Finance:Income disparity in Malaysia
From HandWiki
According to the UNDP 1997 Human Development Report,[1] and the 2004 United Nations Human Development (UNHDP) report,[2] Malaysia has the highest income disparity between the rich and poor in Southeast Asia, greater than that of Philippines , Thailand, Singapore, Vietnam and Indonesia.
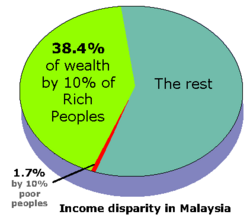
The UNHDP Report shows that the richest 10% in Malaysia control 38.4% of the economic income as compared to the poorest 10% who control only 1.7%. However, according to official statistics from the Prime Minister's Department, inequality has been decreasing steadily since 1970, with the Gini coefficient dropping to an all-time low of 0.40 in 2014.[3]
See also
- Poverty in Malaysia
References
- ↑ Asian Analysis 1998 by Asean Focus Group, Professor Michael Leigh Director Institute of East Asian Studies University Malaysia, Sarawak.
- ↑ Speech at the Meeting between DAPSY National and Perak State Leaders In Teluk Intan by Lim Guan Eng, If the 2004 Petronas profits of RM 35.6 billion (US$9.89 billion) were distributed to the poor, Malaysia would not have wealth distribution problems.
- ↑ "Table 6: Gini Coefficient by Ethnic Group, Strata and State, Malaysia, 1970-2014". 2014. http://www.epu.gov.my/documents/10124/cb197b81-d86b-418b-b5e9-841f55a68914.