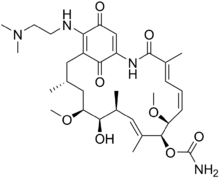
Chemistry:17-Dimethylaminoethylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[(3R,5S,6R,7S,8E,10S,11S,12Z,14E)-21-(2-dimethylaminoethylamino)-6-hydroxy-5,11-dimethoxy-3,7,9,15-tetramethyl-16,20,22-trioxo-17-azabicyclo[16.3.1]docosa-1(21),8,12,14,18-pentaen-10-yl] carbamate
| |
| Other names
17-DMAG; Alvespimycin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C32H48N4O8 | |
| Molar mass | 616.756 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
17-Dimethylaminoethylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-DMAG) is a chemical compound which is a semi-synthetic derivative of the antibiotic geldanamycin.[1][2] It is being studied for the possibility of treating cancer.[3]
References
- ↑ Snader, Kenneth M.; Vishnuvajjala, B. Rao; Hollingshead, Melinda G.; Sausville, Edward A., "Preparation of geldanamycin derivatives for the treatment of cancer", WO patent application 2002079167, published 2002
- ↑ Rastelli, Giulio; Tian, Zong-Qiang; Wang, Zhan; Myles, David; Liu, Yaoquan (2005). "Structure-based design of 7-carbamate analogs of geldanamycin". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 15 (22): 5016–5021. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.08.013. PMID 16165354.
- ↑ Sausville, E. A.; Tomaszewski, J. E.; Ivy, P. (2003). "Clinical development of 17-allylamino, 17-demethoxygeldanamycin". Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 3 (5): 377–83. doi:10.2174/1568009033481831. PMID 14529389. https://zenodo.org/record/1235858.
 |

