Software:Xpra
| Original author(s) | Nathaniel Smith |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Nathaniel Smith, Antoine Martin |
| Initial release | February 20, 2008 |
| Stable release | 4.4.6[1]
/ June 20, 2023 |
| Written in | Python |
| Operating system | Unix-like, MS Windows, Mac OS X |
| Available in | English |
| License | GPL-2.0-or-later |
| Website | xpra |
xpra, abbreviated from X Persistent Remote Applications, is a set of software utilities that run X clients, typically on a remote host, and direct their display to the local machine without the X clients closing or losing any state in case the network connection between the local machine and the remote host is lost.[2]
Xpra differs from standard X forwarding primarily in allowing disconnection and reconnection without disrupting the forwarded application.[3] It also differs from VNC and similar remote display technologies in being rootless, so applications forwarded by Xpra appear on the local desktop as normal windows managed by the local window manager, rather than being all "trapped in a box together". Xpra also uses a custom protocol that is self-tuning and relatively latency-insensitive, and thus is usable over worse links than standard X.[citation needed]
The original inspiration for making Xpra came from the original author's experience of attempting to use various setups based on NX technology.[4]
Operation
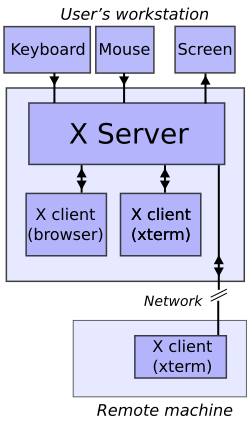
Xpra connects as a compositing window manager to an Xvfb display server. However, instead of combining the window images to present on the screen, it directs the window images into a network connection to the Xpra client, where they are displayed on the remote screen. The Xpra server also supports direct attachment, which makes it behave as a persistent application server, for example in the case where there is only an X server available at the remote end.
Xpra also acts as a window manager for the X server it is running against, but it does not actually have any window manager policy built into it. Instead, it takes all the window management requests from the applications, sends them over the wire to the client, which then issues those same requests on the real display, waits for further answer the real window manager gives, and then forwards that answer back to the Xpra server. In addition to the normal Xpra client, it also supports using an HTML 5 capable web browser as a client.[5]
See also
- GNU Screen and tmux – terminal multiplexers for console (terminal) applications
- xmove – a tool that allows moving programs between X Window System displays
- Low Bandwidth X – a protocol to use X over network links with low bandwidth and high latency
References
- ↑ Martin, Antoine (20 June 2023). "[winswitch] [ANNOUNCE] Xpra 4.4.6: a few minor client-side issues". shifter-users@lists.devloop.org.uk (Mailing list). Retrieved 28 July 2023.
- ↑ Michael Larabel (2013-08-19). "XPRA: Persistent Remote Applications On X". Phoronix. https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTQzOTk.
- ↑ "Xpra - ArchWiki". https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/Xpra.
- ↑ Smith, Nathaniel (2009-07-25). "Comment #343389". Google releases Neatx NX server. LWN. https://lwn.net/Articles/343389/. "... I was so frustrated that I wrote a competitor, 'xpra'."
- ↑ Williams, Al (31 March 2017). "Linux-Fu: Applications on the web". https://hackaday.com/2017/03/31/linux-fu-applications-on-the-web/.
External links
 |

