Token-based replay
Token-based replay technique is a conformance checking algorithm [1] that checks how well a process conforms with its model by replaying each trace on the model (in Petri net notation ).[2] Using the four counters produced tokens, consumed tokens, missing tokens, and remaining tokens, it records the situations where a transition is forced to fire and the remaining tokens after the replay ends. Based on the count at each counter, we can compute the fitness value between the trace and the model.
The algorithm [2]
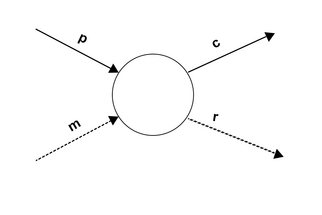
The token-replay technique uses four counters to keep track of a trace during the replaying:
- p: Produced tokens
- c: Consumed tokens
- m: Missing tokens (consumed while not there)
- r: Remaining tokens (produced but not consumed)
Invariants:
- At any time:
- At the end:
At the beginning, a token is produced for the source place (p = 1) and at the end, a token is consumed from the sink place (c' = c + 1). When the replay ends, the fitness value can be computed as follows:
Example
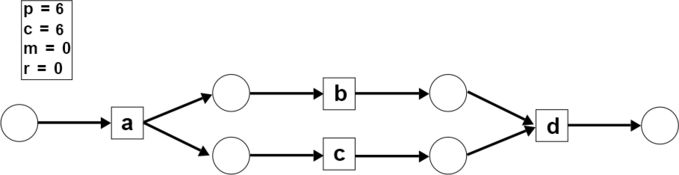
Suppose there is a process model in Petri net notation as follows:
Example 1: Replay the trace (a, b, c, d) on the model M
- Step 1: A token is initiated. There is one produced token ().
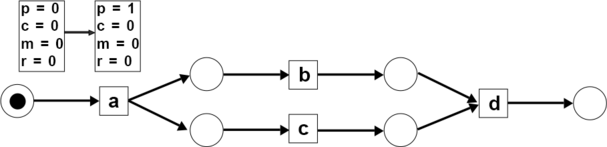
- Step 2: The activity consumes 1 token to be fired and produces 2 tokens ( and ).
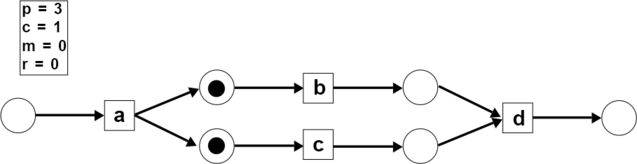
- Step 3: The activity consumes 1 token and produces 1 token ( and ).
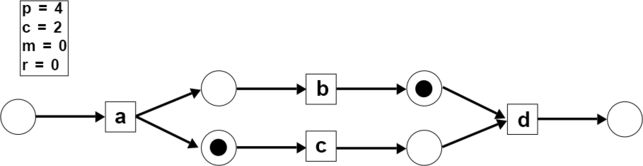
- Step 4: The activity consumes 1 token and produces 1 token ( and ).
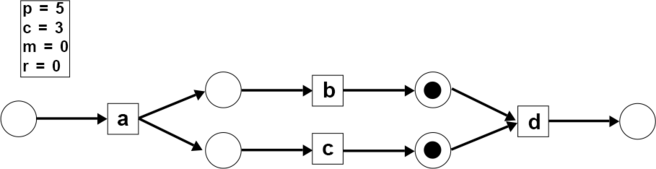
- Step 5: The activity consumes 2 tokens and produces 1 token (, ).
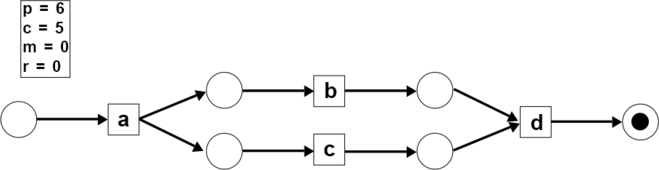
The fitness of the trace () on the model is:
Example 2: Replay the trace (a, b, d) on the model M
- Step 1: A token is initiated. There is one produced token ().

- Step 2: The activity consumes 1 token to be fired and produces 2 tokens ( and ).

- Step 3: The activity consumes 1 token and produces 1 token ( and ).

- Step 4: The activity needs to be fired but there are not enough tokens. One artificial token was produced and the missing token counter is increased by one (). The artificial token and the token at place are consumed () and one token is produced at place end ().
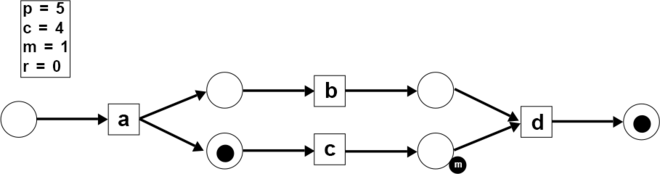
- Step 5: The token in the end place is consumed (). The trace is complete. There is one remaining token at place ().
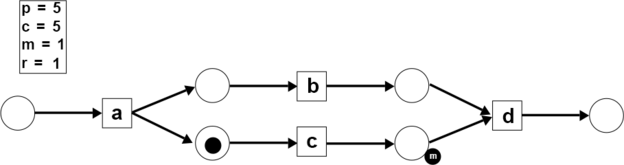
The fitness of the trace () on the model is:
References
- ↑ van der Aalst, Wil (2016), van der Aalst, Wil, ed., "Data Science in Action" (in en), Process Mining: Data Science in Action (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer): pp. 3–23, doi:10.1007/978-3-662-49851-4_1, ISBN 978-3-662-49851-4, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49851-4_1, retrieved 2021-11-16
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Rozinat, A.; van der Aalst, W.M.P. (March 2008). "Conformance checking of processes based on monitoring real behavior". Information Systems 33 (1): 64–95. doi:10.1016/j.is.2007.07.001. ISSN 0306-4379. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.is.2007.07.001.
 |