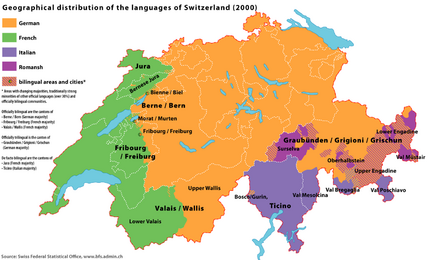
Place:Röstigraben
Röstigraben (German pronunciation: [ˈrøːstiˌɡraːbən]; literally "Rösti ditch" or "Rösti trench" also transcribed Röschtigraben to reflect the Swiss German pronunciation [ˈrøːʃtiˌɡrabə]) is a term used to refer to the cultural boundary between German-speaking and French-speaking parts of Switzerland , the latter known in French as the Suisse romande. There is also the term Polentagraben, referring to the boundary between German-speaking cantons, and the Italian-speaking canton of Ticino.[1]
The term first appeared during World War I, when neutral Switzerland stood between the warring German Empire and the French Republic.[citation needed]
Etymology
The first part of the term is derived from the Swiss German name for hashed potatoes, rösti, which originated in the canton of Bern and is considered typical of Swiss German cuisine.[2]
Graben has both the concrete and abstract meaning of "rift", with the Saane/Sarine river valley in the bilingual canton of Fribourg separating the linguistic areas. The Swiss-French use a similar expression: barrière de rös(ch)ti, literally "rösti barrier", or rideau de rös(ch)ti "rösti curtain" (reminiscent of the Iron Curtain). Just like Röstigraben it has become a familiar facetious expression used whenever differences arise, e.g. different voting results.
Definition
Geographically the line stretches from the Jura Mountains (canton of Jura and Bernese Jura) in the north along Lake Biel, Lake Neuchâtel and Lake Morat through the Swiss Plateau, then crosses the Swiss Alps and the Rhone valley, separating Lower and Upper Valais, and finally reaches the Italian border between the municipalities of Evolène and Zermatt. Folklorists lay emphasis on the importance of the parallel Brünig-Napf-Reuss line further in the east, separating the historic Alemannic (East) and Burgundian (West) spheres of influence.
By analogy, the term Polentagraben is used to refer to cultural and political differences between Italian-speaking Ticino and German-speaking Switzerland.[3] The canton of Ticino is seen as having a tougher stance towards migrant workers and a greater attachment to the notion of Swissness.[4]
See also
- Languages of Switzerland
- Culture of Switzerland
- Weißwurstäquator, which, similar to the Röstigraben, represents the Bavarian-German Kulturgrenze (Culture Border).
- Barassi Line
Notes
- ↑ Franciolli, Riccardo (12 April 2022). "In Svizzera i confini sono fatti di patate e polenta" (in it). https://www.tvsvizzera.it/tvs/qui-svizzera/in-svizzera-i-confini-sono-fatti-di-patate-e-polenta/47473910.
- ↑ "Rösti". Switzerland Tourism. http://www.myswitzerland.com/en/roesti.html. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ↑ Jankovsky, Peter. "Der Polentagraben lockt". NZZ.ch. http://www.nzz.ch/aktuell/tessin/der-polentagraben-lockt-1.18108822. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ↑ Bradley, Simon (6 October 2014). "The evolving Swiss identity: 1964-2014". swissinfo.ch. http://www.swissinfo.ch/eng/the-evolving-swiss-identity--1964-2014/40874250. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
Further reading
- Büchi Christophe: Röstigraben. Buchverlag NZZ. Zürich, 2001. ISBN:3-85823-940-2.
 |