Earth:Fried Egg structure
| Impact crater/structure | |
|---|---|
| Confidence | Potential[1] |
| Diameter | 3 km (1.9 mi) |
| Depth | 110 m (360 ft) |
| Rise | 300 m (980 ft) |
| Age | <17 Ma Neogene |
| Exposed | No |
| Drilled | No |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] : 36°48′N 26°30′W / 36.8°N 26.5°W[1] |
| Country | Portugal |
| State | Azores |
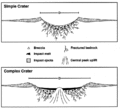
The Fried Egg is an informal name for an underwater geomorphic structure in the North Atlantic that is a suspected impact crater. This structure is at a depth of 2 kilometres (1.2 miles) and is about 150 km (93 mi) south of the Azores archipelago.[2] It consists of a dome 300 meters (980 feet) high and 3 km (1.9 mi) in diameter that lies within a larger and roughly circular depression 110 m (360 ft) deep and 6 km (3.7 mi) in diameter. It is this morphology on which its informal name is based.[3] Images that accompany media reports show the presence of a well-defined rim that surrounds the depression. These images also show a second but smaller circular depression, which also has a central peak, lying adjacent to the Fried Egg structure.[2][4]
This structure is less than 17 million years old as constrained by the age of the ocean floor of which it is a part. Based on its morphology and the absence of any obvious lava flows that can be seen in the multibeam echosounder bathymetric data, it is hypothesized that this structure is a possible oceanic impact crater.[3]
It was reported that the Fried Egg structure was first identified using data acquired during a 2008 multibeam echosounder hydrographic survey. Its presence was confirmed during a research cruise from September to November 2009. In addition, gravity and magnetic data were also acquired during the September 2009 research cruise and that a third expedition using remotely operated underwater vehicles to gather samples from this structure was planned.[2]
See also
- Earth:Eltanin impact – Prehistoric asteroid impact in southeast Pacific Ocean
- Earth:List of possible impact structures on Earth – None
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mikheeva, 2017
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Amos, J (18 December 2009). "'Fried Egg' may be impact crater". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/sci/tech/8400264.stm.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Dias et al., 2009
- ↑ "Fried Egg" 1 & 2 location
Bibliography
- Dias, F.C.; Lourenco, N.; Lobo, A.; Santos de Campos, A.; Pinto de Abreu, M. (2009). ""Fried Egg": An Oceanic Impact Crater in the Mid-Atlantic?". American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting: P43B. Bibcode: 2009AGUFM.P43B1435D.
- Mikheeva, Anna (2017). The Complete Catalog of the Earth's Impact structures. Russian Academy of Sciences. pp. 1. http://labmpg.sscc.ru/impact/index1.html. Retrieved 2019-03-14.