Illusory contours
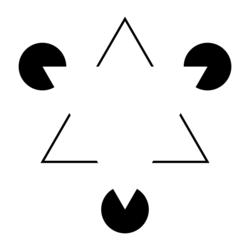
Illusory contours or subjective contours are visual illusions that evoke the perception of an edge without a luminance or color change across that edge. Illusory brightness and depth ordering often accompany illusory contours. Friedrich Schumann is often credited with the discovery of illusory contours around the beginning of the 20th century,[1] but they are present in art dating to the Middle Ages. Gaetano Kanizsa’s 1976 Scientific American paper marked the resurgence of interest in illusory contours for vision scientists.
Common types of illusory contours
Kanizsa figures
Perhaps the most famous example of an illusory contour is the Pac-Man configuration popularized by Gaetano Kanizsa.[2]
Kanizsa figures trigger the percept of an illusory contour by aligning Pac-Man-shaped inducers in the visual field such that the edges form a shape. Although not explicitly part of the image, Kanizsa figures evoke the Perception of a shape, defined by a sharp illusory contour.[2]
Typically, the shape seems brighter than the background, even though the luminance is in reality homogeneous. Additionally, the illusory shape seem to be closer to the viewer than the inducers. Kanizsa figures involve modal completion of the illusory shape and amodal completion of the inducers.[2]
Ehrenstein illusion
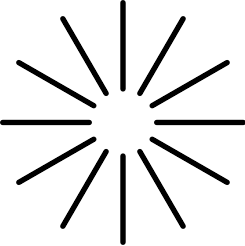
Closely related to Kanizsa figures is the Ehrenstein illusion. Instead of employing Pac-Man inducers, the Ehrenstein illusion triggers an illusory contour percept via radial line segments. Ehrenstein's discovery was originally contextualized as a modification of the Hermann grid.[3]
Abutting line gratings
Illusory contours are created at the boundary between two misaligned gratings.[4] In these so-called abutting line gratings, the illusory contour is perpendicular to the inducing elements.
In art and graphic design
Olympic logos from 1972, 1984, 1988, and 1994 all feature illusory contours, as does Ellsworth Kelly's 1950s series.
Jacob Gestman Geradts often used the Kanizsa illusion in his silkscreen prints, for instance in his work Formula 1 (1991).
Cortical responses
It is thought that early visual cortical regions such as V1 V2 in the visual system are responsible for forming illusory contours.[5][6] Studies using human neuroimaging techniques have found that illusory contours are associated with activity in the deep layers of primary visual cortex.[7]
Related visual phenomena
Visual illusions are useful stimuli for studying the neural basis of perception because they hijack the visual system's innate mechanisms for interpreting the visual world under normal conditions. For example, objects in the natural world are often only partially visible. Illusory contours provide clues for how the visual system constructs surfaces when portions of the surface's edge are not visible.
The encoding of surfaces is thought to be an indispensable part of visual perception, forming a critical intermediate stage of visual processing between the initial analysis of visual features and the ability to recognize complex stimuli like faces and scenes.[8]
- Amodal perception
- Autostereogram
- Filling-in
- Gestalt psychology
- Negative space
- Phantom contour
- Reification
References
- ↑ Schumann, F (1900), "Beiträge zur Analyse der Gesichtswahrnehmungen. Erste Abhandlung. Einige Beobachtungen über die Zusammenfassung von Gesichtseindrücken zu Einheiten.", Zeitschrift für Psychologie und Physiologie der Sinnesorgane 23: 1–32
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Kanizsa, G (1955), "Margini quasi-percettivi in campi con stimolazione omogenea.", Rivista di Psicologia 49 (1): 7–30
- ↑ Ehrenstein, W (1941), "Über Abwandlungen der L. Hermannschen Helligkeitserscheinung (Modifications of the Brightness Phenomenon of L. Hermann).", Zeitschrift für Psychologie 150: 83–91
- ↑ Soriano, M; Spillmann, L; Bach, M (1996), "The abutting grating illusion.", Vision Res. 36 (1): 109–116, doi:10.1016/0042-6989(95)00107-b, PMID 8746248
- ↑ von der Heydt, R; Peterhans, E; Baumgartner, G (1984), "Illusory contours and cortical neuron responses", Science 224 (4654): 1260–1262, doi:10.1126/science.6539501, PMID 6539501
- ↑ Barghout, Lauren (2014). Vision. Global Conceptual Context Changes Local Contrast Processing (Ph.D. Dissertation 2003). Updated to include Computer Vision Techniques. Scholars' Press. ISBN 978-3-639-70962-9. https://www.morebooks.de/store/gb/book/vision/isbn/978-3-639-70962-9.
- ↑ Kok, Peter; Bains, Lauren; van Mourik, Tim; Norris, David G.; de Lange, Floris (2016-02-08). "Selective Activation of the Deep Layers of the Human Primary Visual Cortex by Top-Down Feedback" (in en). Current Biology 26 (3): 371–376. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.12.038. ISSN 0960-9822. PMID 26832438.
- ↑ Nakayama, K; He, Z; Shimojo, S (1995). "Visual surface representation: a critical link between lower-level and higher level vision". An Invitation to Cognitive Science: Visual cognition. 2. pp. 1–70. http://visionlab.harvard.edu/members/ken/Papers/077NKHeShimojoMIT1995b.pdf.
Further reading
- Coren, S (1972), "Subjective contour and apparent depth", Psychological Review 79 (4): 359–367, doi:10.1037/h0032940, PMID 5038153
- Peterhans, E.; von der Heydt, R. (1991). "Subjective contours--bridging the gap between psychophysics and physiology.". Trends Neurosci 14 (3): 112–119. doi:10.1016/0166-2236(91)90072-3. PMID 1709535. "Phenomena of contour, color and movement perception have been used to identify functions of neurons and to reveal functional differences between cortical areas that application of classical receptive-field concepts has not suggested.".
External links
- Illusory contours figures Many unpublished drawings (fr)
