Social:Orangism (Belgium)
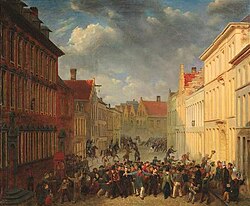
Orangism (Orangisme in French and Dutch) was a political tradition in Belgium that supported its reintegration into the short-lived United Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815–1830) under the rule of the Dutch House of Orange. It existed principally in the 1830s and 1840s.
After the secession of Belgium in the Belgian Revolution in 1830, Orangist sentiment in Flanders and Wallonia for a time sought a restoration of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. It was a movement directed by William I of the Netherlands as part of his "Volhardingspolitiek" and containing most of the Belgian elites (including members of the nobility and industrialists) and particularly concentrated in Ghent and Liège. Some of the most prominent Flemish Orangists were Jan Frans Willems and Hippolyte Metdepenningen. Although refusing to participate in parliamentary elections, as they deemed Belgian national institutions to be illegitimate, the Orangists did take part in local elections at the provincial and municipal levels, from which they militated against the new Belgian state through political actions and an activist press. At least three Orangist coups were foiled during the 1830s. Although losing Dutch financial and political support after the Treaty of London (1839) and William I's abdication (1840), the weakening Belgian Orangism survived well into the 1850s, strongly opposing the Belgian Revolution and rallying against independence.[1]
It was one inspiration for the later Greater Netherlands movement, although that movement was not all monarchist.
Known Belgian Orangists
Present day
- Louis Tobback (Socialist politician)[2]
- Siegfried Bracke (Flemish nationalist politician, former journalist)[3]
- Herman Balthazar (Historian, professor, former governor of East Flanders)[4]
- Geert van Istendael (Writer, poet, essayist)[5]
- Bob Cools (Socialist politician, former mayor of Antwerp)[6]
See also
- Orangism (Luxembourg)
- Orange-Nassau (disambiguation)
References
- ↑ Els Witte, Het verloren Koninkrijk, De Bezige Bij, Antwerp, 2014, p. 688
- ↑ "Oranje onder: Brandpunt bezoekt Louis Tobback, orangist en burgemeester van Leuven". besteburen.eu. http://www.besteburen.eu/nieuws/oranje-onder-brandpunt-bezoekt-louis-tobback-orangist-en-burgemeester-van-leuven.
- ↑ VANDERHAEGEN, door Kris. "Ik ben al jaren overtuigd Groot-Nederlander". http://www.nieuwsblad.be/cnt/nbna12072003_007.
- ↑ Soinne, Mikaël (1 March 2013). "Herman Balthazar: 'Ik droom soms nog dat ik een weelderige haardos heb'". http://intervista.be/2013/03/01/herman-balthazar-ik-droom-soms-nog-dat-ik-een-weelderige-haardos-heb/.
- ↑ "Achille [oude website: Mijn Nederland - Geert van Istendael"]. http://achillevandenbranden.blogspot.be/2010/03/mijn-nederland-geert-van-istendael.html.
- ↑ castelyns, Saskia. "Jammer dat de Nederlanden uiteenvielen". http://www.nieuwsblad.be/cnt/dmf20130426_00557973.
Further reading
- Witte, Els (2015). "De sociale samenstelling van het Belgisch orangisme: een verkenning (1828-1850)". Brood & Rozen 20 (3). doi:10.21825/br.v20i3.7940. https://openjournals.ugent.be/broodenrozen/article/id/64094/.
- Witte, Els (2014). Het verloren koninkrijk. Het harde verzet van de Belgische organisten tegen de revolutie, 1828-1850. Bezige Bij: Antwerpen. ISBN 9789460423062.
External links
 |
