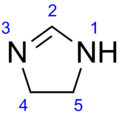
Chemistry:2-Imidazoline
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4,5-Dihydro-1H-imidazole | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,3-Diazacyclopent-2-ene | |
| Other names
2-Imidazoline
4,5-Dihydro-1,3-diazole | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H6N2 | |
| Molar mass | 70.095 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Imidazoline (Preferred IUPAC name: 4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole) is one of three isomers of the nitrogen-containing heterocycle imidazoline, with the formula C3H6N2. The 2-imidazolines are the most common imidazolines commercially, as the ring exists in some natural products and some pharmaceuticals. They also have been examined in the context of organic synthesis, coordination chemistry, and homogeneous catalysis.[1]
Synthesis
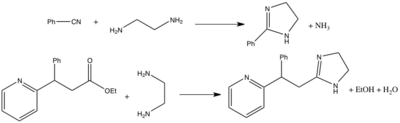
A variety of routes exist for the synthesis of imidazolines,[1][2] with the most common methods involving the condensation of 1,2-diamines (e.g. ethylenediamine) with nitriles or esters. The nitrile based route is essentially a cyclic Pinner reaction; it requires high temperatures and acid catalysis and is effective for both alkyl and aryl nitriles.
As natural products
Imidazoline has been found in various natural products. Natural molecules topsentin D and spongotine B were discovered in several marine sponges. These metabolites have received considerable attention because of their potent properties such as antitumor, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory activities.[3]
Biological role
Many imidazolines are biologically active.[4] Most bio-active derivatives bear a substituent (aryl or alkyl group) on the carbon between the nitrogen centers. Some generic names include oxymetazoline, xylometazoline, tetrahydrozoline, and naphazoline.
Applications
Pharmaceutical
2-imidazolines have been investigated as antihyperglycemic, anti-inflammatory, antihypertensive, antihypercholesterolemic, and antidepressant reagents.[1][5] The imidazoline-containing drug clonidine is used alone or in combination with other medications to treat high blood pressure. It is also used in the treatment of dysmenorrhea, hypertensive crisis, Tourette's syndrome and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).[6]
- 2-Imidazolines
Second generation Grubbs' catalyst
As p53 activators
Cis-imidazolines act as small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. These compounds bind MDM2/X in the p53-binding pocket and activate the p53 pathway in cancer cells, leading to cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and growth inhibition of human tumor xenografts in nude mice. The most active compounds are nutlin-3a[7] and rg-7112,[8] but some other analogs also activate p53.[9][10][11]
Surfactants
Surfactants based around 2-imidazoline, such as sodium lauroamphoacetate, are used in personal care products where mildness and non-irritancy are particularly important (e.g. baby products, "no more tears" shampoos etc.).[12]
As precursors of imidazoles
Imidazoles can be prepared from dehydrogenation of imidazolines.[13]
Homogeneous catalysis
As a structural analogue of 2-oxazolines, 2-imidazolines have been developed as ligands in coordination chemistry. The substitutions on the nitrogen atom in the imidazoline ring provide opportunities for fine-tuning the electronic and steric properties. Some of the complexes function as catalysts for Suzuki–Miyaura couplings, Mizoroki–Heck reactions, Diels–Alder reactions, asymmetric allylic substitution, [3,3] sigmatropic rearrangement, Henry reactions, etc.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "Recent Advances in the Synthesis of 2-Imidazolines and Their Applications in Homogeneous Catalysis". Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis 351 (4): 489–519. March 2009. doi:10.1002/adsc.200800797.
- ↑ "Synthetic routes toward 2-substituted 2-imidazolines". Tetrahedron 65 (12): 2387–2397. March 2009. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2008.12.022.
- ↑ "Total synthesis of marine sponge bis(indole) alkaloids of the topsentin class". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 72 (10): 3972–3975. May 2007. doi:10.1021/jo070286r. PMID 17444688.
- ↑ "Locomotor effects of imidazoline I2-site-specific ligands and monoamine oxidase inhibitors in rats with a unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesion of the nigrostriatal pathway". British Journal of Pharmacology 143 (8): 952–959. December 2004. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706019. PMID 15545290.
- ↑ "Imidazoline binding sites and their ligands: an overview of the different chemical structures". Medicinal Research Reviews 24 (5): 639–661. September 2004. doi:10.1002/med.20007. PMID 15224384.
- ↑ "Clonidine". Pubmed Health. October 2008. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0000623/.
- ↑ "In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2". Science 303 (5659): 844–848. February 2004. doi:10.1126/science.1092472. PMID 14704432. Bibcode: 2004Sci...303..844V.
- ↑ "Discovery of RG7112: A Small-Molecule MDM2 Inhibitor in Clinical Development". ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters 4 (5): 466–469. May 2013. doi:10.1021/ml4000657. PMID 24900694.
- ↑ "Sulfonamide derivatives of cis-imidazolines as potent p53-MDM2/MDMX protein-protein interaction inhibitors" (in en). Medicinal Chemistry Research 30 (12): 2216–2227. December 2021. doi:10.1007/s00044-021-02802-w. ISSN 1054-2523. https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00044-021-02802-w.
- ↑ "2,4,5-Tris(alkoxyaryl)imidazoline derivatives as potent scaffold for novel p53-MDM2 interaction inhibitors: Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 29 (16): 2364–2368. August 2019. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.06.007. PMID 31196710.
- ↑ "Synthetic Design and Biological Evaluation of New p53-MDM2 Interaction Inhibitors Based on Imidazoline Core". Pharmaceuticals 15 (4): 444. April 2022. doi:10.3390/ph15040444. PMID 35455441.
- ↑ "Imidazoline and its derivatives: an overview". Journal of Oleo Science 56 (5): 211–222. 2007. doi:10.5650/jos.56.211. PMID 17898484.
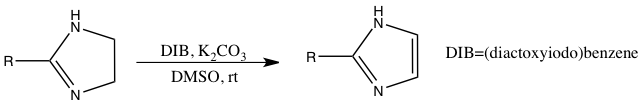
- ↑ "An Efficient Preparation of 2-Imidazolines and Imidazoles from Aldehydes with Molecular Iodine and (Diacetoxyiodo)benzene". Synlett (2): 227–230. 2006. doi:10.1055/s-2005-923604.
 |