Medicine:Absence of fingerprints-congenital milia syndrome
| Absence of fingerprints-congenital milia syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Absence of dermatoglyphics congenital milia, Baird syndrome, Adermatoglyphia with congenital facial milia and acral blisters, digital contractures, and nail abnormalities, Basan syndrome.[1] |
 | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | adermatoglyphia with neo-natal blisters and facial milia |
| Complications | Usually none (health-wise), however; hypohidrosis may lead to heat exhaustion or even a heat stroke, and the absence of fingerprints may complicate the use of systems that require fingerprint-identification |
| Usual onset | Birth |
| Duration | Life-long |
| Types | Adermatoglyphia syndromes |
| Causes | Genetic mutation |
| Risk factors | Having a parent with the disorder |
| Diagnostic method | Physical examination, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Isolated adermatoglyphia |
| Prevention | none |
| Prognosis | Good |
| Frequency | extremely rare, only 10 families worldwide are known to be affected with this disorder. |
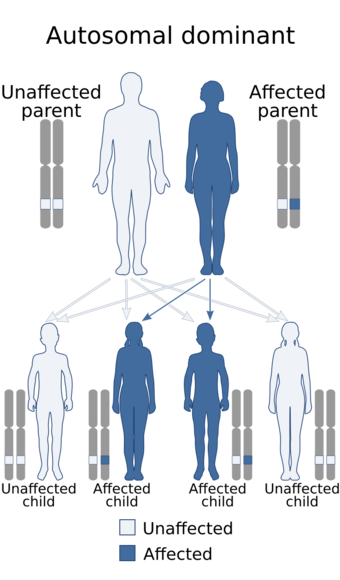
Absence of fingerprints-congenital milia syndrome, also known simply as Baird syndrome is an extremely rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder which is characterized by a lack of fingerprints and the appearance of blisters and facial milia soon after birth.[2] It has been described in ten families worldwide.[3][4]
Presentation
People with this disorder often have congenital adermatoglyphia, facial milia and blisters soon after birth, hypohidrosis (less sweating than average), and either thin or thickened skin throughout the body.[5][6][7][8]
Single transversal palmar lines, plantar keratoderma, nail grooving, toe syndactyly and finger camptodactyly have also been reported.[9][10][11] Rarely, constriction ring syndrome is reported.[12]
Causes
Through a large Han Chinese family with the disorder, it was found to be caused by mutations in the SMARCAD1 gene, in chromosome 4.[13][14][15][16][17][18][19] This gene produces a protein that is believed to control genes associated with the development of the fingerprints.[20]
References
- ↑ "Absence of fingerprints congenital milia". https://rarediseases.org/gard-rare-disease/absence-of-fingerprints-congenital-milia/.
- ↑ RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Baird syndrome" (in en). https://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/Disease_Search.php?lng=EN&data_id=1746&Disease_Disease_Search_diseaseType=ORPHA&Disease_Disease_Search_diseaseGroup=1658&Disease(s)/group%20of%20diseases=Baird-syndrome&title=Baird-syndrome&search=Disease_Search_Simple.
- ↑ Elhaji, Youssef; van Henten, Tessa M. A.; Ruivenkamp, Claudia A. L.; Nightingale, Mathew; Santen, Gijs WE; Vos, Lydia E.; Hull, Peter R. (2021-09-01). "Two SMARCAD1 Variants Causing Basan Syndrome in a Canadian and a Dutch Family" (in en). JID Innovations 1 (3): 100022. doi:10.1016/j.xjidi.2021.100022. ISSN 2667-0267. PMID 34909722.
- ↑ "Absence of fingerprints-congenital milia syndrome". https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ols/ontologies/ORDO/terms?iri=http://www.orpha.net/ORDO/Orphanet_1658#:~:text=A%20rare%20syndrome%20syndrome%20characterized,on%20the%20hands%20and%20feet..
- ↑ "ABSENCE OF FINGERPRINTS-CONGENITAL MILIA SYNDROME" (in en). 2022-05-17. http://www.mendelian.co/diseases/absence-of-fingerprints-congenital-milia-syndrome.
- ↑ "OMIM Entry - # 129200 - BASAN SYNDROME" (in en-us). https://omim.org/entry/129200.
- ↑ Límová, M.; Blacker, K. L.; LeBoit, P. E. (August 1993). "Congenital absence of dermatoglyphs". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 29 (2 Pt 2): 355–358. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(93)70195-y. ISSN 0190-9622. PMID 8340514. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8340514/.
- ↑ "PomBase". https://www.pombase.org/term/MONDO:0007507.
- ↑ "Basan syndrome - NIH Genetic Testing Registry (GTR) - NCBI". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gtr/conditions/C0406707/.
- ↑ "Absence of Fingerprints Congenital Milia Syndrome" (in en). http://www.dovemed.com/diseases-conditions/absence-fingerprints-congenital-milia-syndrome/.
- ↑ "beautiful source". https://rarediseases.oscar.ncsu.edu/disease/absence-of-fingerprints-congenital-milia-syndrome/about/.
- ↑ "Absence of fingerprints congenital milia – Rare Hematology News" (in en-US). https://www.rarehematologynews.com/rarediseases/absence-of-fingerprints-congenital-milia/.
- ↑ Li, Ming; Wang, Jianbo; Li, Zhenlu; Zhang, Jia; Ni, Cheng; Cheng, Ruhong; Yao, Zhirong (August 2016). "Genome-wide linkage analysis and whole-genome sequencing identify a recurrent SMARCAD1 variant in a unique Chinese family with Basan syndrome". European Journal of Human Genetics 24 (9): 1367–1370. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2016.15. ISSN 1018-4813. PMID 26932190.
- ↑ "Figure 2 | Association between Mutation in SMARCAD1 and Basan Syndrome with Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma". https://www.hindawi.com/journals/dm/2022/7840710/fig2/.
- ↑ Nieto‐Benito, Lula María; Molina‐López, Irene; Feito‐Rodríguez, Marta; Martínez‐González, Víctor; Suárez‐Fernández, Ricardo; Campos‐Dominguez, Minia (March 2021). "Ectodermal dysplasia with congenital adermatoglyphia (Basan syndrome): Report of two cases presenting with extensive congenital milia" (in en). Pediatric Dermatology 38 (2): 530–532. doi:10.1111/pde.14512. ISSN 0736-8046. PMID 33486784. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/pde.14512.
- ↑ Valentin, Monica N.; Solomon, Benjamin D.; Richard, Gabriele; Ferreira, Carlos R.; Kirkorian, Anna Yasmine (November 2018). "Basan gets a new fingerprint: Mutations in the skin-specific isoform of SMARCAD1 cause ectodermal dysplasia syndromes with adermatoglyphia" (in en). American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A 176 (11): 2451–2455. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.40485. PMID 30289605. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ajmg.a.40485.
- ↑ Li, Ming; Wang, Jianbo; Li, Zhenlu; Zhang, Jia; Ni, Cheng; Cheng, Ruhong; Yao, Zhirong (September 2016). "Genome-wide linkage analysis and whole-genome sequencing identify a recurrent SMARCAD1 variant in a unique Chinese family with Basan syndrome" (in en). European Journal of Human Genetics 24 (9): 1367–1370. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2016.15. ISSN 1476-5438. PMID 26932190.
- ↑ "Basan Syndrome (BSNS)". https://www.malacards.org/card/basan_syndrome.
- ↑ "KEGG DISEASE: Basan syndrome". https://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?H02296.
- ↑ "Why some people don't have fingerprints" (in en). http://www.nbcnews.com/health/body-odd/why-some-people-dont-have-fingerprints-flna1C6437284.

