Medicine:Wiggers diagram
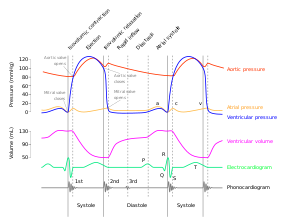
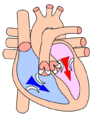
A Wiggers diagram, named after its developer, Carl Wiggers, is a unique diagram that has been used in teaching cardiac physiology for more than a century.[1][2] In the Wiggers diagram, the X-axis is used to plot time subdivided into the cardiac phases, while the Y-axis typically contains the following on a single grid:
- Blood pressure
- Aortic pressure
- Ventricular pressure
- Atrial pressure
- Ventricular volume
- Electrocardiogram
- Arterial flow (optional)
- Heart sounds (optional)
The Wiggers diagram clearly illustrates the coordinated variation of these values as the heart beats, assisting one in understanding the entire cardiac cycle.[1]
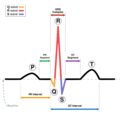
Events
| Phase | EKG | Heart sounds | Semilunar valves | Atrioventricular valves | |
| A | Atrial systole | P | S4* | closed | open |
| B | Ventricular systole – Isovolumetric/isovolumic contraction | QRS | S1 ("lub") | closed | closed |
| C1 | Ventricular systole – Ejection 1 | ST | open | closed | |
| C2 | Ventricular systole – Ejection 2 | T | open | closed | |
| D | Ventricular diastole – Isovolumetric/isovolumic relaxation | – | S2 ("dub") | closed | closed |
| E1 | Ventricular diastole – Ventricular filling 1 | – | S3* | closed | open |
| E2 | Ventricular diastole – Ventricular filling 2 | – | closed | open |
Note that during isovolumetric/isovolumic contraction and relaxation, all the heart valves are closed; at no time are all the heart valves open.[1] *S3 and S4 heart sounds are associated with pathologies and are not routinely heard.
Additional images
Wiggers diagram with mechanical (echo), electrical (ECG), and aortic pressure (catheter) waveforms, together with an in-ear dynamic pressure waveform measured using a novel infrasonic hemodynography technology, for a patient with severe aortic stenosis. Modified from [3]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Mitchell, Jamie R.; Wang, Jiun Jr (2014-06-01). "Expanding application of the Wiggers diagram to teach cardiovascular physiology". Advances in Physiology Education 38 (2): 170–175. doi:10.1152/advan.00123.2013. ISSN 1043-4046. PMID 24913453.
- ↑ Wiggers, Carl (1915). Circulation in Health and Disease. Philadelphia, PA: Lea & Febiger.
- ↑ Waldman, Carly E; Patel, Siddarth (16 November 2021). "Abstract 13654: Can a Novel Earbud Technology Detect Severe Aortic Stenosis? Modernizing the Wiggers Diagram Through Infrasonic Hemodynography Synchronized With Echocardiography and Cardiac Catheterization". Circulation (American Heart Association) 144 (Suppl_1): A13654–A13654. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/circ.144.suppl_1.13654.
 |