Physics:Magnetovision
Magnetovision is the measuring technique enabling the visualization of magnetic field distribution in a given space.
Measuring setup
Magnetovision measuring stand consists of a magnetometer, X-Y or X-Y-Z movement mechanism and data processing and visualization system. Following modes of magnetovision signal acquisition are possible:
- magnetometer moves in the measurement area (e.g. over tested object)
- tested object moves against the magnetometer
- array of magnetic field sensors is used
Magnetometers
Typically, following types of sensors may be used:
- magnetoresistance effect based sensors[1]
- fluxgate magnetometers
- Hall effect sensors
- SQUIDs
Types
There are different modes of magnetovision measurements. Measurements may be performed in 2D (X-Y) or 3D (X-Y-Z). Moreover, measurements of magnetic field may be absolute, differential or gradiometric.
Applications
Magnetovision may be used for:
- nondestructive testing in civil engineering
- detection of dangerous metallic objects[1]
- archeology
Data fusion
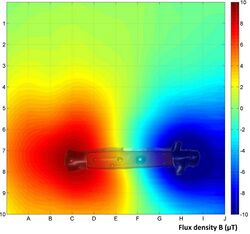
Magnetovision images may be used for data fusion with visual signal. This creates new possibility of presentation of magnetic field distribution for further analyses.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Nowicki, M.; Szewczyk, R. (2013). "Ferromagnetic Objects Magnetovision Detection System". Materials (MDPI) 6 (12): 5593–5601. doi:10.3390/ma6125593. PMID 28788410. Bibcode: 2013Mate....6.5593N.
 |
