Chemistry:Disuccinimidyl suberate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
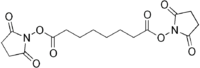
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bis(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) octanedioate | |
| Other names
DSS; Suberic acid bis(N-hydroxysuccinimide ester)
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H20N2O8 | |
| Molar mass | 368.342 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Disuccinimidyl suberate (DSS) is a six-carbon lysine-reactive non-cleavable cross-linking agent.
It consists of functional groups It is a homobifunctional N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) ester formed by carbodiimide-activation of carboxylate molecules, with identical reactive groups at either end.[2] The reactive groups are separated by a spacer and in this molecule it is a six carbon alkyl chain.[3] This reagent is mainly used to form intramolecular crosslinks and preparation of polymers from monomers. It is ideal for receptor ligand cross-linking.
DSS is reactive towards amine groups (primary amines) at pH 7.0-9.0. It is membrane permeable, therefore permitting intracellular cross-linking, has high purity, is non-cleavable, and is water-insoluble (it must be dissolved in a polar organic solvent such as DMF or DMSO before addition to sample.)[4]
Its reaction specificity, reaction product stability, and lack of reaction by-products make it a commonly used cross-linking agent.[3]
See also
- Bissulfosuccinimidyl suberate, a water-soluble version
Applications
- Chemical crosslinking of intracellular proteins prior to cell lysis and immunoprecipitation
- 'Fix' protein interactions to allow identification of weak or transient protein interactions
- Protein crosslinking to create bioconjugates via single-step reactions
- Immobilize proteins onto amine-coated surfaces[5]
- Crosslinking mass spectrometry (crosslinking-MS) provides insight into protein structure, organization, and interactions[6]
Size Exclusion Chromatography
A study was done looking at the application of size exclusion chromatography in the purification of cross-link peptides within samples. When the eluted peptides were analyzed, cross-linked peptides could be detected at higher concentrations in the earlier fractions, eluting before modified or unmodified peptides.[7]
DSS Cross-linking with Hemoglobin-albumin
Disuccinimidyl suberate's reactivity toward primary amines allows it to serve as a cross-linking agent for proteins, without toxic side-products and forming peptide bonds with the lysine residues in a single step. In a study on blood substitutes, DSS was shown to cross-link Hemoglobin intramolecularly, yielding a relatively stable protein (polymerized Hb or polyHb), whose oxygen affinity was almost halved compared to that of native Hb. This was shown to be reversed when Hemoglobin was copolymerized with bovine serum albumin (BSA), showing very little change in auto-oxidation and oxygen affinity compared to the native Hb.[8]
References
- ↑ Suberic acid bis(N-hydroxysuccinimide ester) at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Crosslinking Reagents Handbook. Thermo Fisher Scientific. 2012. https://tools.thermofisher.com/content/sfs/brochures/1602163-Crosslinking-Reagents-Handbook.pdf.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Anatomy of a crosslinker". Current Opinion in Chemical Biology. Omics 60: 39–46. February 2021. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2020.07.008. PMID 32829152.
- ↑ "Probing native protein structures by chemical cross-linking, mass spectrometry, and bioinformatics" (in English). Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 9 (8): 1634–1649. August 2010. doi:10.1074/mcp.R000001-MCP201. PMID 20360032.
- ↑ "DSS (disuccinimidyl suberate)" (in en). https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/21655.
- ↑ "Leveraging crosslinking mass spectrometry in structural and cell biology" (in English). Structure 30 (1): 37–54. January 2022. doi:10.1016/j.str.2021.11.007. PMID 34895473.
- ↑ "XL-MS: Protein cross-linking coupled with mass spectrometry". Methods. Mass Spectrometry-Based Structural Biology 89: 54–63. November 2015. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.06.010. PMID 26079926.
- ↑ "Hemoglobin-albumin cross-linking with disuccinimidyl suberate (DSS) and/or glutaraldehyde for blood substitutes". Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology 42 (1): 13–17. February 2014. doi:10.3109/21691401.2012.762652. PMID 23342991.
 |

