Medicine:CSF tap test
| CSF tap test | |
|---|---|
| Medical diagnostics | |
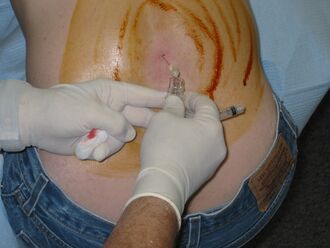 Lumbar puncture | |
| Synonyms | Lumbar tap test |
| Purpose | test to decide shunting of cerebrospinal fluid |
The CSF tap test, sometimes lumbar tap test or Miller Fisher Test, is a medical test that is used to decide whether shunting of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) would be helpful in a patient with suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH). The test involves removing 30-50 ml of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through a lumbar puncture, after which motor and cognitive function is clinically reassessed.[1] The name "Fisher test" is after C. Miller Fisher, a Canadian neurologist working in Boston, Massachusetts, who described the test.[2]
Clinical improvement showed a high predictive value for subsequent success with shunting. A "negative" test has a very low predictive accuracy, as many patients may improve after a shunt in spite of lack of improvement after CSF removal.[3]
References
- ↑ Virhammar, J.; Cesarini, K. G.; Laurell, K. (2011-07-30). "The CSF tap test in normal pressure hydrocephalus: evaluation time, reliability and the influence of pain". European Journal of Neurology 19 (2): 271–276. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03486.x. ISSN 1351-5101. PMID 21801282. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03486.x.
- ↑ "Evaluation and Management of Dementia". Reichel's care of the elderly : clinical aspects of aging. (6th ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2009. p. 180. ISBN 9780521869294. https://books.google.com/books?id=74FPjVwzGDUC&dq=%22fisher%20test%22%20NPH&pg=PA180.
- ↑ Wikkelsø, C., Hellström, P., Klinge, P. M., Tans, J. T. J., & European iNPH Multicentre Study Group (2013). "The European iNPH Multicentre Study on the predictive values of resistance to CSF outflow and the CSF Tap Test in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 84 (5): 562–568. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2012-303314. PMID 23250963.
 |

