Place:Hacienda San Antonio Tahdzibichén
Hacienda San Antonio Tahdzibichén | |
|---|---|
Private Event Venue | |
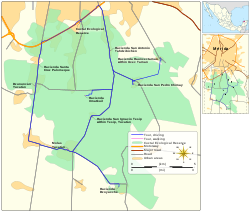
 Entrance Hacienda San Antonio Tahdzibichén, Yucatán. | |
 | |
| Coordinates: [ ⚑ ] : 20°53′06″N 89°35′52″W / 20.885°N 89.59778°W | |
| Country | Mexico |
| Mexican States | Yucatán |
| Municipalities | Mérida Municipality |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (CST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Postal code | 97316[1] |
| Area code | 999[2] |
Hacienda San Antonio Tahdzibichén (also known as Tahdzibichén) is located in the Mérida Municipality in the state of Yucatán in southeastern Mexico. It is one of the properties that arose during the nineteenth century henequen boom. It is part of the Cuxtal Ecological Reserve which was set aside in 1993 to protect both the man-made and natural history of the reserve area of Mérida.
Toponymy
The name (San Antonio Tahdzibichén) is a combination of Maya and Spanish terms. "San Antonio" is Spanish for the patron saint of the chapel and "Tahdzibichén" is from the Mayan language. It comes from the words "tah" meaning "very", "ts’ib or dzib" meaning "written" and "chen" which means "well", thus it means very well written.[3]
How to get there
The property is located 4.5 km south of Mérida on the Carretera Mérida–Timucuy.[4]
History
The Tahdzibichén estate was founded in 1873 as a henequen plantation and operated as a sisal production farm until the last decade.[5]
On 28 June 1993 the Cuxtal Ecological Reserve was designated to protect the history of the 7 large haciendas, their adjoining pueblas, 12 minor archaeological sites, 6 cenotes and one of Merida's important water supply stations.[6] Hacienda San Antonio Tahdzibichén was part of this historic designation.[7]
Within the reserve are the following protected haciendas:[7]
- Hacienda Hunxectamán in the village of Uxec Taman
- Hacienda San Antonio Tahdzibichén
- Hacienda San Ignacio Tesip in the village of Tesip
- Hacienda San Nicolás Dzoyaxché, contains Cenote Dzonot-Ich on its grounds[8]
- Hacienda San Pedro Chimay
- Hacienda Santa Cruz Palomeque
- Hacienda Xmatkuil
Currently the estate can be rented for private events, such as tours, photo sessions, weddings and fiestas.[4]
Architecture
The main house of the Hacienda San Antonio Tahdzibichén is unadorned, having 4 bedrooms, a hall, a living room and a dining area. No furniture remains, but there are pictures throughout the house of Pedro Infante who visited it often at the height of his fame. The power house and other working buildings of the farm are in ruins, but the gardens are extensive and have a citrus orchard.[5]
Demographics
All of the henequen plantations ceased to exist as autonomous communities with the agrarian land reform implemented by President Lazaro Cardenas in 1937. His decree turned the haciendas into collective ejidos, leaving only 150 hectares to the former landowners for use as private property.[9] Figures before 1937 indicate populations living on the farm. After 1937, figures indicate those living in the community, as the remaining Hacienda San Antonio Tahdzibichén houses only the owner's immediate family.
According to the 2005 census conducted by the INEGI, the population of the city was 678 inhabitants, of whom 338 were men and 340 were women.[10]
| Year | 1910 | 1921 | 1930 | 1940 | 1950 | 1960 | 1970 | 1980 | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | 230 | ? | 180 | 195 | 233 | 148 | 481 | 398 | 495 | 569 | 610 | 678 |
References
- ↑ "Consulta Códigos Postales". Correos de México. http://www.sepomex.gob.mx/ServiciosLinea/Paginas/ccpostales.aspx. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ↑ "Yucatan Mexico Telephone Area Codes". Travel Yucatan. http://www.travelyucatan.com/info-7a.htm. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ↑ "E" (in Spanish). Mérida, Mexico: Universidad Autónoma de Yucatán. http://www.mayas.uady.mx/diccionario/e_esp.html. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Hacienda San Antonio Tahdzibichén" (in Spanish). Mérida, Mexico: Gobierno del Estado de Yucatán. http://www.haciendasenyucatan.com/tahdzibichen/. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Haciendas » Tahdzibichén" (in Spanish). Mérida, Mexico: Gobierno del Estado de Yucatán. http://www.yucatan.gob.mx/menu/?id=tahdzibichen. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- ↑ Lougheed, Vivien (2009). Yucatan Chetumal, Merida, Campeche. Edison, N.J.: Hunter Publishing. p. 22. ISBN 978-1-588-43734-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=obJ1SBww48gC&pg=PT22. Retrieved 8 May 2015.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Reserva Ecologica Municipal Cuxtal". Mérida, Mexico: Municipal Government of Merida, Yucatán. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. https://web.archive.org/web/20150924021033/http://www.gcbo.org/html/cuxtal.pdf. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ "Haciendas » Dzoyaxché" (in Spanish). Mérida, Mexico: Gobierno del Estado de Yucatán. http://www.yucatan.gob.mx/menu/?id=dzoyaxche. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ Joseph, Gilbert Michael (1988). Revolution from without : Yucatán, Mexico, and the United States, 1880-1924 (Pbk. ed.). Durham: Duke University Press. p. 292. ISBN 0-8223-0822-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=YFS2oNvg1ygC&pg=PA297. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ↑ "Principales resultados por localidad (ITER)" (in Spanish). Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. 2010. http://www.inegi.org.mx/sistemas/consulta_resultados/iter2010.aspx?c=27329&s=est. Retrieved 30 April 2015.
Bibliography
- Bracamonte, P and Solís, R., Los espacios de autonomía maya, Ed. UADY, Mérida, 1997.
- Gobierno del Estado de Yucatán, "Los municipios de Yucatán", 1988.
- Kurjack, Edward y Silvia Garza, Atlas arqueológico del Estado de Yucatán, Ed. INAH, 1980.
- Patch, Robert, La formación de las estancias y haciendas en Yucatán durante la colonia, Ed. UADY, 1976.
- Peón Ancona, J. F., "Las antiguas haciendas de Yucatán", en Diario de Yucatán, Mérida, 1971.
Photo gallery