Software:Machine Identification Code
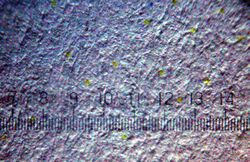
A Machine Identification Code (MIC), also known as printer steganography, yellow dots, tracking dots or secret dots, is a digital watermark which certain color laser printers and copiers leave on every printed page, allowing identification of the device which was used to print a document and giving clues to the originator. Developed by Xerox and Canon in the mid-1980s, its existence became public only in 2004. In 2018, scientists developed privacy software to anonymize prints in order to support whistleblowers publishing their work.[1][2][3]
History
In the mid-1980s Xerox pioneered an encoding mechanism for a unique number represented by tiny dots spread over the entire print area. Xerox developed this machine identification code (MIC) "to assuage fears that their color copiers could be used to counterfeit bills"[4] and received U.S. Patent No 5515451 describing the use of the yellow dots to identify the source of a copied or printed document.[5][6]
The public first became aware of MIC in October 2004, when it was used by Dutch authorities to track counterfeiters who had used a Canon color laser printer.[7] In November 2004, PC World reported the machine identification code had been used for decades in some printers, allowing law enforcement to identify and track counterfeiters.[4] The Central Bank Counterfeit Deterrence Group (CBCDG) has denied that it developed the feature.[5]

In 2005, the civil rights group Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) encouraged the public to send in sample printouts and subsequently decoded the pattern.[8] The pattern has been demonstrated on a wide range of printers from different manufacturers and models.[9] The EFF stated in 2015 that the documents that they previously received through the FOIA[10] suggested that all major manufacturers of color laser printers entered a secret agreement with governments to ensure that the output of those printers is forensically traceable.[11]
In 2007, the European Parliament was asked about the question of invasion of privacy.[12][5]
Technical aspects

The pattern consists of a dot-matrix spread of yellow dots, which can barely be seen with the naked eye. The dots have a diameter of a tenth of a millimeter (0.004") and a spacing of about one millimeter (0.039"). Their arrangement encodes the serial number of the device, date and time of the printing, and is repeated several times across the printing area in case of errors. For example, if the code consists of 8 × 16 dots in a square or hexagonal pattern, it spreads over a surface of about 4 square centimetres (0.62 sq in) and appears on a sheet of size A4 paper about 150 times. Thus, it can be analyzed even if only fragments or excerpts are available. Some printers arrange yellow dots in seemingly random point clouds.
According to the Chaos Computer Club in 2005, color printers leave the code in a matrix of 32 × 16 dots and thus can store 64 bytes of data (64×8).[13]
As of 2011[update], Xerox was one of the few manufacturers to draw attention to the marked pages, stating in a product description, "The digital color printing system is equipped with an anti-counterfeit identification and banknote recognition system according to the requirements of numerous governments. Each copy shall be marked with a label which, if necessary, allows identification of the printing system with which it was created. This code is not visible under normal conditions."[14]
In 2018, scientists at the TU Dresden analyzed the patterns of 106 printer models from 18 manufacturers and found four different encoding schemes.[2]
Visibility

The Machine Identification Code can be made visible by printing or copying a page and subsequently scanning a small section with a high-resolution scanner. The yellow color channel can then be enhanced with an image processing program, to make any dots of the MIC clearly visible. Under good lighting conditions, a magnifying glass may be enough to see the pattern. Under UV-light the yellow dots are clearly recognizable.[15]

Using this steganographic process, high-quality copies of an original (e.g. a bank note) under blue light can be made identifiable. Using this process, even shredded prints can be identified: the 2011 "Shredder Challenge" initiated by the DARPA was solved by a team called "All Your Shreds Are Belong To U.S." consisting of Otavio Good and two colleagues.[16][17]
Practical application
Both journalists and security experts have suggested that The Intercept's handling of the leaks by whistleblower Reality Winner, which included publishing secret NSA documents unredacted and including the printer tracking dots, was used to identify Winner as the leaker, leading to her arrest in 2017 and conviction.[18][19]
Protection of privacy and circumvention
Copies or printouts of documents with confidential personal information, for example health care information, account statements, tax declaration or balance sheets, can be traced to the owner of the printer and the inception date of the documents can be revealed. This traceability is unknown to many users and inaccessible, as manufacturers do not publicize the code that produces these patterns. It is unclear which data may be unintentionally passed on with a copy or printout. In particular, there are no mentions of the technique in the support materials of most affected printers. In 2005 the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) sought a decoding method and made available a Python script for analysis.[20]
In 2018, scientists from TU Dresden developed and published a tool to extract and analyze the steganographic codes of a given color printer and subsequently to anonymize prints from that printer. The anonymization works by printing additional yellow dots on top of the Machine Identification Code.[1][2][3] The scientists made the software available to support whistleblowers in their efforts to publicize grievances.[21]
Comparable processes
Other methods of identification are not as easily recognizable as yellow dots. For example, a modulation of laser intensity and a variation of shades of grey in texts are already feasible. As of 2006[update], it was unknown whether manufacturers were also using these techniques.[22]
See also
- EURion constellation, a dot matrix spread over a bank note, which stops some printers and color copiers from processing
- Taggant § Explosive taggants
- Typewriter § Forensic examination
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 DEDA - tracking Dots Extraction, Decoding and Anonymisation toolkit: on GitHub
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Richter, Timo; Escher, Stephan; Schönfeld, Dagmar; Strufe, Thorsten (2018-06-14). "Forensic Analysis and Anonymisation of Printed Documents". Proceedings of the 6th ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security. ACM. pp. 127–138. doi:10.1145/3206004.3206019. ISBN 9781450356251. https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3206004.3206019.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Dresdner Forscher überlisten Tracking-Punkte bei Laserdruckern" (in de-DE). 25 June 2018. https://www.heise.de/newsticker/meldung/Dresdner-Forscher-ueberlisten-Tracking-Punkte-bei-Laserdruckern-4090876.html.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Tuohey, Jason (22 November 2004). "Government Uses Color Laser Printer Technology to Track Documents". PC World. https://www.pcworld.com/article/118664/article.html.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Escher, Stephan (28 June 2018). "Tracking Dots unlesbar machen: Interview mit Uli Blumenthal" (in de). Deutschlandfunk. https://www.deutschlandfunk.de/farblaserdrucker-tracking-dots-unlesbar-machen.676.de.html?dram:article_id=421558.
- ↑ , Masato; Masao Seki & Svay Leng et al."Image processing system for selectively reproducing documents" patent US5515451A, issued 1996-05-07
- ↑ de Vries, Wilbert (26 October 2004). "Dutch track counterfeits via printer serial numbers". PC World. https://www.pcworld.idg.com.au/article/8305/dutch_track_counterfeits_via_printer_serial_numbers/.
- ↑ "DocuColor Tracking Dot Decoding Guide" (in en). 2005. https://w2.eff.org/Privacy/printers/docucolor/.
- ↑ "Electronic Frontier Foundation". https://w2.eff.org/Privacy/printers/list.php.
- ↑ Lee, Robert (2005-07-27). "Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) request" (PDF). Letter to Latita M. Huff. Electronic Frontier Foundation. Retrieved 2016-11-07.
- ↑ "List of Printers Which Do or Do Not Display Tracking Dots". September 20, 2007. https://www.eff.org/pages/list-printers-which-do-or-do-not-display-tracking-dots.
- ↑ "Tracking codes in photocopiers and colour laser printers". Parliamentary questions (European Parliament). 20 November 2007. http://www.europarl.europa.eu/sides/getDoc.do?reference=E-2007-5724&language=EN.
- ↑ Frank Rosengart (2005). "Datenspur Papier". Die Datenschleuder, Das wissenschaftliche Fachblatt für Datenreisende. Hamburg: Chaos Computer Club. 19–21. https://chaosradio.ccc.de/media/ds/ds086.pdf. Retrieved 2011-02-27.
- ↑ "Abschnitt „Technische Daten des Digitalen Farbdrucksystems Xerox DocuColor 6060"". Xerox DocuColor® 6060 Digitales Farbdrucksystem (Prospectus). Neuss: Xerox GmbH. pp. 8. https://www.xerox.com/downloads/deu/de/7/708P86985DED.pdf. Retrieved 2011-02-27.
- ↑ "Beitrag bei Druckerchannel: Big Brother is watching you: Code bei Farblasern entschlüsselt". Druckerchannel.de. October 26, 2005. https://www.druckerchannel.de/artikel.php?ID=1239.
- ↑ "CONGRATULATIONS to "All Your Shreds Are Belong To U.S."!". 2011-11-21. http://archive.darpa.mil/shredderchallenge/.
- ↑ "Tip for Bad Guys: Burn, Don't Shred". 2011-12-15. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2011-12-15/tip-for-bad-guys-burn-dont-shred.
- ↑ Anderson, L.V. (June 6, 2017). "Did The Intercept Betray Its NSA Source With Sloppy Reporting?". Digg. https://digg.com/2017/did-intercept-burn-reality-winner.
- ↑ Wemple, Erik (June 6, 2017). "Did the Intercept bungle the NSA leak?". The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/erik-wemple/wp/2017/06/06/did-the-intercept-bungle-nsa-leak/.
- ↑ "docucolor.cgi - CGI script to interpret Xerox DocuColor forensic dot pattern". 2005. https://w2.eff.org/Privacy/printers/docucolor/docucolor.cgi.
- ↑ "So verpfeift dich dein Drucker nicht" (in de). Deutschlandfunk Nova. 26 June 2018. https://www.deutschlandfunknova.de/nachrichten/it-sicherheit-so-verpfeift-dich-dein-drucker-nicht.
- ↑ Printer Characterization and Signature Embedding for Security and Forensic Applications Pei-Ju Chiang, Aravind K. Mikkilineni, Sungjoo Suh, Jan P. Allebach, George T.-C. Chiu, Edward J. Delp., Purdue University, 2006 (poster)
External links
- Laudatio der deutschen BigBrotherAwards 2004 Script error: The function "in_lang" does not exist.
- Information by the Chaos Computer Club
- Information by the Electronic Frontier Foundation
- EFF list of printers, which do or don't print dots (last updated 2017)
