Langley’s Adventitious Angles
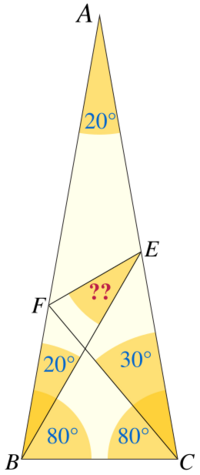
Langley’s Adventitious Angles is a mathematical problem posed by Edward Mann Langley in The Mathematical Gazette in 1922.[1][2]
The problem
In its original form the problem was as follows: is an isosceles triangle.
- at to cuts in
- at to cuts in
- Draw
Solution
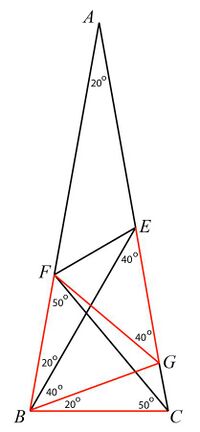
A solution was developed by James Mercer in 1923.[2] This solution involves drawing one additional line, and then making repeated use of the fact that the internal angles of a triangle add up to 180° to prove that several triangles drawn within the large triangle are all isosceles.
- Draw at to intersecting at and draw (See figure on the lower right.)
- Since and then and triangle is isosceles with
- Since and then and triangle is isosceles with
- Since and then triangle is equilateral.
- Since and then and triangle is isosceles with
- Therefore all the red lines in the figure are equal.
- Since triangle is isosceles with
- Therefore
Many other solutions are possible. Cut the Knot list twelve different solutions and several alternative problems with the same 80-80-20 triangle but different internal angles.[4]
Generalization
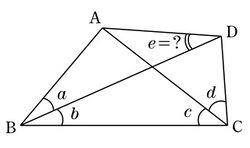
A quadrilateral such as BCEF in which the angles formed by the diagonals with the sides are all rational (when measured in degrees) is called an adventitious quadrangle. Numerous constructions for other adventitious quadrangles beyond the one appearing in Langley's puzzle are known. They form several infinite families and an additional set of sporadic examples.[5]
Classifying the adventitious quadrangles (which need not be convex) turns out to be equivalent to classifying all triple intersections of diagonals in regular polygons. This was solved by Gerrit Bol in 1936 (Beantwoording van prijsvraag # 17, Nieuw-Archief voor Wiskunde 18, pages 14-66). He in fact classified (though with a few errors) all multiple intersections of diagonals in regular polygons. His results (all done by hand) were confirmed with computer, and the errors corrected, by Bjorn Poonen and Michael Rubinstein in 1998.[6] The article contains a history of the problem and a picture featuring the regular triacontagon and its diagonals.
In 2015, an anonymous Japanese woman using the pen name "aerile re" published the first known method (the method of 3 circumcenters) for using elementary geometry to find a special class of adventitious quadrangles.[7][8][9] This work solves the first of the three unsolved problems listed by Rigby in his 1978 paper.[5]
References
- ↑ Langley, E. M. (1922), "Problem 644", The Mathematical Gazette 11: 173.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Darling, David (2004), The Universal Book of Mathematics: From Abracadabra to Zeno's Paradoxes, John Wiley & Sons, p. 180, https://books.google.com/books?id=nnpChqstvg0C&pg=PA180.
- ↑ Tripp, Colin (1975), "Adventitious angles", The Mathematical Gazette 59: 98–106.
- ↑ Bogomolny, Alexander. "The 80-80-20 Triangle". https://www.cut-the-knot.org/triangle/80-80-20/index.shtml.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Rigby, J. F. (1978), "Adventitious quadrangles: a geometrical approach", The Mathematical Gazette 62 (421): 183–191, doi:10.2307/3616687.
- ↑ Poonen, Bjorn; Rubinstein, Michael (1998), "The number of intersection points made by the diagonals of a regular polygon", SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics 11 (1): 135-156, http://www-math.mit.edu/~poonen/papers/ngon.pdf.
- ↑ Saito, Hiroshi (2016), "The adventitious quadrangles was solved completely by the elementary solution" (in ja), Gendaisūgaku (現代数学) 49 (590): 66–73, ISSN 2187-6495, http://www.gensu.co.jp/gekkan_print.cgi?date=201602.
- ↑ aerile_re (2015-10-27) (in ja), The last challenge from Geometry the Great, archived from the original on 2016-04-16, https://web.archive.org/web/20160416025436/http://note.chiebukuro.yahoo.co.jp/detail/n365238.
- ↑ Saito, Hiroshi (2016-12-11) (in en), Introducing "3 circumcenter method", http://www.gensu.co.jp/saito/challenge/3circumcenter_en.html - English translation of the article from Gendaisūgaku (現代数学).
External links
- Angular Angst, MathPages

