Physics:End-to-end vector
From HandWiki
Short description: Vector that points from one end of a polymer to the other
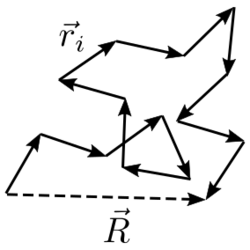
In the physical chemistry study of polymers, the end-to-end vector is the vector that points from one end of a polymer to the other end.
If each monomer unit in a polymer is represented by a point in space, the translation vectors connect between these points. The end-to-end vector is the sum of these translation vectors:
The norm of the end-to-end vector is called the end-to-end distance.
Relation to other quantities
The quadratic mean of the end-to-end distance can be related to the quadratic mean of the radius of gyration of a polymer by the relation:[1]
Notes
- ↑ Gedde, Ulf W. (1995). Polymer Physics. Springer. p. 21. ISBN 0-412-62640-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=Iem3fC7XdnkC.
See also
- Freely Jointed Chain
- Worm-like chain
 |
