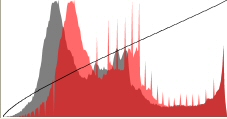
Image histogram
An image histogram is a type of histogram that acts as a graphical representation of the tonal distribution in a digital image.[1] It plots the number of pixels for each tonal value. By looking at the histogram for a specific image a viewer will be able to judge the entire tonal distribution at a glance.
Image histograms are present on many modern services. Photographers can use them as an aid to show the distribution of tones captured, and whether image detail has been lost to blown-out highlights or blacked-out shadows.[2] This is less useful when using a raw image format, as the dynamic range of the displayed image may only be an approximation to that in the raw file.[3]
The horizontal axis of the graph represents the tonal variations, while the vertical axis represents the total number of pixels in that particular tone.[1]
The left side of the horizontal axis represents the dark areas, the middle represents mid-tone values and the right hand side represents light areas. The vertical axis represents the size of the area (total number of pixels) that is captured in each one of these zones.
Thus, the histogram for a very dark image will have most of its data points on the left side and center of the graph.
Conversely, the histogram for a very bright image with few dark areas and/or shadows will have most of its data points on the right side and center of the graph.
Image manipulation and histograms
Image editors typically create a histogram of the image being edited. The histogram plots the number of pixels in the image (vertical axis) with a particular brightness or tonal value (horizontal axis). Algorithms in the digital editor allow the user to visually adjust the brightness value of each pixel and to dynamically display the results as adjustments are made.[4] Histogram equalization is a popular example of these algorithms. Improvements in picture brightness and contrast can thus be obtained.
In the field of computer vision, image histograms can be useful tools for thresholding. Because the information contained in the graph is a representation of pixel distribution as a function of tonal variation, image histograms can be analyzed for peaks and/or valleys. This threshold value can then be used for edge detection, image segmentation, and co-occurrence matrices.
See also
- Color histogram, a multidimensional histogram of the distribution of color in an image
- Curve (tonality)
- Histogram equalization
- Histogram matching
- Image editing
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Ed Sutton. "Histograms and the Zone System". Illustrated Photography. http://www.illustratedphotography.net/basic-photography/zone-system-histograms.
- ↑ Michael Freeman (2005). The Digital SLR Handbook. Ilex. ISBN 1-904705-36-7.
- ↑ Todd Vorenkamp. "How to Read Your Camera's Histogram". B&H Explora. https://www.bhphotovideo.com/explora/photography/tips-and-solutions/how-read-your-cameras-histogram.
- ↑ Martin Evening (2007). Adobe Photoshop CS3 for Photographers: A Professional Image Editor's Guide.... Focal Press. ISBN 978-0-240-52028-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=0XZO93ZcbqkC&dq=%22image+histogram%22&pg=PA136.
External links
- CAMERA HISTOGRAMS: TONES & CONTRAST at cambridgeincolour.com
 |