History:Hamangia culture
 | |
| Horizon | Old Europe |
|---|---|
| Period | Neolithic, Chalcolithic |
| Dates | circa 5250 BC — circa 4,500 BC |
| Type site | Durankulak |
| Preceded by | Karanovo culture, Starcevo culture |
| Followed by | Varna culture, Boian culture, Gumelnița culture |
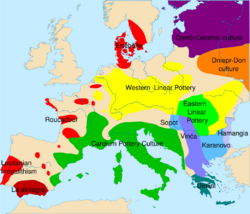
The Hamangia culture is a Late Neolithic archaeological culture of Dobruja (Romania and Bulgaria) between the Danube and the Black Sea and Muntenia in the south. It is named after the site of Baia-Hamangia, discovered in 1952 along Golovița Lake.[1]
Genesis and successor
The Hamangia culture began around 5250/5200 BC and lasted until around 4550/4500 BC. It was absorbed by the expanding Boian culture in its transition towards the Gumelnița culture.[2] Its cultural links with Anatolia suggest that it was the result of a recent settlement by people from Anatolia, unlike the neighbouring cultures, which appear descended from earlier Neolithic settlement.[3]
Art
The Hamangia culture attracted and attracts the attention of many art historians because of its exceptional clay figures.
Pottery
Painted vessels with complex geometrical patterns based on spiral-motifs are typical. The shapes include: bowls and cylindric glasses (most of them with arched walls). They are decorated with dots, straight parallel lines and zig-zags, which make Hamangia pottery very original.
Figurines
Pottery figurines are normally extremely stylized and show standing naked faceless women with emphasized breasts and buttocks. Two figurines known as "The Thinker of Cernavodă" and "The Sitting woman" are considered masterpieces of Neolithic art.
Gallery
Settlements
Settlements consist of rectangular houses with one or two rooms, built of wattle and daub, sometimes with stone foundations (in Durankulak). They are normally arranged on a rectangular grid and may form small tells. Settlements are located along the coast, on the coast of lakes, on lower or middle river terraces.
Important sites
- The Durankulak lake settlement, now Archaeological Complex Durankulak, commenced on a small island, approximately 7000 BC and around 4700/4600 BC the stone architecture was already in general use and became a characteristic phenomenon that was unique in Europe.
- Cernavodă, the necropolis where the famous statues "The Thinker" and "The Sitting Woman" were discovered
- The eponymous site of Baia-Hamangia, discovered in 1953 along Lake Golovița, close to the Black Sea coast, in the Romanian province of Dobrogea.
Inhumation
Crouched or extended inhumation in cemeteries. Grave-goods tend to be without pottery in Hamangia I. Grave-goods include flint, worked shells, bone tools and shell-ornaments.
See also
- Cucuteni-Trypillia culture
- Cycladic art
- History of Bulgaria
- Old Europe
- Prehistoric art
- Prehistory of Southeastern Europe
- Prehistoric Romania
- Varna culture
- Vinča culture
- List of Stone Age art
References
- ↑ Dumitru Berciu, Cultura Hamangia. București: Editura Academiei Republicii Socialiste România (1966).
- ↑ Vladimir Slavchev, Monuments of the final phase of Cultures Hamangia and Savia on the territory of Bulgaria, Revista Pontica vols. 37-38 (2004-2005), pp. 9-20.
- ↑ M. Nica, Unitate şi diversitate în culturile neolitice de la dunărea de jos = Unity and diversity of Neolithic cultures along the lower Danube, Revista Pontica vol. 30 (1997), pp. 105-116.
External links
HAMANGIA CULTURE – DEVELOPMENT AND OVERVIEW
 |












