Medicine:Mietens syndrome
From HandWiki
| Mietens syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | |
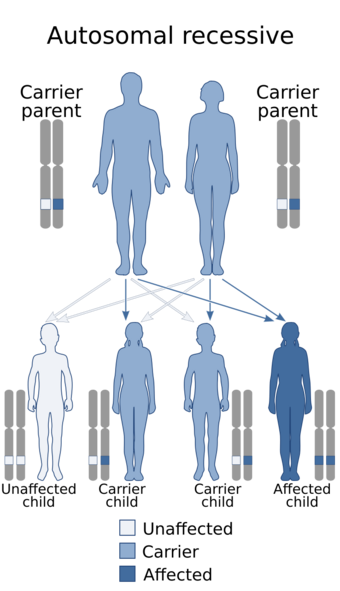 | |
| This condition is inherited via an autosomal recessive pattern | |
Mietens syndrome is a autosomal recessive disorder first described by Mietens and Weber.[3] The condition is named after a German physician named Carl Mietens.[4]
Only 9 cases have been reported.[5]
Symptoms and signs
- Intellectual disability[6]
- Flat feet[6]
- Crossed eyes[6]
- Severe postnatal growth retardation[6]
- Nystagmus[6]
- Narrow nose[6]
- Short forearm bones[6]
- Absent proximal radial epiphyses[6]
- Autosomal recessive inheritance[6]
- Dislocated radial head[6]
- Sclerocornea has been reported in this condition.[7]
History
In 1966, Carl Mietens and Helge Weber reported cases of four children, 3 sisters and 1 brother. Who suffered from a cluster of congenital anomalies and mental retardantion.[8]
In 2006, two documented has been reported.[9]
References
- ↑ "Mietens-Weber syndrome | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/3524/mietens-weber-syndrome.
- ↑ "Mietens-Weber syndrome". https://rarediseases.org/gard-rare-disease/mietens-weber-syndrome/.
- ↑ Jones, H. Royden; Vivo, Darryl C. De; Darras, Basil T. (2003) (in en). Neuromuscular Disorders of Infancy, Childhood, and Adolescence: A Clinician's Approach. Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 137. ISBN 978-0-7506-7190-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=ilPXTTWImh4C&q=Mietens+syndrome&pg=PA137.
- ↑ Beighton, Greta (2012-12-06) (in en). The Person Behind the Syndrome. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4471-0925-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=d0cIBgAAQBAJ&q=mietens+syndrome&pg=PT607.
- ↑ RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Mietens syndrome" (in en). https://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?lng=EN&Expert=2557.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 "Mietens-Weber syndrome | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/3524/mietens-weber-syndrome.
- ↑ Traboulsi, Elias I. (2012-01-12) (in en). Genetic Diseases of the Eye. Oxford University Press, USA. pp. 93. ISBN 978-0-19-532614-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=Yq-TISoByisC&q=Mietens-Weber+syndrome&pg=PA105.
- ↑ Winter, Robin M.; Baraitser, Michael (2013-12-20) (in en). Multiple Congenital Anomalies: A Diagnostic Compendium. Springer. pp. 406. ISBN 978-1-4899-3109-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=2XP1BwAAQBAJ&q=Mietens-Weber+syndrome&pg=PA406.
- ↑ Martínez-Glez, Víctor; Lapunzina, Pablo; Delicado, Alicia; Tendero, Adrián; Mori, María Angeles; de Torres, María Luisa; Fernández, Luis; Palomares, María et al. (July 2006). "Mietens-Weber syndrome: two new patients and a review". Clinical Dysmorphology 15 (3): 175–177. doi:10.1097/01.mcd.0000204985.54366.a7. ISSN 0962-8827. PMID 16760739. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16760739/.
 |

