Engineering:Meteoroid Technology Satellite
From HandWiki
Revision as of 01:40, 11 July 2022 by imported>NBrush (simplify)
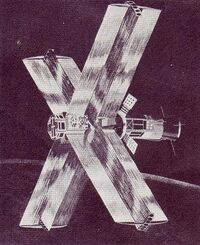 Design of MTS. | |
| Mission type | Research of meteoroids |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA[1] |
| COSPAR ID | 1972-061A[2] |
| SATCAT no. | 6142[3] |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | Langley Research Center |
| Launch mass | 90 kg (200 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 13 August 1972, 15:10 UTC[4] |
| Rocket | Scout D-1 S184C[4] |
| Launch site | Wallops LA-3A[4] |
| End of mission | |
| Decay date | 2 November 1979[3] |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Eccentricity | 0.02259[2] |
| Perigee altitude | 496 km (308 mi)[2] |
| Apogee altitude | 814 km (506 mi)[2] |
| Inclination | 37.7°[2] |
| Period | 97.80 minutes[2] |
| Epoch | 14 November 1971[2] |
Explorers | |
Meteoroid Technology Satellite (also called as MTS or Explorer 46) was a NASA satellite launched as part of Explorers program.[5] MTS was launched on August 13, 1972 on Wallops Flight Facility, with a Scout-D rocket. The objectives of the MTS were to measure the meteoroid penetration rates in the bumper-protected target, and to obtain data on meteoroid velocity and flux distribution. The central hub of the satellite was 3.20 metres (10.5 ft) long and carried the velocity and impact experiments. Bumper targets extended from the satellite, giving it an overall width of 7.015 metres (23.02 ft).[2]
MTS reentered in the atmosphere on November 2, 1979.[3]
Instruments
- Multi-sheet bumper, 7 metres (23 ft) across, its detectors filled with gas, to register and telemeter loss of pressure;
- 12 box-shaped velocity detectors at various locations along the spacecraft;
- Impact flux detectors, with 64 detectors to assess the population of very small particles.[2]
References
- ↑ "Explorer 46/MTC". Space Encyclopedia. Claude Lafleur. 2010. http://claudelafleur.qc.ca/Spacecrafts-1972.html#Explorer-46. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 "Meteoroid Technology Satellite". NSSDC Master Catalog. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=1972-061A. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "EXPLORER 46 (MTS)". n2yo.com. 2011. http://www.n2yo.com/satellite/?s=6142. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 McDowell, Jonathan. "Launch Log". Jonathan's Space Page. http://www.planet4589.org/space/log/launchlog.txt. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- ↑ "Letter dated 27 October 1972 from the Permanent Representative of the United States of America to the United Nations addressed to the Secretary-General". (72-22115). UNOOSA. 1972-11-08. http://www.unoosa.org/oosa/download.do?file_uid=865. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
External links
- Satellite, Explorer 46: Meteoroid Technology Satellite, Backup. Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum


