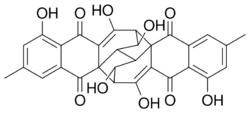
Chemistry:Rugulosin
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
8,10,14,23,25,28-hexahydroxy-6,21-dimethyloctacyclo[14.11.1.02,11.02,15.04,9.013,17.017,26.019,24]octacosa-4(9),5,7,10,19(24),20,22,25-octaene-3,12,18,27-tetrone
| |
| Other names
NSC 160880
NSC 249990 Rugulosin A | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H22O10 | |
| Molar mass | 542.496 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Rugulosin is an anthraquinoid mycotoxin with the molecular formula C30H22O10 which is produced by Penicillium species.[1][2][3] Rugulosin is hepatotoxic and is cancerogenic.[4]
References
- ↑ "Rugulosin" (in en). Pubchem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Rugulosin.
- ↑ Ueno, Yoshio; Sato, Norio; Ito, Teruo; Ueno, Ikuko; Enomoto, Makoto; Tsunoda, Hiroshi (1980). "Chronic Toxicity and Hepatocarcinogenicity of (+) Rugulosin, an Anthraquinoid Mycotoxin from Penicillium Species: Preliminary Surveys in Mice". The Journal of Toxicological Sciences 5 (4): 295–302. doi:10.2131/jts.5.295. PMID 7218376.
- ↑ Ueno, Y; Ueno, I; Sato, N; Iitoi, Y; Saito, M (June 1971). "Toxicological approach to (+) rugulosin, an anthraquinoid mycotoxin of Penicillium rugulosum Thom.". The Japanese Journal of Experimental Medicine 41 (3): 177–188. PMID 5314585.
- ↑ Eisenbrand, Gerhard; Schreier, Peter (28 May 2014) (in de). RÖMPP Lexikon Lebensmittelchemie, 2. Auflage, 2006. Georg Thieme Verlag. ISBN 978-3-13-179532-8.
Further reading
- Eckardt, Christiane (1981) (in de). Mykotoxine in Lebensmitteln. Fischer. p. 23. ISBN 978-3-437-10650-7.
- (in en) Studies in Natural Products Chemistry. Elsevier. 24 April 2015. ISBN 978-0-444-63469-6.
- Steyn, Pieter (2 December 2012) (in en). The Biosynthesis of Mycotoxins: A study in secondary Metabolism. Elsevier. p. 375. ISBN 978-0-323-14993-8.
- Pirttilä, Anna Maria; Frank, A. Carolin (11 July 2011) (in en). Endophytes of Forest Trees: Biology and Applications. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 244. ISBN 978-94-007-1599-8.
- Nicolaou, K. C.; Lim, Yee Hwee; Piper, Jared L.; Papageorgiou, Charles D. (1 April 2007). "Total Syntheses of 2,2'-epi-Cytoskyrin A, Rugulosin, and the Alleged Structure of Rugulin". Journal of the American Chemical Society 129 (13): 4001–4013. doi:10.1021/ja0685708. ISSN 0002-7863. PMID 17355133.
- Mondal, Amit; Singh, Shailesh Kumar; Manna, Tanaya; Husain, Syed Masood (17 March 2020). "Chemoenzymatic, biomimetic total synthesis of (−)-rugulosin B, C and rugulin analogues and their biosynthetic implications" (in en). Chemical Communications 56 (22): 3337–3340. doi:10.1039/D0CC00406E. ISSN 1364-548X. PMID 32090214.
- Nicolaou, K. C.; Lim, Yee Hwee; Papageorgiou, Charles D.; Piper, Jared L. (2005). "Total Synthesis of (+)-Rugulosin and (+)-2,2′-epi-Cytoskyrin A through Cascade Reactions". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 44 (48): 7917–7921. doi:10.1002/anie.200503678. ISSN 1521-3773. PMID 16342134.
- Sumarah, Mark W.; Miller, J. David; Adams, Gregory W. (1 September 2005). "Measurement of a rugulosin-producing endophyte in white spruce seedlings". Mycologia 97 (4): 770–776. doi:10.1080/15572536.2006.11832768. ISSN 0027-5514. PMID 16457346.
 |

