TILE64
| General Info | |
|---|---|
| Launched | 2007 |
| Common manufacturer(s) | |
| Performance | |
| Max. CPU clock rate | 600 MHz to 900 MHz |
| Architecture and classification | |
| Min. feature size | 45 nm to 90 nm |
| Physical specifications | |
| Cores |
|
| History | |
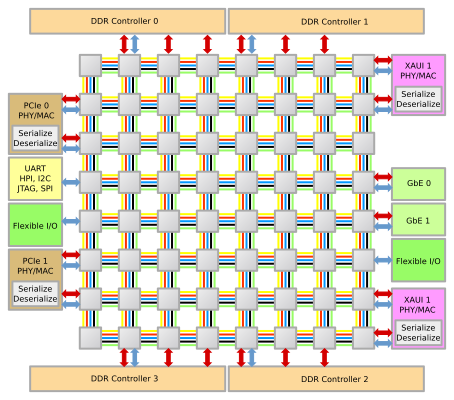
TILE64[1] is a VLIW ISA multicore processor manufactured by Tilera. It consists of a mesh network of 64 "tiles", where each tile houses a general purpose processor, cache, and a non-blocking router, which the tile uses to communicate with the other tiles on the processor.
The short-pipeline, in-order, three-issue cores implement a MIPS-inspired[2] VLIW instruction set. Each core has a register file and three functional units: two integer arithmetic logic units and a load–store unit. Each of the cores ("tile") has its own L1 and L2 caches plus an overall virtual L3 cache which is an aggregate of all the L2 caches.[3] A core is able to run a full operating system on its own or multiple cores can be used to run a symmetrical multi-processing operating system.
TILE64 has four DDR2 controllers, two 10-gigabit Ethernet interfaces, two four-lane PCIe interfaces, and a "flexible" input/output interface, which can be software-configured to handle a number of protocols. The processor is fabricated using a 90 nm process and runs at speeds of 600 to 900 MHz.
According to CTO and co-founder Anant Agarwal, Tilera will target the chip at networking equipment and digital video markets where the demands for computing processing are high.[4]
Support for the TILE64 architecture was added to Linux kernel version 2.6.36[5] but was dropped in kernel version 4.16.[6] A non-official LLVM back-end for Tilera exists.[7]
References
- ↑ Keckler, Stephen W.; Olukotun, Kunle; Peter Hofstee, H. (August 29, 2009). Multicore Processors and Systems - Google Books. ISBN 9781441902634. https://books.google.com/books?id=aLaRfJq-59sC&q=Tilera+TILE+isa+vliw&pg=PA29.
- ↑ "Compiler construction - What instruction set is used by Tilera microprocessors?". https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6515358/what-instruction-set-is-used-by-tilera-microprocessors.
- ↑ Kingman, Henry (August 20, 2007). "Massively multicore processor runs Linux". linuxdevices.com. Archived from the original on September 6, 2012. https://archive.today/20120906054352/http://www.linuxfordevices.com/c/a/News/Massively-multicore-processor-runs-Linux/.
- ↑ Boslet, Mark (August 20, 2007). "Start-up Tilera to Unveil 64-core chip". San Jose Mercury News. http://origin.mercurynews.com/businessheadlines/ci_6668379.
- ↑ "Tilera architecture support". Kernel Newbies. October 20, 2010. http://kernelnewbies.org/Linux_2_6_36#head-3f060090317e345261a208f3ed5a3d639a71bbcb.
- ↑ Simon Sharwood (3 April 2018). "Linux 4.16 arrives, erases eight CPUs and keeps melting Meltdown". theregister.co.uk (Situation Publishing). Archived from the original on 3 April 2018. https://web.archive.org/web/20180403102729/https://www.theregister.co.uk/2018/04/03/linux_4_16_released/. Retrieved 3 April 2018.
- ↑ Tilera TILE64 Back-End For LLVM Published // Phoronix, September 6, 2012
External links
 |