Physics:Boron nitride aerogel

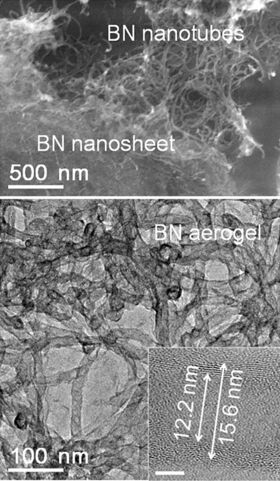
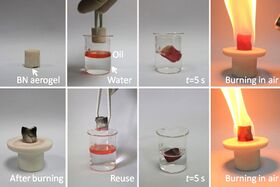
Boron nitride aerogel is an aerogel made of highly porous boron nitride (BN). It typically consists of a mixture of deformed boron nitride nanotubes and nanosheets. It can have a density as low as 0.6 mg/cm3 and a specific surface area as high as 1050 m2/g, and therefore has potential applications as an absorbent, catalyst support and gas storage medium. BN aerogels are highly hydrophobic and can absorb up to 160 times their mass in oil. They are resistant to oxidation in air at temperatures up to 1200 °C, and hence can be reused after the absorbed oil is burned out by flame. BN aerogels can be prepared by template-assisted chemical vapor deposition at a temperature ~900 °C using borazine as the feed gas.[1] Alternatively it can be produced by ball milling h-BN powder, ultrasonically dispersing it in water, and freeze-drying the dispersion.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Song, Yangxi; Li, Bin; Yang, Siwei; Ding, Guqiao; Zhang, Changrui; Xie, Xiaoming (2015). "Ultralight boron nitride aerogels via template-assisted chemical vapor deposition". Scientific Reports 5: 10337. doi:10.1038/srep10337. PMID 25976019. Bibcode: 2015NatSR...510337S.
- ↑ Lei, Weiwei; Mochalin, Vadym N.; Liu, Dan; Qin, Si; Gogotsi, Yury; Chen, Ying (2015). "Boron nitride colloidal solutions, ultralight aerogels and freestanding membranes through one-step exfoliation and functionalization". Nature Communications 6: 8849. doi:10.1038/ncomms9849. PMID 26611437. Bibcode: 2015NatCo...6.8849L.
 |

