Chemistry:Yariv reagent
From HandWiki
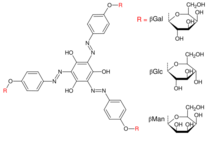 Yariv reagent. Three example R groups shown: β-D-Galactose (βGal), β-D-Glucose (βGlc), β-D-Mannose (βMan).
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C42H48N6O21 | |
| Molar mass | 972.867 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Yariv reagent (1,3,5-tri(p-glycosyloxyphenylazo)-2,4,6-trihydroxybenzene) is a glycosylated phenolic compound that binds strongly to galactans and arabinogalactan proteins.[1][2][3] It can therefore be used in their detection, quantification, precipitation, isolation, staining, and interfere with their function.[3][4] It was initially synthesised in 1962 as an antigen for carbohydrate-binding antibodies but has subsequently become more broadly used.[1][5] There are many variants of Yariv reagents which vary in the glycosyl groups on the outside of the structure, typically glucose, galactose, and mannose.[6]
A biographical article about Joseph Yariv was published by the Journal of Applied Crystallography. [7]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 , Wikidata Q30798155
- ↑ , Wikidata Q33531883
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 , Wikidata Q38318749
- ↑ , Wikidata Q74315380
- ↑ , Wikidata Q42554063
- ↑ "Yariv reagents for detection and quantitation of arabinogalactan-proteins". Biosupplies Australia. http://biosupplies.com.au/assets/files/docs/100-2_3_4_5_6_8.pdf.
- ↑ John R. Helliwell and Yariv family, "Joseph Yariv (1927–2021)", Journal of Applied Crystallography, Volume 54| Part 3| June 2021| Pages 1025-1026, doi:10.1107/S1600576721004453
 |

