Social:Garbary Street
Garbary street is located in the Okole district of Bydgoszcz city, Poland. Its development occurred during the second half of the 19th century and today it displays several buildings listed on the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship Heritage list, with a variety of architectural styles, from eclectic to early modernist. The area also nurtured a series of local successful factories, under the Prussian and the Polish periods.
Location
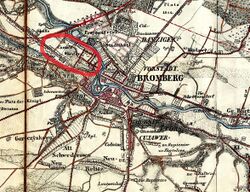
The street is located on an area between the Brda river and the Bydgoszcz Canal, laid on a ESE-WNW axis. It starts from the river bank and crosses a handful of other streets, among which Królowej Jadwigi Street.
History
The plot of land where the street lies was called canalswerder () in the 19th century, as mentioned on a 1857 Prussian map of Bromberg.
Indeed, the area was delimited by the Brda river bed on the north and the Bydgoszcz Canal on the south. Nowadays, the sector is even cut off in the north-west by a second section of the Bydgoszcz canal, built in the early 20th century.
The street is mentioned as early as the mid-19th century, as the address of the successful Buchholz tannery.[1] The rest of the building plots have been completed at the turn of the 20th century.
The street bore only two names through time:[2]
- 19th century - 1920 and during German occupation, Alfred straße;
- 1920 - 1939 and since 1945, Ulica Garbary.
The current appellation Garbary refers to the (Buchholz ) tannery, called garbarnia in Polish.
Main edifices
House at No.1
Today occupied by a modest house, the plot was owned at the end of the 19th century by the Prussian State Bank (German: Seehandlung)[3] and was offering guest rooms.
Former Buchholz's tannery at No.2/4
1877[4]
Registered on Kuyavian-Pomeranian Heritage list N°601293, A/1066 (18 April 1995)[5]
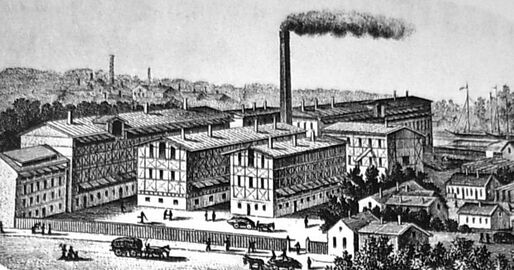
The Ludwig Buchholz's Tannery was a leather complex factory which operated from 1845 to 1992 in Bydgoszcz. The plot and the administrative building are now used by the Private University of Economy of Bydgoszcz (Polish: Wyższa Szkoła Gospodarki w Bydgoszczy).
Tenement at No.3
1880s,[4] Eclecticism
The plot has long been housing manufacturing industries: - in the 1880s, it was the property of Theodor Simons, an entrepreneur in the cigarette business.[6] In the 1900s, he ran there a local printing house, Bromberger Unparteiischen;[7] - in the 1910s, Simons's business was acquired by the company F. Eberhardt, producing cast iron and steam powered engines, located at Swiętej Trojcy street.[8] - during the interwar, Marian Dziatkiewicza set up in 1926 a production of photochemical plates, Alfa.[9] In 1934, the successful business produced a million square meters of photographic papers and 30,000 square meters of photographic plates.[10] The growing success of the company led to the moving of the expanding factories in the area of Piekna street in Bydgoszcz before WWII.
The building retains only its global shape, with a high corner wall gable, but it lacks any architectural motif.
Tenement at No.5
1950[4]
Initially owned by Theodor Simons's firm, the lot moved to the ownership of August Appelt in the late 1890s. He established there, then Albertstrasse 4, a shutter and roller blinds factory, Jalousie Fabrik.[3]
During Communist period, the area housed the production site No.5 of the state-owned enterprise of food industry (Polish: Przedsiębiorstwo Przemysłu Spożywczego) Jutrzenka, specialized in sweets and chocolates.[11] In 2014, the Polish company Colian which succeeded Jutrzenka after the fall of communism, announced that the lot will be transformed into a housing estate.[12]
Tenements at No.6/8
1937-1938,[4] Early modernism
In the end of the 19th century, the land at Albertstrasse 32/34 had been acquired by the tanning firm of Buchholz.[7] It remained the case until the early 1930s, when modernist buildings were erected in 1937-1938. These tenements were very popular at the time, as one can still notice today in downtwon Bydgoszcz (e.g.Kossowski's 20 Stycznia 1920 Street 41 or Ossoliński Alley 17 and 19 from Bolesław Polakiewicz).
The edifices kept their modern style entrance, the main door flanked by brick columns, covered by a square roof, with glazed brick surrounding the glass opening running through the stairs. Urban renovation planning included these tenements for 2019.[13]
Tenement at No.9
1894-1895,[4] Eclecticism
Earliest record of this building dates back to 1896, with the mention of the name of Friedrich Meyer, a builder, for landlord. However, he never lived there.[14]
Although damaged, the elevation still displays interesting motifs: cartouches, a large entrance door with a semi-circle transom light, pedimented windows on the first floor and a corbel table carrying the roof. The western frontage onto Królowej Jadwigi Street has been decorated with old style visual advertising, prequel to the future global overhaul of the edifice.[13]
ßrojahn tenement at No.12
1904-1905,[4] Neo-gothic
Registered on Kuyavian-Pomeranian Heritage list N°735495, A/1556 (26 March 2010)[5]
This corner building has been commissioned by Theodor ßrojahn, a master locksmith, who lived in the neighbouring Holzhostraße (today's Naruszewicza street).[15] He kept ownership of the tenement till 1920.
Gorgeously restored in 2018, this neo-gothic housing is teeming with architectural motifs and minute decoration, such as the corner bay window topped by an onion dome, the delicate framing of the openings, the pinnacles crowning the wall gable or the adorned main entry door.
House at No.14
1880s[16]
This old tenement has been first owned in the 1880s by a shoemaker, Martin Krusziński[16]
Tenement at Królowej Jadwigi Street 1, corner with Garbary street
1890s[5]
Eclecticism
Initially at Albertstraße 12, then Viktoria Straße 8, the tenement had been owned since 1878 by Gustav Modrakowski, a butcher,[17] living at Feldstraße 7 (today's Jackowskiego street).
The corner building displays eclectic features on both facades. On the ground floor, bossage and round top windows topped by young female mascarons. On Królowej Jadwigi Street, the main portal is flanked by columns. The first floor boasts pedimented openings, with balustrade. On the corner, a bay window stretches through two levels, supported by ornamented brackets. On the right end of Królowej Jadwigi Street's facade, a slight avant-corps is underlined by two tall Corinthian order columns.
Tenement at Królowej Jadwigi Street 2, corner with Garbary street
Registered on Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship Heritage list, N°601372 Reg.A/824 (May 30, 1994)[5]
1900-1901,[5] by Paul Böhm, Historicism
Paul Böhm, architect and designer of several buildings in Bydgoszcz (Słowackiego Street,3, Cieszkowskiego Street, 1&3, Józef Weyssenhoff Square, 5), also realized this corner edifice.[18] He did not live there, preferring his house at Danzigerstraße 61 (Gdańska Street 107, building is gone).
The house features picturesque settings, with medieval references. Material is a mix of brick and plaster, with a particular notice to the facade on Królowej Jadwigi Street, where several architectural pieces are to be underlined. The corner is highlighted by a tall bay window adorned with gothic-shaped windows, oeil-de-boeuf and stucoed motifs, topped by an octagonal tower capped by a crenellated conical roof. The frontage onto Jadwigi Street possesses another grand bay window with the same gothic-medieval allusions (e.g. the crow-stepped gable). In addition, the highest part displays in a medallion a figure of Tadeusz Kościuszko (by Piotr Triebler[19]); above the medallion, a statue of Queen Jadwiga stands in a niche, towering the whole street that bears her name.
Tenement at No.16
1906-1907,[4] Art Nouveau
Registered on Kuyavian-Pomeranian Heritage list N°727946, A/1535 (23 July 2009)[5]
This building had as first landlord Gottlob Götting, an ex-carpenter, then a rentier, who also owned other tenements in the same street (No.18, 28 and 30).[15]
The facade underwent a full overhaul in the late 2018, underlining Art Nouveau features and stuccoed motifs.
Tenement at No.17
1875-1900, Eclecticism
First recorded landlord was Johann Pfefferkorn, a teacher.[16]
Main elevation on the street displays an eclectic architectural style.
Götting tenement at No.18
1882,[4] Eclecticism
Gottlob Götting, a carpenter at the time, acquired this building in the 1880s, located then at ALbertstraße 23.[16] Later on, he commissioned or bought several tenements in the street (No.16, 28 and 30).
Main elevation on the street displays an eclectic architectural style, mirroring No.17's facade.
Tenement at No.19
1906-1907,[4] Art Nouveau
Julius Thiede, a butcher, is recorded as the first landlord of this building.[15] At the time, the address was Albertstraße 11.
The facade underwent a renovation in 2018, underlining Art Nouveau stuccoed motifs.
Viktor Petrikowski tenement at No.20
1903-1904,[4] Art Nouveau
Registered on Kuyavian-Pomeranian Heritage list N°601294, A/823/1-2 (25 May 1994)[5]
This building has been commissioned and designed by a local carpenter and construction entrepreneur, Viktor Petrikowski.[15] A year later, he built another tenement, at the corner of Zamoyskiego and 20 Stycznia 1920 Streets. He kept ownership of Garbary street's edifice until the end of WWI.[8]
Registered on the voivodship heritage list, the edifice is almost derelict. However, one can still appreciate various Art Nouveau features, from the decorated arched frame, to the vegetal-and-figure motifs, to the wattle and daub upper part of the elevation and dormers.
Wattle and daub gable
Tenements at No.26/28
1894 (No.28), 1906-1907 (No.26),[4] Eclecticism
Both tenements have been commissioned and managed by the city Housing Association (German: wohnungs verein).[20][14] Indeed, both edifices had on average 19 to 20 tenants.
Main frontages, restored in 2018-2019, exhibit a classical eclectic architectural style. No.28's facade, however, exposes more interesting features.
Tenement at No.27
1893,[21] Eclecticism
The building has been first owned by a painter, Hugo ßomrencke. Surprisingly enough, it is today famous for its mural, representing Marian Rejewski. The picture has been realized in 2018 by students from the UTP University of Sciences and Technology in Bydgoszcz (Polish: Uniwersytet Technologiczno-Przyrodniczy im. Jana i Jędrzeja Śniadeckich w Bydgoszczy, UTP).[22]
The main frontage, in need of a clean up, features eclectic style.
Tenement at No.29, corner with Jackowskiego street
1893,[4] Eclecticism
August Götting, a carpenter and a relative of No.16's owner, was the commissionner of this tenement, which he never inhabited.[21]
Both facades exhibit eclectic features: bossage, openings with pediments and corbel table on top.
Tenement at No.30, corner with Jackowskiego street
1906,[4] Eclecticism
Like No.29, the landlord of this tenement, Mr Junker, a merchant, never lived in his property.[20]
Very similar to No.29's elevation, No.30's displays a bay window on its corner, together with several additional levels and dormers on the top.
See also
- Ludwig Buchholz's tannery in Bydgoszcz
- Królowej Jadwigi Street in Bydgoszcz
- Marshal Ferdinand Foch Street in Bydgoszcz
- Bydgoszcz
References
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedcinq zero - ↑ Czachorowski, Antoni (1997). Atlas historyczny miast polskich. Tom II Kujawy. Zeszyt I Bydgoszcz. Toruń: Uniwersytet Mikołaja Kopernika.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten auf das Jahr 1895:auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1895. pp. 8.
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 Prezidenta Miasta Bydgoszczy (7 August 2015). Gminna Ewidencja Zabytków Miasta Bydgosky zarządzenie NR 439/2015. Bydgoszcz: Miast Bydgoszczy.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Załącznik do uchwały Nr XXXIV/601/13 Sejmiku Województwa Kujawsko-Pomorskiego z dnia 20 maja 2013 r.
- ↑ Wohnungs-Anzeiger nebst Adress- und Geschäfts-Handbuch für Bromberg und Umgebung : auf das Jahr 1885. Bromberg: Mittlersche Buchhandlung. 1885. pp. 111.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten auf das Jahr 1900 : auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1900. pp. 193, 291.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Adressbuch nebst Allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg mit Vororten für das Jahr 1915 : auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1915. pp. 71,264.
- ↑ Książka Adresowa Miasta Bydgoszczy : na rok 1933. Bydgoszcz: Władysław Weber. 1933. pp. 109.
- ↑ Brakowski, Konrad (1973). Bez fotografii ani rusz... Kalendarz Bydgoski. Bydgoszcz: Towarzystwo Miłośników Miasta Bydgoszczy. pp. 154–157.
- ↑ ml (8 February 2018). "Była fabryka słodyczy, będą mieszkania. Budzą duże emocje". bydgoszcz.wyborcza. http://bydgoszcz.wyborcza.pl/bydgoszcz/7,48722,22995850,byla-fabryka-slodyczy-beda-mieszkania-w-samym-centrum.html#Z_BoxLokBydLink.
- ↑ j (8 August 2017). "Na terenie Jutrzenki przy Garbarach będzie mieszkaniówka". bydgoszcz24. https://bydgoszcz24.pl/pl/11_wiadomosci/15950_na_terenie_jutrzenki_przy_garbarach_bedzie_mieszkaniowka.html.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Kamienice na ulicy Garbary w Bydgoszczy zyskają nowe elewacje". kujawskopomorskie.naszemiasto. 2 February 2018. http://kujawskopomorskie.naszemiasto.pl/artykul/kamienice-na-ulicy-garbary-w-bydgoszczy-zyskaja-nowe,4396742,art,t,id,tm.html.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten auf das Jahr 1896 : auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1896. pp. 8.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten auf das Jahr 1904: auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1904. pp. 149, 155, 205.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 Wohnungs-Anzeiger nebst Adress- und Geschäfts-Handbuch für Bromberg und Umgebung : auf das Jahr 1883. Bromberg: Mittlersche Buchhandlung. 1883. pp. III,85,147.
- ↑ Wohnungs-Anzeiger nebst Adress- und Geschäfts-Handbuch für Bromberg und Umgebung : auf das Jahr 1878. Bromberg: Mittler. 1878. pp. III,76, 96.
- ↑ "Straßen". Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten auf das Jahr 1902 : auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1902. p. 71.
- ↑ Szmańda, Edward (1981). Piotr Triebler. Kalendarz Bydgoski. Bydgoszcz: Towarzystwo Miłośników Miasta Bydgoszczy. p. 141.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten auf das Jahr 1906: auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1906. pp. 12,291.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Adressbuch nebst allgemeinem Geschäfts-Anzeiger von Bromberg und dessen Vororten auf das Jahr 1893: auf Grund amtlicher und privater Unterlagen. Bromberg: Dittmann. 1893. pp. 63,163.
- ↑ ml (6 August 2018). "Powstał drugi mural z Marianem Rejewskim. Gdzie go szukać?". bydgoszcz.wyborcza. http://bydgoszcz.wyborcza.pl/bydgoszcz/7,48722,23757659,powstal-drugi-mural-z-marianem-rejewskim-gdzie-go-szukac.html.
Bibliography
- (in Polish) Agnieszka Wysocka: Ul. Garbary 2 – dawna willa Buchholza. W: Bydgoszcz w stronę Okola. Bydgoszcz: Urząd Miasta Bydgoszczy – Rada Osiedla Okole, 2004. ISBN:83-921725-0-7.
- (in Polish) Agnieszka Wysocka: Ul. Garbary 2 – kominek w dawnej willi Buchholza. W: Bydgoszcz w stronę Okola. Bydgoszcz: Urząd Miasta Bydgoszczy – Rada Osiedla Okole, 2004. ISBN:83-921725-0-7.
- Brakowski, Konrad (1973) (in pl). Bez fotografii ani rusz... Kalendarz Bydgoski. Bydgoszcz: Towarzystwo Miłośników Miasta Bydgoszczy. pp. 154–157..
External links
[ ⚑ ] 53°07′39″N 17°59′29″E / 53.1275°N 17.99139°E
 |