins (South Ossetian zarin) pegged to the Russian ruble)[55]
South Ossetia (de facto independent state, but recognized as a part of Georgia internationally; issues non-circulating collector coins (South Ossetian zarin) pegged to the Russian ruble)[55]
- Singapore dollar:
 Brunei (alongside the Brunei dollar)
Brunei (alongside the Brunei dollar) - Swiss franc:
- Turkish lira:
 Northern Cyprus (de facto independent state, but recognized as a part of Cyprus by all UN member states except Turkey)
Northern Cyprus (de facto independent state, but recognized as a part of Cyprus by all UN member states except Turkey)
See also
- Currency union
- Currency board
- Dedollarisation
- Domestic liability dollarization
- Petrocurrency
- Bitcoin, a cryptocurrency
- World currency
References
Footnotes
- ↑ New estimates of U.S. currency abroad, the domestic money supply and the unreported Economy Edgar L. Feige September 2011.
- ↑ Moleiro, Alonso (2025-01-18). "Venezuela grapples with economic collapse" (in en-us). https://english.elpais.com/international/2025-01-18/venezuela-grapples-with-economic-collapse.html.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Berg, Andrew; Borensztein, Eduardo (2000). "The Pros and Cons of Full Dollarization". IMF Working Paper; Full Dollarization (IMF) (/50). http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/issues/issues24/index.htm. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- ↑ Yeyati (2003) at 1.
- ↑ Rochon, Louis-Philippe (2003). Dollarization Lessons from Europe and the Americas. London and New York: Routledge. pp. 1. ISBN 9780415298780. https://archive.org/details/dollarizationles00roch.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Yeyati (2003) at 3.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Savastano at 7.
- ↑ Yeyati (2003) at 5.
- ↑ Balino; Berensztein (1999). "Monetary Policy in Dollarized Economies". IMF Occasional Paper 171.
- ↑ Mundell, R. A. (1961). "A Theory of Optimum Currency Areas". American Economic Review 51 (4): 657–665.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Bogetic (200). "Official Dollarization: Current Experiences and Issues". Cato Journal 20 (2): 179–213.
- ↑ Berkmen, S. Pelin; Cavallo, Eduardo (2010). "Exchange Rate Policy and Liability currency substitution: What Do the Data Reveal about Causality?". Review of International Economics 18 (5): 781–795. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9396.2010.00890.x. http://elibrary.imf.org/view/IMF001/02183-9781451865974/02183-9781451865974/02183-9781451865974.xml.
- ↑ Pinon, Marco (2008). Macroeconomic Implications of Financial currency substitution The Case of Uruguay. Washington DC: International Monetary Fund. pp. 22.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Alesina, Alberto; Barro (2001). "Dollarization". The American Economic Review 91 (2): 381–385. doi:10.1257/aer.91.2.381.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Yeyati (2003) at 22.
- ↑ Rose, Andrew (2000). "One Money, One Market: the effect of common currencies on trade". Economic Policy 15 (30): 8–0. doi:10.1111/1468-0327.00056.
- ↑ Honohan, Patrick (2007). "Dollarization and Exchange Rate Fluctuations". World Bank Policy Research Working Paper. Policy Research Working Papers (4172). doi:10.1596/1813-9450-4172. http://www-wds.worldbank.org/external/default/WDSContentServer/WDSP/IB/2007/03/14/000016406_20070314160847/Rendered/PDF/wps4172.pdf.
- ↑ Alesina, Alberto; Barro (2001). "Dollarization". The American Economic Review 91 (2): 382. doi:10.1257/aer.91.2.381.
- ↑ Yeyati (2003) at 23.
- ↑ Edwards, Sebastian; Magendzo, I. Igal (2003). "Dollarization And Economic Performance: What Do We Really Know?". International Journal of Finance and Economics 8 (4): 351–363. doi:10.1002/ijfe.217.
- ↑ Broda, Levy Yeyati, Christian, Eduardo (2003). Endogenous deposit dollarization. Federal Reserve Bank of New York. https://ideas.repec.org/p/fip/fednsr/160.html.
- ↑ Moreno-Bird, Juan Carlos (Fall 1999). "Dollarization in Latin America: Is it desirable?". ReVista: Harvard Review of Latin America. http://www.drclas.harvard.edu/revista/articles/view/473. Retrieved 27 June 2012.
- ↑ John, Kareken; Wallace (1981). "On the Indeterminacy of Equilibrium Exchange Rates". Quarterly Journal of Economics 96 (2): 207–222. doi:10.2307/1882388.
- ↑ Yeyati, Eduardo Levy (2008). "Liquidity Insurance in a Financially Dollarized Economy". in Edwards; Garcia. Financial Markets Volatility and Performance in Emerging Markets. University of Chicago Press. pp. 185–218. ISBN 978-0-226-18495-1. https://www.nber.org/chapters/c4778.
- ↑ Bencivenga, Valerie; Huybens, Smith (2001). "Dollarization and the Integration of International Capital Markets: a Contribution to the Theory of Optimal Currency Areas". Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 33 (2, Part 2): 548–589. doi:10.2307/2673916.
- ↑ Broda, Christian; Yeyati (2001). "Dollarization and the Lender of Last Resort". Book: Dollarization: 100–131.
- ↑ Yeyati (2003) at 31.
- ↑ Kutan, Rengifo, Ozsoz, Ali, Erick, Emre. "Evaluating the Effects of Deposit Dollarization in Bank Profitability". Fordham University Economics Department. http://stage.web.fordham.edu/images/academics/graduate_schools/gsas/economics/dp2010_07_kutan_rengifo_ozsoz.pdf.
- ↑ Yeyati (2003) at 34.
- ↑ "Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, Official Dollarization and the Banking System in Ecuador and El Salvador, 2006". http://www.frbatlanta.org/filelegacydocs/erq306_quispe.pdf.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 Savastano.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 Sahay, Ratna; Vegh, Carlos (September 1995). "Dollarization in Transition Economies: Evidence and Policy Implications". IMF Working Paper No. 95/96. https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WP/Issues/2016/12/30/Dollarization-in-Transition-Economies-Evidence-and-Policy-Implications-1905.
- ↑ Catão, Luis; Terrrones, Marco E. (August 2000). "Determinants of Dollarization: The Banking Side". IMF Working Paper No. 00/146: 5. https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WP/Issues/2016/12/30/Determinants-of-Dollarization-The-Banking-Side-3721.
- ↑ 34.00 34.01 34.02 34.03 34.04 34.05 34.06 34.07 34.08 34.09 Edwards, Sebastian (May 2001). "Dollarization and Economic Performance: An Empirical Investigation". NBER Working Paper No. 8274. doi:10.3386/w8274.
- ↑ Catalog of the coins of Nauru Numista (https://en.numista.com). Retrieved on 2023-02-17.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 Ruwitch, John; Park, Ju-min (2013-06-02). "Insight: North Korean economy surrenders to foreign currency invasion". Reuters (Changbai, China/Seoul). https://www.reuters.com/article/us-korea-north-money-idUSBRE9510E720130603.
- ↑ Catalog of the coins of the British Antarctic Territory Numista (https://en.numista.com). Retrieved on 2023-01-17.
- ↑ Catalog of the coins of the British Indian Ocean Territory Numista (https://en.numista.com). Retrieved on 2023-01-17.
- ↑ Catalog of the coins of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Numista (https://en.numista.com). Retrieved on 2023-01-17.
- ↑ Catalog of the coins of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Numista (https://en.numista.com). Retrieved on 2023-01-17.
- ↑ Catalog of the coins of Alderney Numista (https://en.numista.com). Retrieved on 2023-01-17.
- ↑ Catalog of the coins of the British Virgin Islands Numista (https://en.numista.com). Retrieved on 2022-09-03.
- ↑ Catalog of the coins of the Marshall Islands Numista (https://en.numista.com). Retrieved on 2022-09-03.
- ↑ Catalog of the coins of Palau Numista (https://en.numista.com). Retrieved on 2022-07-22.
- ↑ Catalog of the coins of the Turks and Caicos Islands Numista (https://en.numista.com). Retrieved on 2022-09-03.
- ↑ "Money & Cost". lonelyplanet.com. http://www.lonelyplanet.com/cambodia/practical-information/money-costs.
- ↑ Pilling, David; Peel, Michael (2014-07-28). "Cambodia: Wave of discontent". Financial Times. http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/b01c354e-13f2-11e4-8485-00144feabdc0.html. "Dollars account for 90 per cent of money in Cambodia’s banking system and almost the same proportion of cash used in everyday transactions, according to official estimates."
- ↑ Kharpal, Arjun (2021-06-09). "El Salvador becomes first country to adopt bitcoin as legal tender after passing law" (in en). https://www.cnbc.com/2021/06/09/el-salvador-proposes-law-to-make-bitcoin-legal-tender.html.
- ↑ Carter, Chris (2013-05-08). "Economy: The effect of dollarisation in Honduras". Pulsamerica. http://www.pulsamerica.co.uk/2013/05/economy-the-effect-of-dollarization-in-honduras/. Retrieved 2017-01-11.
- ↑ Aden, AK Muktar. "Overcoming Challenges in an Unrecognized Economy". https://slmof.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Overcoming-Challenges-in-an-Unrecognized-Economy.pdf.
- ↑ Pinon, Marco; Gelos, Gaston (28 August 2008). "Uruguay's Monetary Policy Effective Despite Dollarization". IMF Survey Magazine. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/survey/so/2008/CAR082808A.htm.
- ↑ Zerpa, Fabiola (5 November 2019). "Venezuela Is Now More Than 50% Dollarized, Study Finds". https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2019-11-05/venezuela-is-now-more-than-50-dollarized-study-finds.
- ↑ "Maduro says 'thank God' for dollarization in Venezuela". Reuters. 17 November 2019. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-venezuela-economy/maduro-says-thank-god-for-dollarization-in-venezuela-idUSKBN1XR0RV.
- ↑ Catalog of the coins of Abkhazia Numista (https://en.numista.com). Retrieved on 2022-10-14.
- ↑ Catalog of the coins of South Ossetia Numista (https://en.numista.com). Retrieved on 2022-10-14.
Works cited
- Savastano, Miguel (1996). "Dollarization in Latin America: Recent Evidence and Some Policy Issues". IMF Working Paper WP/96/4.
- Yeyati, Eduardo (2003). Dollarization. Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
 |
