Medicine:Procerus muscle
| Procerus muscle | |
|---|---|
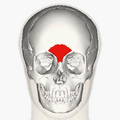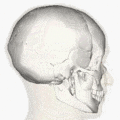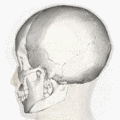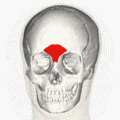
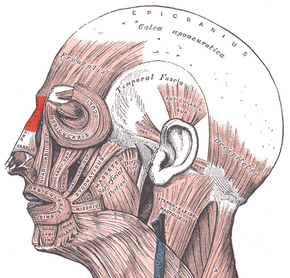 Muscles of the head, face, and neck (Procerus visible at upper left, at top of nose) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | From fascia over the lower part of the nasal bone |
| Insertion | Into the skin of the lower part of the forehead between the eyebrows |
| Artery | Facial artery |
| Nerve | Temporal branch of the facial nerve |
| Actions | Draws down the medial angle of the eyebrow giving expressions of frowning |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus procerus, pyramidalis nasi, depressor glabellae |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The procerus muscle (or pyramidalis nasi) is a small pyramidal muscle in the glabella. It is involved in facial expressions such as frowning and those associated with attentional control, and it indirectly helps shield the eyes from bright light. Because it contributes to wrinkle formation on the nasal bridge, it is often targeted in non-surgical facial rejuvenation treatments, such as botulinum toxin injections.[1]: 558 Procerus is Latin, meaning tall or extended.
Structure
The procerus muscle arises by tendinous fibers from the fascia covering the lower part of the nasal bone and upper part of the lateral nasal cartilage. It is inserted into the skin over the lower part of the forehead between the two eyebrows on either side of the midline, its fibers merging with those of the frontalis muscle.[2]
Nerve supply
The procerus muscle is supplied by the temporal branch of the facial nerve (VII).[3] It may also be supplied by other branches of the facial nerve, which can be varied,[3] including the lower zygomatic branches. A supply from its buccal branch has also been described.[4] Its contraction can produce transverse wrinkles.
Function
The procerus muscle helps to pull that part of the skin between the eyebrows downwards, which assists in flaring the nostrils. It can also contribute to an expression of anger.
Clinical significance
Procerus sign
Dystonia of the procerus muscle is involved in the procerus sign, which is indicative of progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP).[5]
Denervation
The procerus muscle may be denervated to reduce furrow lines around the glabella caused by frowning.[3] This may be for cosmetic purposes. Surgery can be used to transect the temporal branch of the facial nerve, although other branches of the facial nerve may also need to be cut.[3]
Additional images
-
Procerus muscle (red).
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ Hopkins, Claire (2016). "Chapter 33. Nose, nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses". in Standring, Susan. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (41st ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 9780702052309.
- ↑ "eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD 2009
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Caminer, D.M.; Newman, M.I.; Boyd, J.B. (April 2006). "Angular nerve: New insights on innervation of the corrugator supercilii and procerus muscles". Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery 59 (4): 366–372. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2005.09.011. PMID 16756251.
- ↑ "Nose, nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses" CHAPTER 32. Gray's Anatomy
- ↑ Batla, Amit; Nehru, Ravi; Vijay, Tarun (November 2010). "Vertical wrinkling of the forehead or Procerus sign in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy". Journal of the Neurological Sciences 298 (1–2): 148–149. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2010.08.010. PMID 20810128.
 |