Medicine:Incisive foramen
| Incisive foramen | |
|---|---|
 The bony palate and alveolar arch. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | hard palate |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | foramen incisivum |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
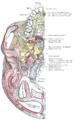
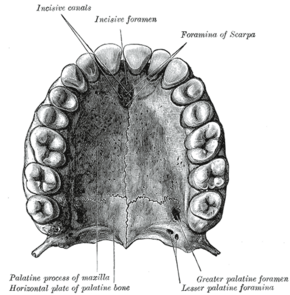
In the human mouth, the incisive foramen (also known as: "anterior palatine foramen", or "nasopalatine foramen") is the opening of the incisive canals on the hard palate immediately behind the incisor teeth. It gives passage to blood vessels and nerves. The incisive foramen is situated within the incisive fossa of the maxilla.
The incisive foramen is used as an anatomical landmark for defining the severity of cleft lip and cleft palate.
The incisive foramen exists in a variety of species.
Structure
The incisive foramen is a funnel-shaped opening in the bone of the oral hard palate representing the inferior termination of the incisive canal.[citation needed] An oral prominence - the incisive papilla - overlies the incisive fossa.[1]
The incisive foramen is situated immediately behind the incisor teeth, and in between the two premaxillae.[citation needed]
Contents
The incisive foramen allows for blood vessels and nerves to pass. These include:
- the pterygopalatine nerves to the hard palate.[2]
- the nasopalatine nerves from the floor of the nasal cavity.[3]
- the sopalatine branches of the infratrochlear nerve, a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve.[4]
- the sphenopalatine artery supplying the mucous membrane covering the hard palate of the mouth.[3]
- the sphenopalatine vein draining the mucous membrane covering the hard palate of the mouth.
Clinical significance
As many nerves exit the incisive canal at the incisive foramen, it may be used for injection of local anaesthetic.[3]
When plain radiographs are taken of the mouth, the incisive foramen may be mistaken for a periapical lesion.[5]
The incisive foramen can be used as a landmark when describing cleft lip and cleft palate, which can either extend in front of (primary) or behind (secondary) the foramen.[6][7] It is also important as a surgical landmark to avoid damaging its nerves and vascular structures.[3]
History
The incisive foramen is also known as the anterior palatine foramen,[5] the nasopalatine foramen, and the incisive fossa.
Other animals
In many other species, the incisive foramina allow for passage of ducts to the vomeronasal organ.[2] It can be found in cats,[6] and alligators.[8]
Additional images
References
- ↑ Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (41st ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier Limited. 2016. pp. 510. ISBN 978-0-7020-5230-9. OCLC 920806541.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Maynard, Robert Lewis; Downes, Noel (2019-01-01). "10 - Nasal Cavity" (in en). Anatomy and Histology of the Laboratory Rat in Toxicology and Biomedical Research. Academic Press. pp. 109–121. ISBN 978-0-12-811837-5. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128118375000101.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Tomaszewska, Iwona M.; Popieluszko, Patrick; Tomaszewski, Krzysztof A.; Walocha, Jerzy A. (2019), Iwanaga, Joe; Tubbs, R. Shane, eds., "Anatomy and Variations of the Incisive Foramen" (in en), Anatomical Variations in Clinical Dentistry (Cham: Springer International Publishing): pp. 117–123, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-97961-8_11, ISBN 978-3-319-97961-8, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-97961-8_11, retrieved 2021-09-16
- ↑ Moskovitz, Joshua B.; Choi, Andrew (2015). "11 - Regional Nerve Blocks of the Head and Neck" (in en). Nerves and nerve injuries. 1 - History, embryology, anatomy, imaging, and diagnostics. Amsterdam: Academic Press. pp. 147–151. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-410390-0.00011-1. ISBN 978-0-12-410447-1. OCLC 908128669. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/908128669.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Gorrel, Cecilia; Andersson, Susanne; Verhaert, Leen (2013-01-01). "7 - Dental radiography" (in en). Veterinary Dentistry for the General Practitioner (2nd ed.). Saunders. pp. 67–80. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-4943-9.00012-0. ISBN 978-0-7020-4943-9. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780702049439000120.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Rochette, Judy (2016). "103 - Disorders and Normal Variations of the Oral Cavity of Kittens and Senior Cats" (in en). August's Consultations in Feline Internal Medicine. 7. Saunders. pp. 1024–1033. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-22652-3.00103-1. ISBN 978-0-323-22652-3. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323226523001031.
- ↑ Mitchell, Barry S.; Sharma, Ram (2009). "11 - Development of the head and neck, the eye and ear". Embryology (2nd ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 63–72. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-3225-7.50014-2. ISBN 978-0-7020-3225-7. OCLC 245507391. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/245507391.
- ↑ De Iuliis, Gerardo; Pulerà, Dino (2011-01-01). "8 - Reptile Skulls and Mandibles" (in en). The Dissection of Vertebrates (2nd ed.). Academic Press. pp. 253–285. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-375060-0.00008-5. ISBN 978-0-12-375060-0. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123750600000085.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 22:4b-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
 |