Software:Axiom (computer algebra system)
| Developer(s) | Independent group of people |
|---|---|
| Stable release | |
| Preview release | Sourceforge master
/ February 6, 2022 |
| Repository | https://sourceforge.net/p/axiom/code/ |
| Written in | Lisp |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Type | Computer algebra system |
| License | Modified BSD License |
| Website | www |
Axiom is a free, general-purpose computer algebra system. It consists of an interpreter environment, a compiler and a library, which defines a strongly typed hierarchy.
History
Two computer algebra systems named Scratchpad were developed by IBM. The first one was started in 1965 by James Griesmer[2] at the request of Ralph Gomory, and written in Fortran.[3] The development of this software was stopped before any public release. The second Scratchpad, originally named Scratchpad II, was developed from 1977 on, at Thomas J. Watson Research Center, under the direction of Richard Dimick Jenks.[4]
The design is principally due to Richard D. Jenks (IBM Research), James H. Davenport (University of Bath), Barry M. Trager (IBM Research), David Y.Y. Yun (Southern Methodist University) and Victor S. Miller (IBM Research). Early consultants on the project were David Barton (University of California, Berkeley) and James W. Thatcher (IBM Research). Implementation included Robert Sutor (IBM Research), Scott C. Morrison (University of California, Berkeley), Christine J. Sundaresan (IBM Research), Timothy Daly (IBM Research), Patrizia Gianni (University of Pisa), Albrecht Fortenbacher (Universitaet Karlsruhe), Stephen M. Watt (IBM Research and University of Waterloo), Josh Cohen (Yale University), Michael Rothstein (Kent State University), Manuel Bronstein (IBM Research), Michael Monagan (Simon Fraser University), Jonathan Steinbach (IBM Research), William Burge (IBM Research), Jim Wen (IBM Research), William Sit (City College of New York), and Clifton Williamson (IBM Research)[5]
Scratchpad II was renamed Axiom when IBM decided, circa 1990, to make it a commercial product. A few years later, it was sold to NAG. In 2001, it was withdrawn from the market and re-released under the Modified BSD License. Since then, the project's lead developer has been Tim Daly.
In 2007, Axiom was forked twice, originating two different open-source projects: OpenAxiom[6] and FriCAS,[7] following "serious disagreement about project goals".[8] The Axiom project continued to be developed by Tim Daly.
The current research direction is "Proving Axiom Sane", that is, logical, rational, judicious, and sound.
Documentation
Axiom is a literate program.[9] The source code is becoming available in a set of volumes which are available on the axiom-developer.org website. These volumes contain the actual source code of the system.
The currently available documents are:
- Combined Table of Contents
- Volume 0: Axiom Jenks and Sutor—The main textbook
- Volume 1: Axiom Tutorial—A simple introduction
- Volume 2: Axiom Users Guide—Detailed examples of domain use (incomplete)
- Volume 3: Axiom Programmers Guide—Guided examples of program writing (incomplete)
- Volume 4: Axiom Developers Guide—Short essays on developer-specific topics (incomplete)
- Volume 5: Axiom Interpreter—Source code for Axiom interpreter (incomplete)
- Volume 6: Axiom Command—Source code for system commands and scripts (incomplete)
- Volume 7: Axiom Hyperdoc—Source code and explanation of X11 Hyperdoc help browser
- Volume 7.1 Axiom Hyperdoc Pages—Source code for Hyperdoc pages
- Volume 8: Axiom Graphics—Source code for X11 Graphics subsystem
- Volume 8.1 Axiom Gallery—A Gallery of Axiom images
- Volume 9: Axiom Compiler—Source code for Spad compiler (incomplete)
- Volume 10: Axiom Algebra Implementation—Essays on implementation issues (incomplete)
- Volume 10.1: Axiom Algebra Theory—Essays containing background theory
- Volume 10.2: Axiom Algebra Categories—Source code for Axiom categories
- Volume 10.3: Axiom Algebra Domains—Source code for Axiom domains
- Volume 10.4: Axiom Algebra Packages—Source code for Axiom packages
- Volume 10.5: Axiom Algebra Numerics—Source code for Axiom numerics
- Volume 11: Axiom Browser—Source pages for Axiom Firefox browser front end
- Volume 12: Axiom Crystal—Source code for Axiom Crystal front end (incomplete)
- Volume 13: Proving Axiom Correct—Prove Axiom Algebra (incomplete)
- Volume 15: The Axiom SANE Compiler
- Bibliography: Axiom Bibliography—Literature references
- Bug List: Axiom Bug List-Bug List
- Reference Card: Axiom Reference Card—Useful function summary
Videos
The Axiom project has a major focus on providing documentation. Recently the project announced the first in a series of instructional videos, which are also available on the axiom-developer.org[10] website. The first video[11] provides details on the Axiom information sources.[11]
Philosophy
The Axiom project focuses on the “30 Year Horizon”. The primary philosophy is that Axiom needs to develop several fundamental features in order to be useful to the next generation of computational mathematicians. Knuth's literate programming technique is used throughout the source code. Axiom plans to use proof technology to prove the correctness of the algorithms (such as Coq and ACL2).
Axiom uses Docker Containers as part of a continuous release process. The latest image is available on any platform using docker and the commands:
docker pull daly/axiom
docker run -i -t daly/axiom axiom
Design
In Axiom, each object has a type. Examples of types are mathematical structures (such as rings, fields, polynomials) as well as data structures from computer science (e.g., lists, trees, hash tables).
A function can take a type as argument, and its return value can also be a type. For example, Fraction is a function, that takes an IntegralDomain as argument, and returns the field of fractions of its argument. As another example, the ring of matrices with rational entries would be constructed as SquareMatrix(4, Fraction Integer). Of course, when working in this domain, 1 is interpreted as the identity matrix and A^-1 would give the inverse of the matrix A, if it exists.
Several operations can have the same name, and the types of both the arguments and the result are used to determine which operation is applied (cf. function overloading).
Axiom comes with an extension language called SPAD. All the mathematical knowledge of Axiom is written in this language. The interpreter accepts roughly the same language.
Features
Within the interpreter environment, Axiom uses type inference and a heuristic algorithm to make explicit type annotations mostly unnecessary.
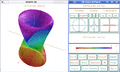
It features 'HyperDoc', an interactive browser-like help system, and can display two and three dimensional graphics, also providing interactive features like rotation and lighting. It also has a specialized interaction mode for Emacs, as well as a plugin for the TeXmacs editor.
-
HyperDoc displaying the available operations for a domain
-
Axiom displaying a surface
-
Axiom Firefox Browser Interface
-
Axiom simplifying a heat equation
-
Axiom matrix manipulation
-
Axiom computing a Risch integral
Axiom has an implementation of the Risch algorithm for elementary integration, which was done by Manuel Bronstein and Barry Trager. While this implementation can find most elementary antiderivatives and whether they exist, it does have some non-implemented branches, and raises an error when such cases are encountered during integration.[12][13]
See also
- A# programming language
- Aldor programming language
- List of computer algebra systems
References
- ↑ "daly/axiom Tags". https://hub.docker.com/r/daly/axiom/tags.
- ↑ Fitch, John (July 23, 2012). "James Griesmer 1929--2011". ACM Communications in Computer Algebra 46 (1/2): 10–11. doi:10.1145/2338496.2338499.
- ↑ "Axiom Computer Algebra System". http://axiom-developer.org/.
- ↑ "Richard D. Jenks Biographical Information". https://www.eecis.udel.edu/~caviness/jenks/jenksbio/.
- ↑ EUROCAL '85 | SpringerLink. https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783540159841.
- ↑ "OpenAxiom: The Open Scientific Computation Platform". http://www.open-axiom.org/.
- ↑ "FriCAS 18a5ef5d99c796a89efeac06df40043a85b3d44d — FriCAS". https://fricas.github.io/.
- ↑ "History — FriCAS". https://fricas.github.io/history.html.
- ↑ Why Literate Programming? at axiom-developer.org website
- ↑ "Axiom Computer Algebra System". http://www.axiom-developer.org/.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Axiom Computer Algebra System Information Sources". YouTube. November 30, 2008. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CV8y3UrpadY.
- ↑ Bronstein, Manuel (September 5, 2003). "Manuel Bronstein on Axiom's Integration Capabilities". https://groups.google.com/g/sci.math.symbolic/c/YXlaU8WA2JI/m/1w1MxrSpm6IJ.
- ↑ "integration - Does there exist a complete implementation of the Risch algorithm?" (in en). Oct 15, 2020. https://mathoverflow.net/questions/374089/does-there-exist-a-complete-implementation-of-the-risch-algorithm.
Further reading
- James H. Griesmer; Richard D. Jenks (1971). SCRATCHPAD/1: An interactive facility for symbolic mathematics | Proceedings of the second ACM symposium on Symbolic and algebraic manipulation (SYMSAC '71). pp. 42–58.
- James H. Griesmer; Richard D. Jenks (1972). Experience with an online symbolic mathematics system | Proceedings of the ONLINE72 Conference. 1. pp. 457–476.
- James H. Griesmer; Richard D. Jenks (1972). "Scratchpad". ACM SIGPLAN Notices 7 (10): 93–102. doi:10.1145/942576.807019.
- Richard D. Jenks (1974). "The SCRATCHPAD language". ACM SIGSAM Bulletin 8 (2): 20–30. doi:10.1145/1086830.1086834.
- Arthur C. Norman (1975). "Computing with Formal Power Series". ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 1 (4): 346–356. doi:10.1145/355656.355660. ISSN 0098-3500.
- Richard D. Jenks (1976). A pattern compiler | Proceedings of the third ACM symposium on Symbolic and algebraic manipulation (SYMSAC '76). pp. 60–65.
- E. Lueken (1977). Ueberlegungen zur Implementierung eines Formelmanipulationssystems (Masters thesis) (in Deutsch). Germany: Technischen Universitat Carolo-Wilhelmina zu Braunschweig.
- George E. Andrews (1984). Ramanujan and SCRATCHPAD | Proceedings of the 1984 MACSYMA Users' Conference. Schenectady: General Electric. pp. 383–408.
- James H. Davenport; P. Gianni; Richard D. Jenks; V. Miller; Scott Morrison; M. Rothstein; C. Sundaresan; Robert S. Sutor et al. (1984). Scratchpad.
- Richard D. Jenks (1984). "The New SCRATCHPAD Language and System for Computer Algebra". Proceedings of the 1984 MACSYMA Users' Conference: 409–416.
- Richard D. Jenks (1984). A primer: 11 keys to New Scratchpad | Proceedings of International Symposium on Symbolic and Algebraic Computation '84. Springer. pp. 123–147.
- Robert S. Sutor (1985). The Scratchpad II Computer Algebra Language and System | Proceedings of International Symposium on Symbolic and Algebraic Computation '85. Springer. pp. 32–33.
- Rüdiger Gebauer; H. Michael Möller (1986). Buchberger's algorithm and staggered linear bases | Proceedings of the fifth ACM symposium on Symbolic and algebraic computation (International Symposium on Symbolic and Algebraic Computation '86). ACM. pp. 218–221. ISBN 978-0-89791-199-3.
- Michael Lucks; Bruce W. Char (1986). A fast implementation of polynomial factorization | Proceedings of SYMSAC '86. ACM. pp. 228–232. ISBN 978-0-89791-199-3.
- J. Purtilo (1986). Applications of a software interconnection system in mathematical problem solving environments | Proceedings of SYMSAC '86. ACM. pp. 16–23. ISBN 978-0-89791-199-3.
- Robert S. Sutor; Richard D. Jenks (1987). "The type inference and coercion facilities in the scratchpad II interpreter". Papers of the Symposium on Interpreters and interpretive techniques - SIGPLAN '87. pp. 56–63. doi:10.1145/29650.29656. ISBN 978-0-89791-235-8.
- George E. Andrews (1988). R. Janssen. ed. Application of SCRATCHPAD to problems in special functions and combinatorics | Trends in Computer Algebra. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer. pp. 159–166.
- James H. Davenport; Yvon Siret; Evelyne Tournier (1993). Computer Algebra: Systems and Algorithms for Algebraic Computation. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0122042300.
- Rüdiger Gebauer; H. Michael Möller (1988). "On an installation of Buchberger's algorithm". Journal of Symbolic Computation 6 (2–3): 275–286. doi:10.1016/s0747-7171(88)80048-8. ISSN 0747-7171.
- Fritz Schwarz (1988). R. Janssen. ed. Programming with abstract data types: the symmetry package (SPDE) in Scratchpad | Trends in Computer Algebra. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer. pp. 167–176.
- David Shannon; Moss Sweedler (1988). "Using Gröbner bases to determine algebra membership, split surjective algebra homomorphisms determine birational equivalence". Journal of Symbolic Computation 6 (2–3): 267–273. doi:10.1016/s0747-7171(88)80047-6.
- Hans-J. Boehm (1989). "Type inference in the presence of type abstraction". ACM SIGPLAN Notices 24 (7): 192–206. doi:10.1145/74818.74835.
- Manuel Bronstein (1989). Simplification of real elementary functions | Proceedings of the International Symposium on Symbolic and Algebraic Computation (SIGSAM '89). ACM. pp. 207–211.
- Claire Dicrescenzo; Dominique Duval (1989). P. Gianni. ed. Algebraic extensions and algebraic closure in Scratchpad II | Symbolic and Algebraic Computation. Springer. pp. 440–446.
- Timothy Daly "Axiom -- Thirty Years of Lisp"
- Timothy Daly "Axiom" Invited Talk, Free Software Conference, Lyon, France, May, 2002
- Timothy Daly "Axiom" Invited Talk, Libre Software Meeting, Metz, France, July 9–12, 2003
External links
- Axiom Homepage
- Online sandbox to try Axiom
- Source code repositories: Github, SourceForge, GNU Savannah
- Jenks, R.D. and Sutor, R. "Axiom, The Scientific Computation System"
- Daly, T. "Axiom Volume 1: Tutorial"
Software forks:
 |