Medicine:Mastoid foramen
| Mastoid foramen | |
|---|---|
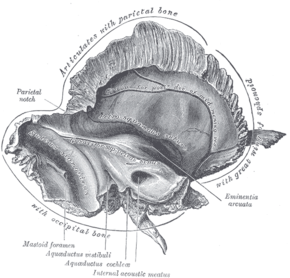 Left temporal bone. Inner surface. (Mastoid foramen labeled at bottom left.) | |
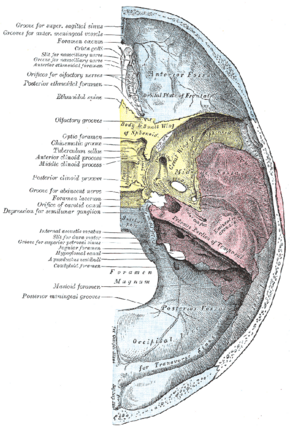 Base of the skull. Upper surface. (Temporal bone is pink, and label for mastoid foramen is at left, second from the bottom.) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | temporal bone of skull |
| System | skeletal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | foramen mastoideum |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone. It transmits an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus, and a small branch of the occipital artery, the posterior meningeal artery to the dura mater.
Structure
The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone of the skull.[1]
The opening of the mastoid foramen is an average of 18 mm from the asterion,[2] and around 34 mm from the external auditory meatus.[3] It is typically very narrow.[1][3] This may be around 2 mm.[3]
Variation
The position and size of this foramen are very variable.[1][3] It is not always present.[1][3] Sometimes, it is duplicated on one side or both sides.[1] Sometimes, it is situated in the occipital bone, or in the suture between the temporal bone and the occipital bone.
Function
The mastoid foramen transmits:
- an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus or the posterior auricular vein.[1][2]
- a small branch of the occipital artery, the posterior meningeal artery, to the dura mater.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Wang, Cindy; Lockwood, Joseph; Iwanaga, Joe; Dumont, Aaron S.; Bui, C. J.; Tubbs, R. Shane (June 2021). "Comprehensive review of the mastoid foramen" (in en). Neurosurgical Review 44 (3): 1255–1258. doi:10.1007/s10143-020-01329-9. ISSN 0344-5607. PMID 32507931. https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10143-020-01329-9.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Hampl, Martin; Kachlik, David; Kikalova, Katerina; Riemer, Roxane; Halaj, Matej; Novak, Vlastimil; Stejskal, Premysl; Vaverka, Miroslav et al. (2018-07-01). "Mastoid foramen, mastoid emissary vein and clinical implications in neurosurgery" (in en). Acta Neurochirurgica 160 (7): 1473–1482. doi:10.1007/s00701-018-3564-2. ISSN 0942-0940. PMID 29779186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-018-3564-2.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Kim, Won Sik; Kim, Soo Il; Kim, Sun; Zheng, Guo Dong; Yang, Eun Jin; Han, Seung Ro (2000-03-31). "Mastoid Foramen and Superficial Mastoid Canals of Korean Men". Korean Journal of Physical Anthropology 13 (1): 11–19. doi:10.11637/kjpa.2000.13.1.11. https://synapse.koreamed.org/articles/1038727.
External links
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22. https://web.archive.org/web/20120722052131/http://www.tk.de/rochelexikon/pics/s34257.000-1.html.
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-2". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2013-06-22. https://web.archive.org/web/20130622050647/http://www.tk.de/rochelexikon/pics/s34257.000-2.html.
- Akram Abood Jaffar: Personal website, Anatomical variations
 |

