Biology:Hewitt's red rock hare
| Hewitt's red rock hare | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Lagomorpha |
| Family: | Leporidae |
| Genus: | Pronolagus |
| Species: | P. saundersiae
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pronolagus saundersiae Hewitt, 1927[2]
| |
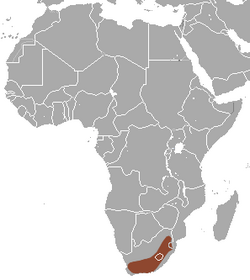
| |
| Hewitt Red Rock Hare range | |
| Synonyms[6][7] | |
The Hewitt's red rock hare (Pronolagus saundersiae) is a species of mammal in the family Leporidae. It had previously been classified as a subspecies of Pronolagus rupestris, but is now regarded as its own species due to differences in morphology and genetic differences in cytochrome b, and 12S rRNA.[8]
Taxonomic history
This species was named by John Hewitt (1880–1961), who was the director of the Albany Museum, South Africa.[9] Hewitt originally described this taxon as a subspecies of Pronolagus crassicaudatus in his 1927 description.[7] Its type locality was Grahamstown.[10][11]
He described this taxon based and skulls from Albany district, collected by Enid Saunders and Frank Bowker; the species is named after Saunders.[12]
It was later classified as a subspecies of Pronolagus rupestris by various zoologists,[13] including Ellerman, Morrison-Scott and Hayman,[10] as well as Hoffman and Smith for the third edition of Mammal Species of the World.[6]
Works which list it as its own species include: the IUCN Red List,[1] Mammals of Africa,[7] and Jonathan Kingdon's field guide.[14]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Robinson, T.J.; Child, M.F.; Matthee, C.M. (2019). "Pronolagus saundersiae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T136713A45194657. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T136713A45194657.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/136713/45194657. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ Hewitt 1927, pp. 434–437; Pl. 26, fig. 2.
- ↑ Roberts, Austen (1949). "A New Pronolagus from Natal". Annals of the Transvaal Museum 21 (1): 179–180.
- ↑ Hewitt 1927, pp. 437–439; Pl. 26, fig. 1; Pl. 27, fig. 7.
- ↑ Roberts, Austin (1933). "Eleven new forms of South African mammals". Annals of the Transvaal Museum 15 (2): 270.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Hoffman, R.S.; Smith, A.T. (2005). "Order Lagomorpha". in Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 207. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494. http://www.departments.bucknell.edu/biology/resources/msw3/browse.asp?id=13500273.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Happold, D. C. D. (2013). "Pronolagus saundersiae Hewitt's Red Rock-hare". in Happold, David C. D.. Rodents, Hares and Rabbits. Mammals of Africa. 3. London: Bloomsbury. p. 717. ISBN 978-1-4081-8992-4.
- ↑ Robinson, T. J.; Matthee, C. A. (2005). "Phylogeny and evolutionary origins of the Leporidae: a review of cytogenetics, molecular analyses and a supermatrix analysis". Mammal Review 35 (3–4): 241. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2907.2005.00073.x.
- ↑ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael, eds (2009). "Hewitt". The Eponym Dictionary of Mammals. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 188. ISBN 9780801895333. https://muse.jhu.edu/chapter/69234.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Ellerman, J. R.; Morrison-Scott, T. C. S.; Hayman, R. W. (1953). "Lagomorpha — Leporidae". Southern African Mammals 1758 to 1951: A Reclassification. London: Tonbridge. p. 221. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/49728490.
- ↑ Meester, J. A. J.; Rautenbach, I. L.; Dippenaar, N. J.; Baker, C. M. (1986). "Order Lagomorpha". Classification of Southern African Mammals. Transvaal Museum Monographs. 5. Transvaal Museum. pp. 298–307. ISBN 0907990061.
- ↑ Hewitt 1927, pp. 434–435.
- ↑ Duthie, A. G.; Robinson, T. J. (1990). "The African Rabbits". in Chapman, Joseph A.; Flux, John E. C.. Rabbits, Hares, and Pikas: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. Gland, Switzerland: International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources. pp. 121–127. ISBN 2-8317-0019-1. https://portals.iucn.org/library/node/6047.
- ↑ Kingdon, Jonathan (2015). "Hewitt's Red Rock-Hare". The Kingdon Field Guide to African Mammals (2nd ed.). London: Bloomsbury. p. 305. ISBN 978-1-4729-1236-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=p1hMCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA305.
Works cited
- Hewitt, John (1927). "On several new Rodents in the Albany Museum". Records of the Albany Museum 3 (5): 430–440; Plates 26, 27.
Further reading
- Matthee, Conrad A.; Robinson, Terence J. (1996). "Mitochondrial DNA differentiation among geographical populations of Pronolagus rupestris, Smith's red rock rabbit (Mammalia: Lagomorpha)". Heredity 76 (5): 514–523. doi:10.1038/hdy.1996.74. PMID 8666547.
- Collins, K. (2005). "Order Lagomorpha". in Skinner, John D.; Chimimba, Christian T.. The Mammals of the Southern African Subregion (3rd ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 73. doi:10.1017/CBO9781107340992.013. ISBN 9780521844185.
Wikidata ☰ Q2924081 entry
 |


