Chemistry:Isobenzofuran
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Benzofuran[1] | |
| Other names
2-Oxa-2H-isoindene; Benzo[c]furan
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H6O | |
| Molar mass | 118.13 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
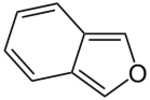
Isobenzofuran is a bicyclic heterocycle consisting of fused cyclohexa-1,3-diene and furan rings. It is isomeric with benzofuran.
Isobenzofuran is highly reactive and rapidly polymerizes; however, it has been identified[2] and prepared by thermolysis of suitable precursors and trapped at low temperature.[3]
Though isobenzofuran itself is not stable, it is the parent of related stable compounds with more complex structures, [4] such as the hindered analogue 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran.
References
- ↑ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 218. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ Fieser, L. F.; Haddadin, M. J. (1964). "Isobenzofuran, a Transient Intermediate". Journal of the American Chemical Society 86 (10): 2081–2082. doi:10.1021/ja01064a044.
- ↑ Wege, D. (1971). "Isolation of Isobenzofuran". Tetrahedron Letters 12 (25): 2337–2338. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)96856-X.
- ↑ Joule, J. A.; Mills, K.; Smith, G. F. (1995). Heterocyclic Chemistry (3rd ed.). CRC Press. pp. 364–365. ISBN 978-0748740697.
 |

