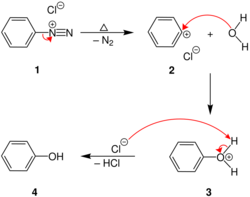
Chemistry:Conversion of diazonium salt to phenol
The thermal decomposition of aryl diazonium salts in aqueous solutions occurs over the time and can be accelerated upon heating.[1] This can occur as an unwanted side reaction leaving phenol as side product(s);[2] or be utilized as a shortcut in Organic Chemistry, for the synthesis of phenols.[3]
Reaction Summary
Primary aryl amines react with Sodium nitrite in acid solution and let to boil. [3] This converts the produced diazonium salt to phenol. To sum up, a convenient conversion of amine to phenol via diazotization.
Mechanism
This thermal decomposition starts with the elimination diazonium group in the form of nitrogen gas that leaves the aromatic moiety as a cation, that is extremely reactive. The produced aryl cation reacts with water and yields the corresponding phenol. Therefore, arylamines can be simply converted to phenols via diazotization and boiling their solution.[3] This has been utilized for the preparation dihydroxyl carrying analogues of the Tröger’s base. [3]
References
- ↑ Carey, F. A.; Sundberg, R. J. (2007). Advanced Organic Chemistry. Vol. B, Chapter 11: Springer. pp. 1028.
- ↑ Khazaei, A.; et. al., (2013). "Diazonium to phenol". J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 129: 3439. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.39069.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "Facile Preparation of Phenol". Synlett 28: 1641. 2017. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1588180.